Digital Photogrammetry Revision
INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS
1. Define Digital Photogrammetry (2 marks)
Digital Photogrammetry is the art of using computers to obtain measurements of objects in an aerial photograph. It involves analyzing one or more photographs and using photogrammetric software to determine spatial relationships.
2. Define Interior Orientation (2 marks)
This is what defines the internal geometry of a camera/sensor at the time of image capture. The variables associated with image space are defined during interior orientation.
3. Explain the exterior orientation process (2 marks)
This is what defines the position and angular orientation of the camera that captured an image. Variables defining the position and orientation of an image are considered to be a part of exterior orientation.
4. Explain the importance of absolute orientation (2 Marks)
This is the process in which the stereomodel is oriented to the ground cooridnate system.
5. Differentiate between Principal point of autocollimation and principal point of symmetry.
(3 marks)
Principal Point of Autocollimation - is the point where the focal length of the lens is measured and the optical axis intersects the image plane.
Principal Point of Symmetry - is what deals with how light rays pass through the focal point and intersects the film.
6. Differentiate between coordinate space and coordinate systems photogrammetry. (3 marks)
Coordinate space refers to a mathematical framework used to represent the positions of points and objects in a three-dimensional space. A single coordinate space can be used for different coordinate systems, each with its own parameters and specifications.
Coordinate system specifies the units, origin, orientation, and datum used to represent locations within the chosen coordinate space.
7. With the aid of a diagram explain the difference between pixel and image coordinates. (3 marks)
Pixel Coordinates - are a system that houses X and Y coordinates, which are horizontal and vertical positions of pixels respectively, where X is column number and Y is row number.
Image Coordinates - Represent the real-world location of a point on the object surface represented by the image and are measured in a selected ground coordinate system
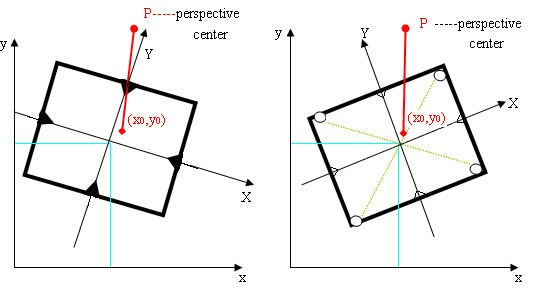
8. What is meant by the term deformation and how can it be corrected?
(3 marks)
Deformation is the shrinkage of the image film when its being processed in the lab and can be determined and corrected during interior orientation.

9. Describe the process of relative orientation? (2 marks)
Relative Orientation is the process of creating the stereomodel, whether analytical or through the use of a Digital Photogrammetry Workstation (DPW).

10. Explain the difference between an Digital photogrammetric work station and an Analytical system (4 marks)
11. In exterior orientation there are three (3) rotation commonly used to define angular rotation. While the angular or rotational elements of exterior orientation describe the relationship between the ground space coordinate system. List the six (6) elements and the three (3) angular rotation.
(6 marks)
X: Coordinate of the camera perspective center in the object space coordinate system along the X-axis.
Y: Coordinate of the camera perspective center in the object space coordinate system along the Y-axis.
Z: Coordinate of the camera perspective center in the object space coordinate system along the Z-axis.
kappa - direction
omega - elevation
phi - orientation
12. What are the fiducial marks? (2 marks)
Fiducial marks are small registration marks placed along an aerial photograph with measured image positions.
13. Indicate two (2) errors associated with two (2) of the following and explain how you would correct these errors: (6 Marks)
(a) Fiducials reading
(b) GCP measurements
(c) Tie point measurements
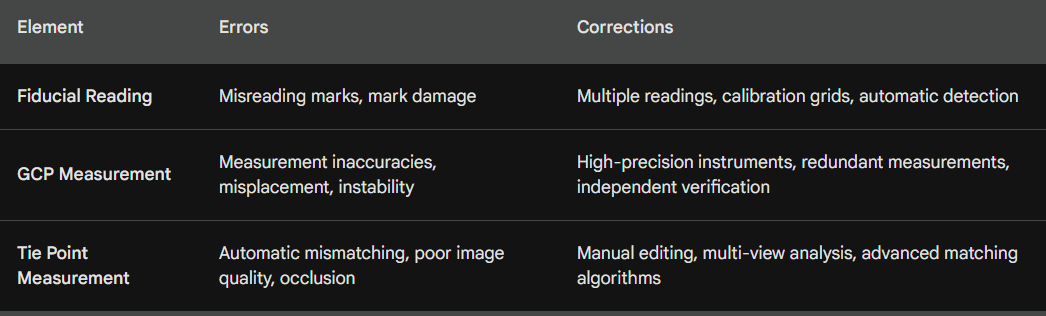 In this context, “marks” are fiducial marks
In this context, “marks” are fiducial marks
Define Aerial Triangulation. (2 marks)
Aerial Triangulation is the process of forming a mathematical relationship between the images in a project, the camera/sensor model and the ground, providing orthorectification.
Define tie points in the work flow of photogrammetric. (4 marks)
Tie points are essential components of photogrammetry because they connect overlapping pictures and allow for the creation of complex 3D models. They improve precision, reduce the requirement for ground control points, and automate some tasks. Manual selection, on the other hand, needs high-quality photographs and a significant time investment, whereas computerized identification may be error-prone.
What is the purpose of the calibration report and how it is use photogrammetry? (4 marks)
The calibration report is a document that summarizes the results of the calibration process. This document contains camera parameters, calibration accuracy and method of calibration.
Define rectification and describe the process of process. (4 marks)
Rectification is the process of removing distortions in images to produce a map or orthophoto that is true to scale and has a defined coordinate system. The rectification process corrects for geometric distortions, transforms the image perspective and and assigns actual ground coordinates to the image.
