5.2: The Chemist's View of Phospholipids and Sterols
phospholipids and sterols only make up 5% of the lipids in the diet
Phospholipids
best known phospholipid is lecithin
chemical structure E-
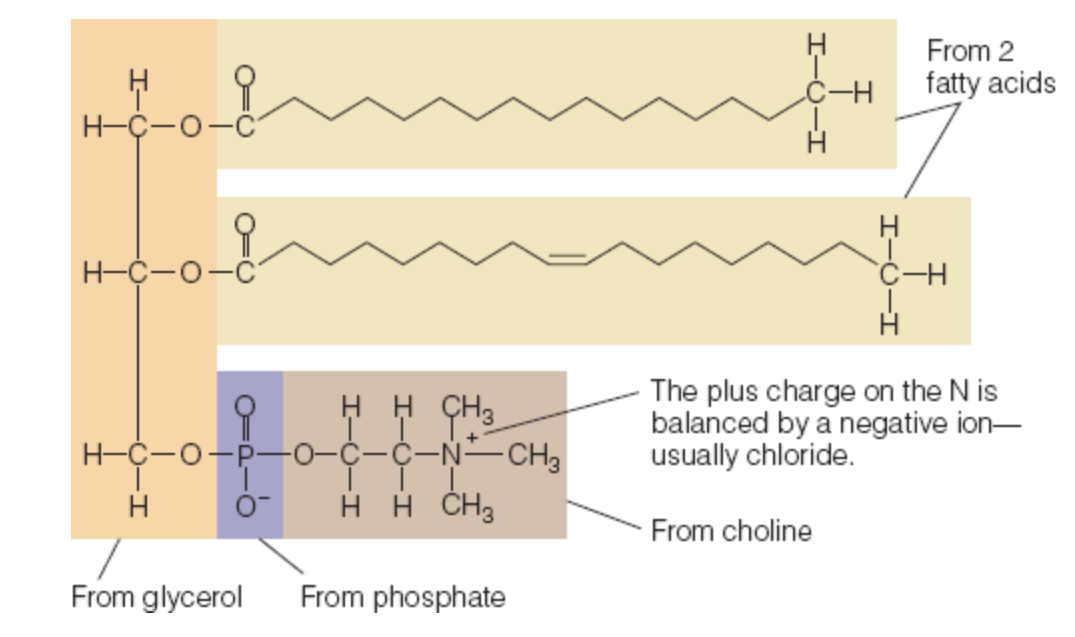
1 glycerol
2/3 attachments are occupied by fatty acids
1/3 attachment is occupied by a phosphate group and a molecule of choline
hydrophobic fatty acids make phospholipids soluble in fat
hydrophilic phosphate group allows phospholipids to dissolve in water
used as emulsifiers to mix fats with water so they don’t separate into layers
Lecithin
Phospholipids in Foods
used in the food industry as emulsifiers
found naturally in foods
richests sources of lecithin-
eggs, liver, soybeans, wheat germ, peanuts
Roles of Phospholipids
parts of cell membranes
help fat-soluble substances (vitamins and hormones) to pass easily in and out of cells
emulsifiers in the body
keeps fats suspended in the blood and body fluids
Sterols
compounds with a multiple-ring structure
cholesterol is the most well-known sterol
vitamin D (fat soluble) is synthesized from cholesterol
Sterols in Foods
found in foods derived from plants and animals
only foods from animals contain significant amounts of sterol
meats, eggs, seafood, poultry, and dairy products
“good” cholesterol-
refers to the way the body transports cholesterol in the blood
sterols other than cholesterol are naturally found in plants
plant sterols-
structurally similar to cholesterol
interfere with cholesterol absorption
limiting cholesterol absorption lowers blood cholesterol levels
fortified foods such as margarine with plant sterols helps reduce blood cholesterol
Roles of Sterols
important body compounds are sterols-
bile acids, sex hormones (testerone, androgen, and estrogen), adrenal hormones (cortisol, cortisone, aldosterone), vitamin D, and cholesterol
cholesterol-
serves as a starting material for the synthesis of body compounds as a structural component of cell membranes
90%+ of all the body’s cholesterol is found in the cells
cannot be used for energy
endogenous: cholesterol that is made in the body
exogenous: cholesterol from outside the body
liver-
manufactures cholesterol from fragments of carbohydrate, protein, and fat
makes about 800-1500 mg of cholesterol per day
contributes much more to the body’s total cholesterol than the diet does
harmful effects on the body-
when cholesterol accumulates in the artery walls and contributes to the formation of plaque, leading to atherosclerosis (disease that causes heart attacks and strokes)