Unit 9: States of Consciousness
1.How to assess someone‘s level of consciousness
Levels of Consciousness
Ask questions that someone should know at all times
First responder asks questions like
What is your name
Where are you
What time is it
Alert & Oriented
A & O x1
A& O x 2
Sleep Depravation
Psychologist James Maas
Cornell University
following questions were used to tell sleep depravation
t - I need an alarm clock to wake up at the appropriate time
t - Its a struggel for me to get out of bed in the morning
f - Weekday mornings I hit the snooze bar several times to get more sleep
t - I feel itred, irritable, and stressed out during the weel
f - I have trouble concentrating and remembering
t - I feel slow with critical thinking, problem solving, and beinig creative
f - I often fall asleep watching television
f - I often fall asleep in boring meetings or lectures or in warm rooms
t - I often fall alseep after heavy meals
f - I often fall asleep while relaxing after dinner
f - I often fall asleep within five minutes of getting into bed
f - I often feel drowsy while driving
t - I often sleep extra hours on weekend mornings
f - I often need a nap to get through the day
f - I have dark circles around my eyes
T = 6
F = 9
What happens to your body when you don‘t get enough sleep
Hormones:
Cortisol → stress hormone
Cortisol plays an important role in waking up
brain has effects if you are stressed all the time of don‘t get enough sleep
can be detrimental to our health
Increasing Sleep Quality
How many hours of sleep do teens need? 10-12 hours
Caffeine: should stop drinking caffeinie at about 2-3pm
Choclate: avoid eating choclate before bed
Wake: go to bed and wake up at the same time every day
Sleeping-in: no sleeping in on the weekends
Naps: are anywhere from 10-20 minutes max
time that won‘t‘ make you tired
Sleep inertia occurs when you take a 2-3 hour nap
Food: eat at least 3 hours before bed
Milk: a glass of milk can help you sleep
Adults need 6-8 hours of sleep
Exercise: Regular exercise
Theories on why people sleep
Evolutionary Perspective:
Ancestor 1→gene= awake at night = walking around = falling off cliffs/getting eated by night predators = dead = not reproducing = not passing on gene of wakefulness at night
Ancestor 2 →(gene = sleep at night = not waling around rocks/cliffs/ getting attacked by night predators = not dying = eventually reproducing = gene passed on) x generation after generation = widespread behavior of sleeping at night
