Unit 12.3 Program Testing & Maintenance
Aims
Know what is meant by the term testing and why testing is important.
Know what is meant by the terms syntax error, logic error and run-time error and how to fix them.
Know the different methods that can be used to test a program to ensure it is functional and robust.
Know what is meant by the terms test strategy and test plan and their likely contents.
Know what is meant by the terms normal data, abnormal data and extreme/boundary data and why these are needed.
Know what is meant by the terms perfective maintenance, adaptive maintenance and corrective maintenance.
Program Testing
Testing - ensure code works as intended (error-free, does as intended, reliable and accurate results)
Syntax Errors - Doesn’t follow grammatical rules of programming language, causes crashes.
Incorrectly spelled statements.
Incorrectly spelled variables.
Missing punctuation e.g. quotes, brackets
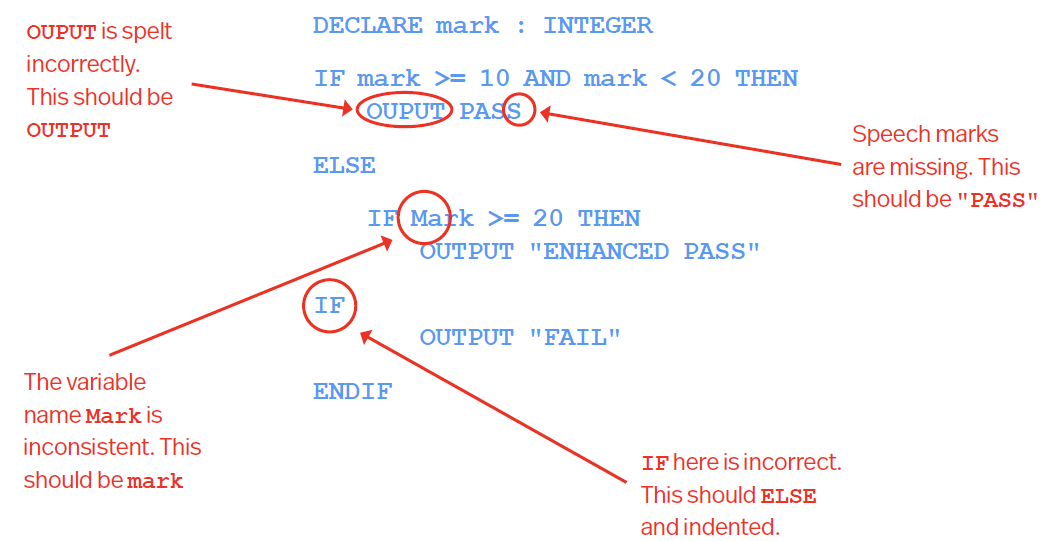
Logic Errors - Programmer hasnt used the correct rules - doesnt crash but does something unexpected such as outputting an incorrect value.
Missing steps out or in the wrong order
Incorrectly using relational operators e.g. <,>,, <=, >=
Incorrectly using logical operators e.g. AND, OR, NOT
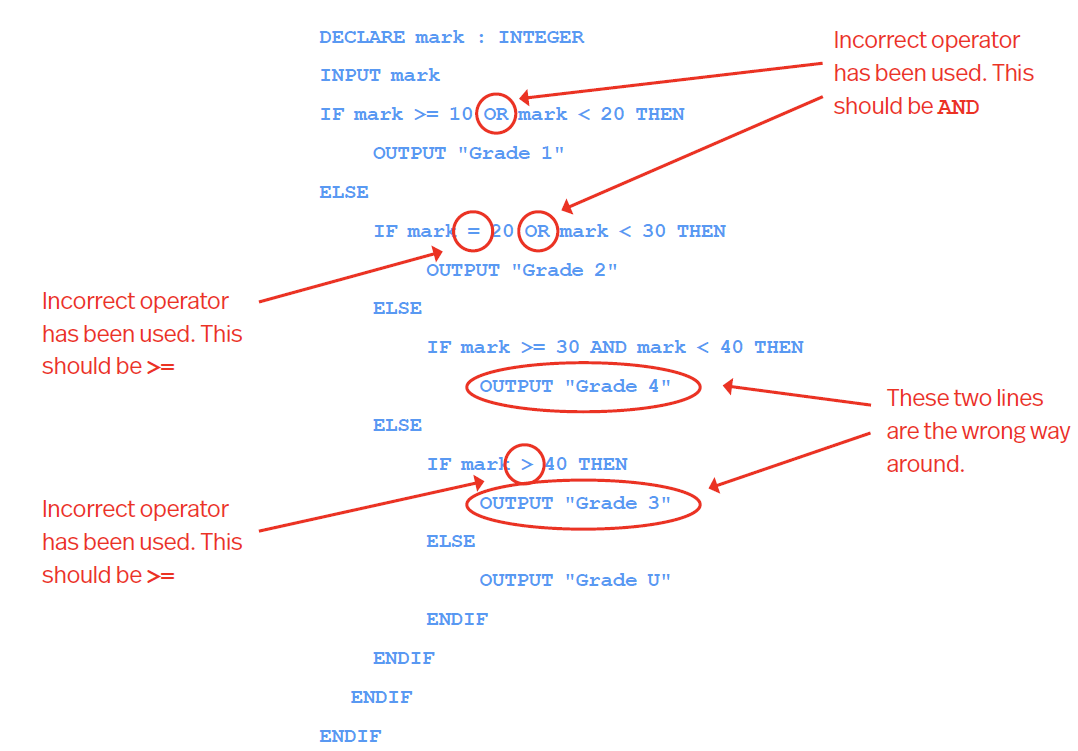
Run-time Errors - occurs whilst programming is running after being successfully compiled - crashes or outputs incorrect value
Example below only contains run-time error and looks correct at first glance but with the wrong combination of parameters, errors can occur.