Identify three methods for providing ground control for photogrammetry. (4 marks)
GCP can be obtained through theodolite/total station surveys, ground GPS and DEM. (other possible answers are planimetric & topo maps, digital orthorectified images)
Explain the difference between GPS and INS technology. (4 marks)
Both GPS (Global Positioning System) and INS (Inertial Navigation System) play crucial roles in photogrammetry, contributing to accurate position and orientation data. However, they function in distinct ways with their respective advantages and limitations:
GPS - Provides absolute positioning data by receiving signals from orbiting satellites, offers global coverage and is easy to use and readily available
INS - Measures changes in position and orientation using accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers with continuous data output at high frequency, resulting in smooth and accurate trajectory measurement and is not affected by signal interference or lack of satellite visibility.
List three types of ground control use in photogrammetry. (3 marks)
GCPs, existing control network, georeferencing (others include aerial triangulation)
Explain the difference desktop and photogrammetric scanners. (4 marks)
Desktop scanners are general-purpose devices. They lack the image detail and geometric accuracy of photogrammetric quality units, but they are much less expensive.
Photogrammetric scanners are special devices capable of producing high image quality and excellent positional accuracy and they are evidently more expensive.
Describe two products that can be obtained from photogrammetry and how these are utilized in survey and mapping. (2 marks)
DEMs - A digital representation of the terrain elevation
Orthophotos - An aerial image that has been geometrically corrected to remove distortions and represent the ground surface with a uniform scale
Explain your understanding of the term ground control points. (4 marks)
A GCP is an identifiable feature on Earth’s surface with known ground coordinates in X, Y and Z.
A full GCP has X,Y,Z
A horizontal GCP has X,Y
A vertical GCP has only Z
Define ortho-rectification and the process. (4 marks)
Orthorectification is the process of reducing geometric errors inherent within photography and imagery. The orthorectification process takes the raw digital imagery and applies a DEM and triangulation results to create an orthorectified image
What is the significance of aerial triangulation in photogrammetry? (2 marks)
It forms a mathematical relationship between project images, the camera/sensor model and the ground, providing orthorectification.
Explain digital terrain model and digital surface model. (4 marks)
A Digital Terrain Model (DTM) displays regularly or irregularly spaced height data, triangular irregular networks (TINs) and shows the bare terrain of the Earth. All vegetation , buildings and other man-made features are removed
A Digital Surface Model (DSM) is presented as a raster image, where pixel values represent elevations according to mean sea level (aMSL) of the ground and all features on it, including trees and buildings
Give two differences between Digital elevation model and triangular Irregular networks. (2 marks)
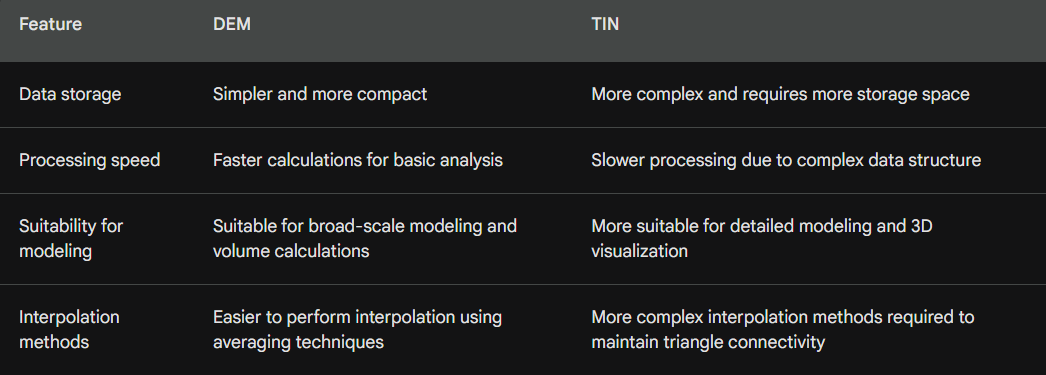
With aid of a diagram describe the DEM principles. (3 marks)
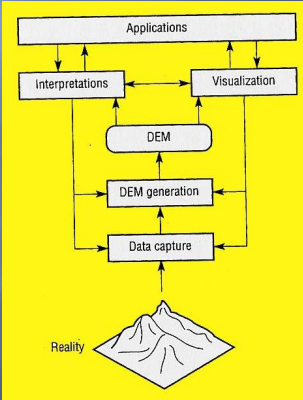 DEM Principles Explained by Image:
DEM Principles Explained by Image:
Sampling:
Each square on the grid represents a pixel in the DEM.
Each pixel holds the elevation value at a specific ground location.
Closely spaced pixels provide a more detailed representation of the terrain.
Interpolation:
Elevation values are measured at certain points (triangles).
Values for unsampled locations are estimated using interpolation algorithms.
Different algorithms prioritize accuracy or computational efficiency.
Raster vs. Vector:
The image shows a raster DEM, with regularly spaced pixels.
Vector DEMs, or TINs, use triangles with variable sizes and shapes.
Raster is simpler and more common, while TINs better represent complex terrain.
Accuracy:
Errors can arise from measurement, interpolation, and sampling density.
RMSE (Root Mean Squared Error) indicates average difference from true values.
Higher accuracy requires denser sampling and sophisticated algorithms.
Applications:
Contour maps: visualize elevation changes with lines connecting equal values.
Shaded relief maps: use simulated light and shadows for 3D visualization.
Terrain analysis: calculate slopes, aspects, and water flow paths.
3D models: combine DEMs with other data for realistic landscapes.
Conclusion:
The image provides a basic overview of DEM principles, highlighting key aspects like sampling, interpolation, data structures, accuracy, and applications.
 Knowt
Knowt