Recuperation:
restore/repair brain tissue
sleep allows resting neurons to repair themselves
sleep allows unused connections to weaken
analogy: leaving the house to get out of the way of electricians = consciousness leaving mind for neural fix up
Occurs during Delta sleep
Memory-Making:
Experiment:
people learn locations of picture cards in room with rose scent
sleep… slow-wave sleep = rose scent = hippocamus activated
next day= remembered locations of picture cards almost perfectly
Occurs during REM
General Physical Growth:
Sleep = pituitaary gland release growth hormone
Age = release less growth bormone and sleep less in deep sleep
Occurs in Delta sleep
Circadian Rhythm
„Circa“ - approx.
„Dian“ - Day
your bodys natural biological schedule
Superachiasmatic Nucleaus (SCN)
Helps you go to sleep/wake up
Melatonin/Serotonin
EEG Machine
way to scan the brain
looks at function but not structure and see how the brain functions
Beta waves → seen when your brain is awake and cognitivly doing something
high frequency but low ampitude
Theta waves → seen in Stage 1 NREM sleep
high frequency and low amplitude
light level of sleep and can be awoken easily
Hypnagogic Sensations → hallucinations like feeling of falling or hearing sounds
Hypnic Jerks → quick wake up after Hypnagogic Sensations
Sleep Spindle & K-complex - NREM 2
high frequenfy and low amplitude
brain is now trying to protect you from waking up
Sleep spindles & k-complex could be reactions to your brain protecting you from waking up
light level of sleep
Delta Waves → NREM 3
lower frequency & higher amplitude
Delta Sleep
Deep sleep
fully feeling the affects of sleep inertia
Restfulness/Rejuvinating
Vitals
heart rate goes down
muscles relax
breathing rate goes down
Sleep disorders
sleep walking, night terrors, sleep apnea
REM sleep → Rapid Eye Movement
transitioned back to Theta waves
Paradoxical sleep → brain is extremley active but this is our deepest sleep
Most active dreaming phase
Body is affectivly paralized
1 cycle of sleep which lasts about 90 minutes
Go through 4-5 cycles a night
Deep Sleep typically occurs on the first 2 cycles
Spend most time in Deep sleep in the first half and more time in REM in the second half of sleep
Body starts to produce serotonin ans Cortisol in the second half to prepare your body to wake up
As the night moves on, we spend less time in DELTA sleep
Sleep Disorders
