Chapter 2 - The First Law
Basic concepts
- Thermodynamics - The study of the transformations of energy.
- Open system - Can exchange matter and energy with its surroundings.
- Closed system - can exchange energy with its surroundings, but not matter.
- Isolated system - No matter or energy is exchanged with the surroundings.
2.1 Work, heat, and energy
- Work - Motion against an opposing force.
- Energy - Capacity to do work.
- Heat - Energy change due to a temperature change between the system and its surroundings.
- Exothermic process - Process that releases energy as heat into its surroundings.
- Endothermic process - Process in which energy is obtained from the surroundings.
Molecular interpretation
- Thermal motion - Disorderly motion of molecules
- Disorderly motion of molecules - It occurs due to heating.
2.2 The internal energy
Internal energy - The total energy of a system, represented by U. It is the total kinetic and potential energy of molecules in the system.
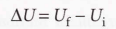
State function - A function where its value only depends on the current state of the system.
- Internal energy is a state function and an extensive property.
Internal energy, heat, and work can be measured in Joule (J), calories (cal), or kilocalories (kcal), but the most used one is Joule.
1 cal = 4.184 J
First Law of Thermodynamics - The internal energy of an isolated system is constant.
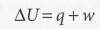
2.3 Expansion work
- Expansion work - Work arising from a change in volume, whether it is positive (expansion) or negative (compression).
The general expression for work
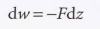
When related to volume:
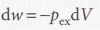

Free expansion
- Free expansion - Expansion against zero opposing force, when Pex = 0.
- In free expansion, w = 0.
Expansion against constant pressure
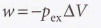
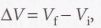
Reversible expansion
- Reversible change - Change that can be reversed by any modification of a variable.
2.4 Heat transactions
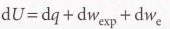
Calorimetry
Calorimetry - Study of heat transfer during chemical and physical processes.
Calorimeter - Devise used for measuring energy transferred as heat.
Adiabatic bomb calorimeter - Used to measure internal energy.
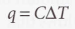
Heat capacity
- Heat capacity - The slope of the tangent to the curve at any temperature.
At constant volume, it’s defined as:
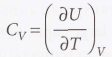
Molar heat capacity at constant volume - The heat capacity per mole of material. It’s an intensive property.
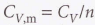
Specific heat capacity - The heat capacity of the sample divided by the mass.
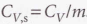
So relating these equations with internal energy, we obtain:
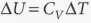
Or:
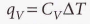
2.5 Enthalpy
Enthalpy (H), is defined as:
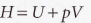
Enthalpy is a state function.
Measurement of an enthalpy change
- Isobaric calorimeter - A calorimeter used for studying processes at constant pressure.
- Adiabatic flame calorimeter - Used to measure the temperature change in a combustion reaction.
Variation of enthalpy with temperature
Heat capacity at constant pressure - The slope of the tangent to a plot of enthalpy against temperature at constant pressure.
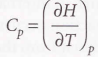
Molar heat capacity at constant pressure - Heat capacity per mole of the material, it’s an intensive property.
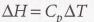
Since enthalpy is the same as heat at constant pressure:
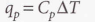
Thermochemistry
- Thermochemistry - Study of the energy transferred as heat during a chemical reaction.
2.7 Standard enthalpy changes
- Standard enthalpy change - The change in enthalpy for a process in which the initial and final substances are in their standard states.
- Standard state - Pure form of a substance at a specified temperature and 1 bar.
Enthalpies of physical change
- Standard enthalpy of transition - Standard enthalpy change that accompanies a change of physical state.
- Standard enthalpy of vaporization - Enthalpy change per mole when a pure liquid at 1 bar vaporizes at 1 bar.
- Standard enthalpy of fusion - Standard enthalpy change accompanying the conversion of a solid to a liquid.
Enthalpies of chemical change
Thermochemical equation - A combination of a chemical equation and the enthalpy change.
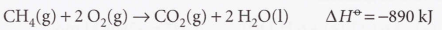
Standard reaction enthalpy
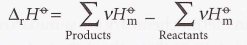
Standard enthalpy of combustion - Standard reaction enthalpy for the complete oxidation of an organic compound to CO2 gas and liquid H2O.
Hess’s Law
- Hess’s Law - The standard enthalpy of an overall reaction is the sum of the standard enthalpies of the individual reactions into which a reaction may be divided.
2.8 Standard enthalpies of formation
- Standard enthalpy of formation - Standard reaction enthalpy for the formation of the compound from its elements in their reference states.
- Reference state - The most stable state of an element at the specified temperature and 1 bar.
Reaction enthalpy of enthalpies of formation
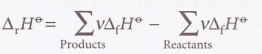
Enthalpy of formation and molecular modeling
- Mean bond enthalpies - Average enthalpy change associated with the breaking of a specific A--B bond.
2.9 Temperature dependence of reaction enthalpies
Kirchhoff’s Law
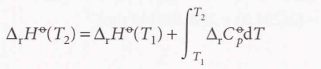
State functions and exact differentials
- Path functions - Processes that describe the preparation of the state.
2.10 Exact and inexact differentials
- Exact differential - An infinitesimal quantity that, when integrated, gives a result that is independent of the path between the initial and final states.
- Inexact differential - An infinitesimal quantity that, when integrated, gives a result that depends on the path between the initial and final states.
2.11 Changes in internal energy
General considerations
When V changes to V + dV at constant temperature, U changes to
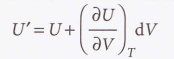
Internal pressure
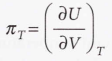
Changes in internal energy at constant pressure
Expansion coefficient - The slope of the plot of volume against temperature at constant pressure.
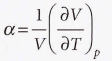
Isothermal compressibility - Measure of the fractional change in volume when the pressure is increased by a small amount.
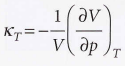
2.12 The Joule-Thomson effect
Joule-Thomson coefficient (µ)
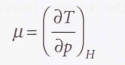
Isenthalpic expansion - Expansion at constant enthalpy.
Joule- Thomson effect - Cooling by isenthalpic expansion.
Isothermal Joule- Thomson coefficient
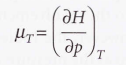
\