If its run with the parameters of result← division (2,0), it will cause an error in the answer←num1/num2 line as 0 is mathematically undefined.
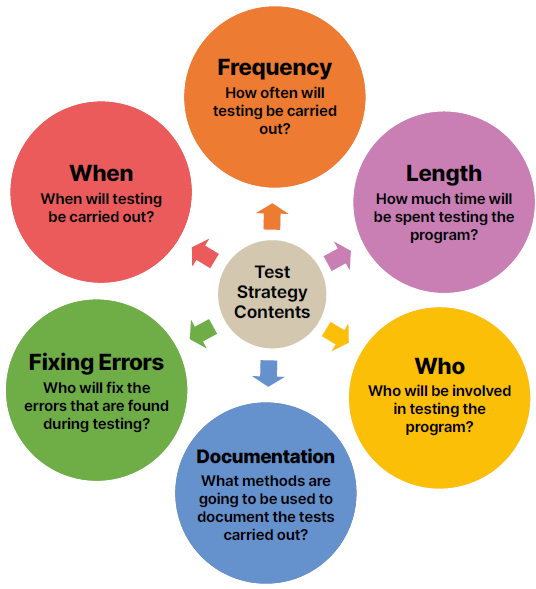
Test Strategy
Describes only the approach that will be taken to test the program (not whats specifically tested) and is dependant on which program development life cycle is used e.g. Iterative will be tested more frequently
Once made the strategy wont change, a test plan is then created to give more specific information.
Testing Methods
Testing type | Description |
Dry-run Testing | Manual read code line by line to find errors and performs as intended. |
Walkthrough Testing | Developer(s) present work to other team members, stakeholders or subject matter experts to receive feedback and suggestions. |
White-box Testing | Tests internal structure and algorithms to make sure its correct, also checks efficiency. |
Black-box Testing | Tests whether input produces expected output - efficiency not important only outcome. (ideally check every input but not always feasible) |
Alpha Testing | Performed by development company to uncover defects before releasing to external users. |
Beta Testing | Release program to limited external group to gather feedback and identify potential issues in real-world usage (think of games in beta). |
Integration Testing | Involves checking the interfaces and interactions between integrated components/modules to ensure they function correctly together. |
Acceptance Testing | Verifies if program meets specified requirements and is ready for release. |
Stub Testing | Test carried out before modules are developed. Module stubs contain simple code/placeholders to provide a known response that simulate the behaviour of a dependent component. |
Tests Data
Different types used to check programs working correctly (covers as many combos of user input as possible)
Data Type | Description | E.g |
Normal Data | Correct & should be accepted with no errors. | No. input (0-3) 1, 2 |
Abnormal Data | Incorrect & shouldn’t be accepted, includes incorrect data type/outside validation range | No Input (0-3) A, /, 4 |
Extreme/Boundary Data | Correct but on edge of being valid, should be accepted with no errors. | No. Input (0-3) 0, 3 |
Test Plans
Doc listing how code’s tested, completed by programmer/tester, tests coutlined on plan are completed and outcome recorded.
Usually includes
Test number of each test
Test description of each test
Test Type of each test
Data used for each test
Expected result of each test.

Test Number | Test Description | Test Type | Data Used | Expected Result |
1 | Program accepts data within acceptable range | Normal | 2 | Data accepted |
2 | Program rejects incorrect data | Abnormal | “Two” | Not Accepted “Invalid Choice” displayed |
3 | Program accepts data that is on the boundary | Extreme/Boundary | 3 | Data accepted |
Program Maintenance
Occurs when program has been given to client, ensuring it continues to meet needs and adapt.
Perfective Maintenance
Making enhancements to improve performance, usability and maintainability, doesnt change existing function, turns Good into Better
e.g..
Making keyboard shortcuts - faster
Adding new help feature - faster/easier
Rewriting code to reduce response time - faster
Changing UI for ease of use - easier
Changing screen prompts to help users understand better - easier
Adaptive Maintenance
Modify program to accommodate a new need, could be due to new changes in organisation/legislation/hardware etc.
E.g.
New product/service being released
Change in legislation
New Security Threat
New hardware/software to be integrated into code
Corrective Maintenance
Fixing/detecting errors or bugs discovered after release
E.g.
Syntax Error
Logic Error
Run-Time Error