Parasomnia → technicall medical term for a sleep disorder
Somnambulism → sleep walking
most often occurs during the first few hours of sleeping and in stage 3 (Delta)
If you have had night terrors, you are more likley to sleep walk when older
REM Behavior Disorder
similar to sleep walking
more intense
is caused when there is a lack of dopamine that does not paralyize the body
causes people to act out their dreams
Insomnia
persistent problem falling/staying asleep
Impacts 10% of population
Primary v Secondary Insomnia
What to do if you cannot fall asleep:
dont clock watch
get better pre-sleep routine
eat earlier
stay off screen
try progressive muscle relaxation
if you cannot fall alseep within 20 minutes of so, then get up and go
sit comfortable in another room untill tired
light exercise
read a book
no bright lights, nothing stressful
racing thoughts
do what you need to do to shut it off
make a to-do list before you go to bed
accomplish something before going to bed
Narcolepsy
suffer from sleeplesness and may fall asleep at unpredictable or inappropriate times
Directly into REM sleep
Less than .001% of population
short on serotonin
treated with anti-depressants because it is for the same neuro-transmitter
SSRI‘s
Sleep Apnea
a person stops breathing during their sleep
wake up momentarily, gasps for air, then falls back asleep
very common, especially in heavy males
can be fatal
Night Terrors
During NREM 3 Sleep
Usually others aware, and child is not
Not a nightmare
Most common in children (boys) between 2-8, 40% of children
Somniloquy
techniquly not a sleep disorder as it does not affect your sleep
can range from lo mumbling to loud yelling or coherent sentences
generally does not impact sleep
lots of people talk in their sleep
management
missing notes
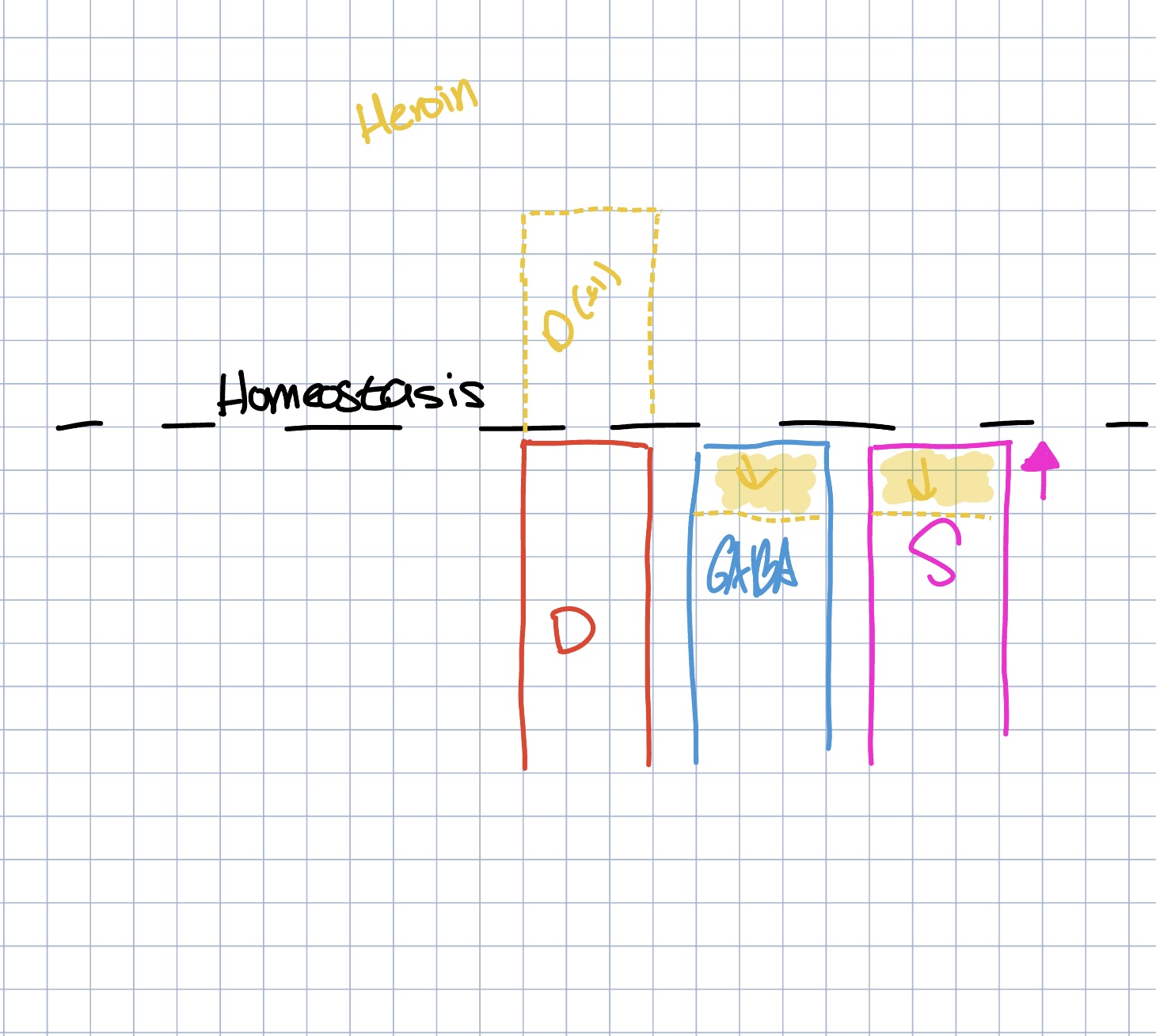
Opiates
has depressive and hallucinogenic qualities
agonist for endorphins
derived from poppy plant
pain-killing
morphine,herion,methoadone and codeine
all these drugs cross the placental barrier…teratogens
anything that negativley impacts the development of a fetus
mimic the effects of the brain’s own endorphins
these chemicals have pain releif properties and produce a felling of well bing
Depressants
act on GABA receptors to produce a calming, sedating effect
Stimulants
mimic the effects of Epinephrine, the nurotransmitter that triggers the sympathetic nervous system
supressed hunger and digestion
epinepherine → triggers your fight or flight
Addiction v Dependence
addiction is psychological and dependence is physical
there is a diffrence between addiction and dependence, even though the two are used interchangeably
with any substance, there is a chance of addiction, there is not always a chance for dependence
Dependency
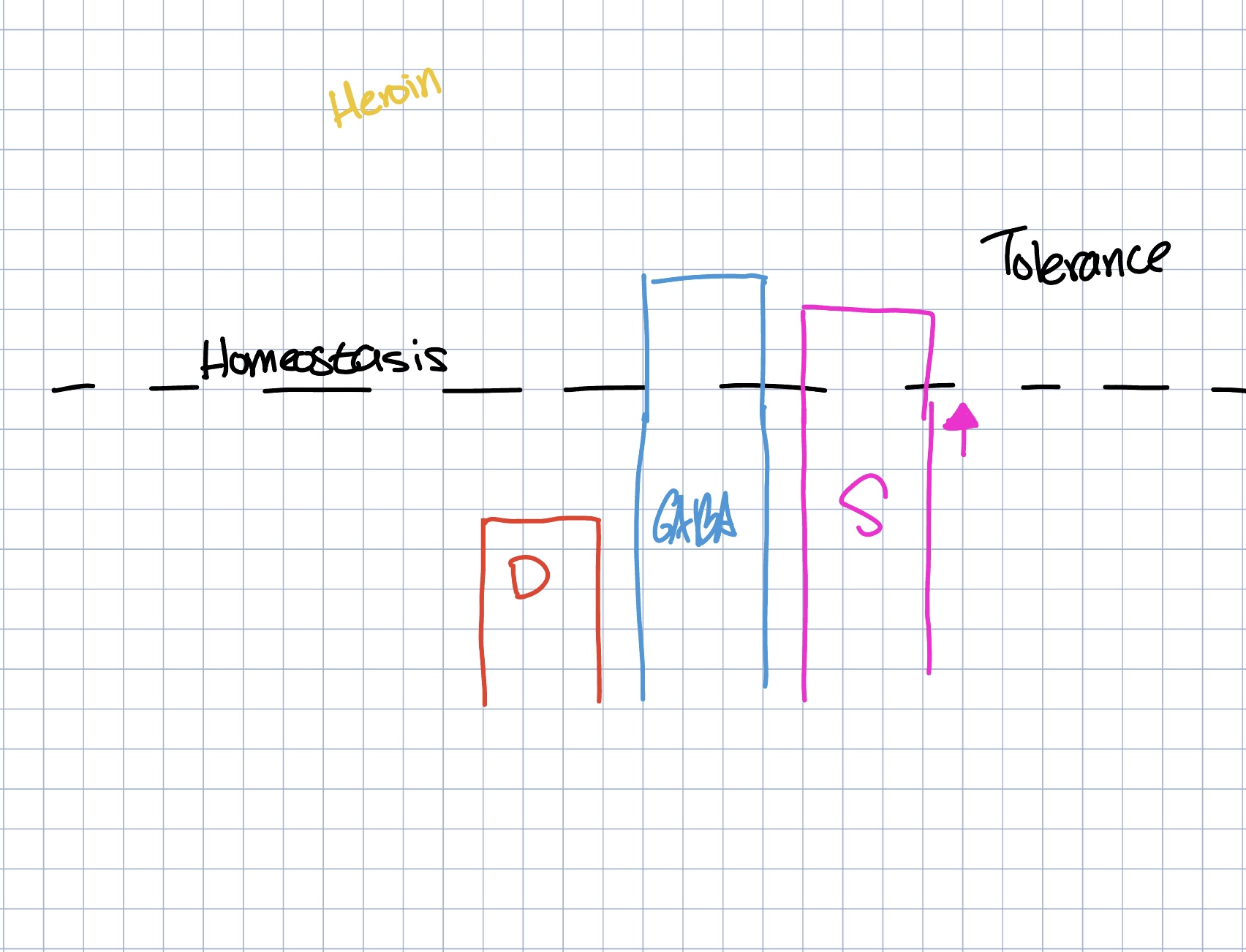
the body adapts to the drug, requiring more of it to achieve a certain effect and eliciting drug-specific physical or mental symptoms if drug use is abruptly ceased
noticeable withdrawal symptoms when stopped
Common Withdrawl symptoms
Caffeine
withdrawal symptoms such as fatigue, headache, irritabilitiy, inability to concentrate, sleepiness or drowsiness, stomach pain, and joint pain
Hypnosis
What hypnosis isn’t:
Myth: everyone can be hypnotized
10% of the population is highly hypnotizable
Myth: people aren’t in control of their body when they’re hypnotized
if you don’t want to do something, you won’t
hypnosis lowers your inhibition but does not stop you from resisting
Myth: Hypnosis is the same thing as sleep
it is not sleep
you are aware of your surroundings
Myth: people can’t lie when they’re hypnotized
no one can make you say anything that you don’t want to say
What hypnosis is:
Heightened state of relaxation or focus
chances are, you have been in hypnosis at some point today already
daydreaming, being in the “zone”
Hypnotic Theories
Role Theory
Hypnosis is NOT an altered state of consciousness
Different people have various states of hypnotic suggestibility
A social phenomenon where people want to beleive
Work better on people with richer fantasy lives
State Theory
Hypnosis is an altered state of consciousness
Dramatic health benefits
It works for pain best
will see:
post-hypnotic suggestibility
people are more likley to follow suggestions if told under hypnosis
Ernest Hilgard
Dissociation Theory
Hypnosis actually splits our consciousness
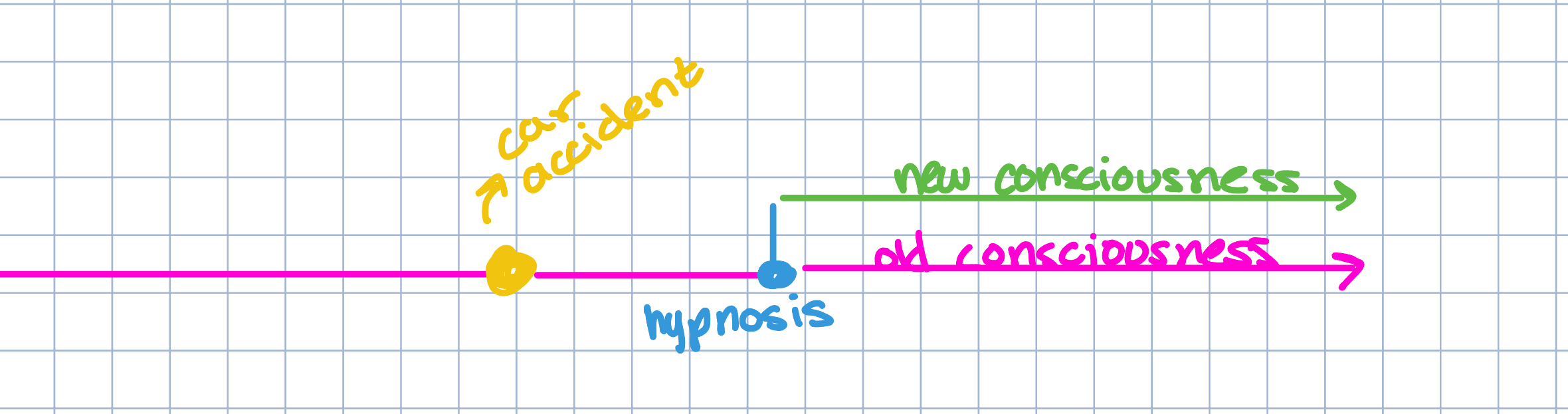
1950s - Pain control
“Hidden Observer”
part of the consciousness that is still watching over you
Case Study #1
Blind student
hypnotized student to beleive that they were deaf
didn’t react to loud noises
whispers: “Perhaps part of you can still hear me…”
raised index finger
Case Study #2
pain control
person submerged entire arm in an ice bath
hypnotized the person to feel no pain
reported no pain at all
when asked to raise a finger they would raise it indicating that they still felt pain