Alkanes
Organic Chemistry
Homologous Series
Definition
All share same general formula
Formula of a homologue differs from its neighbour by CH2
Contain same functional group
Have similar chemical properties
Show a gradual change in physical properties as molar mass increases
Can be prepared by similar methods
Formulae of Organic Compunds
Empirical Formula
Simplest whole number ratio of the elements in a compound.
Molecular Formula
Actual number of each element in a compound
Structural Formula
Illustrates how the atoms are arranged in a molecule
Displayed Formula
Shows how all the atoms are arranged and all the bonds between them
Common Functional Groups
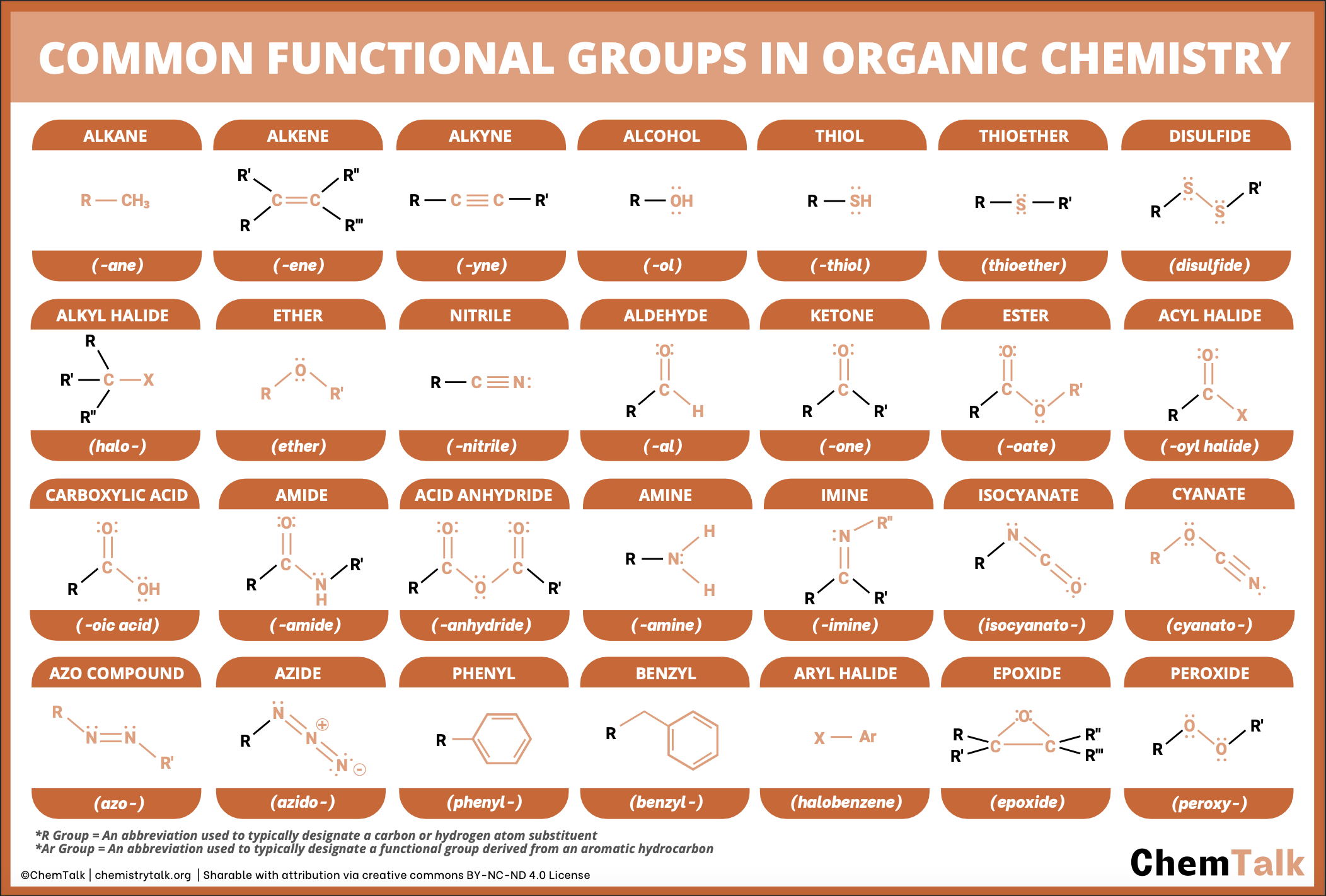
Skeletal Formula
Shows Carbon skeleton only, with any functional groups, hydrogen and carbon atoms part of the main chain are not shown.
Isomerism
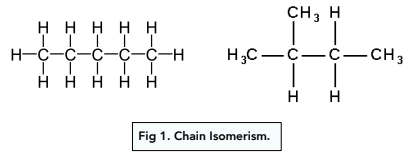
Chain Isomerism
Same molecular formula, but a different structure of the alkane chain (e.g branching).
They have different physical properties
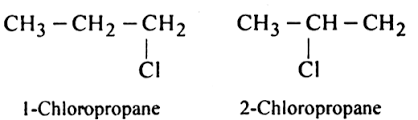
Positional Isomers
Same molecular formula, same chain structure, but different position of the functional group.
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons. They contain no double C=C bonds.
Functional Group Isomerism
Same molecular formula, but a different functional group. E.g. Alkenes and cyclic alkanes
Fractional Distillation
Crude Oil is heated and vaporised and passed into a huge fractionating column
A temperature gradient exists in the fractionating column. The column is coolest at the top and warmest at the bottom.
As the gases cool, they condense at different levels. The lightest (lowest boiling point) fractions are collected at the top of the column, whilst the heaviest (highest boiling point) fractions are collected at the bottom
Cracking
Thermal Cracking
High pressure and high temperatures
Produces high % of alkenes (free radical mechanism) used to produce polymers such as poly(ethene)
FREE RADICAL = A species with an unpaired electron = reactive intermediate
Catalytic Cracking
Reactive intermediate = Carbocation -C+-
Also produces cyclic alkanes and branched alkanes
Catalysts: Platinum, Palladium, Rhodium
Catalysts: Spread over a inert ceramic honeycomb; increases Surface Area
Reactions of Alkanes
Complete Combustion
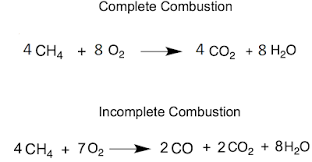
Produces carbon dioxide which causes global warming
Incomplete Combustion

Releases less energy reducing fuel efficiency
CO: Toxic gas that binds to the haemoglobin of RBCs, making them unable to carry oxygen
C: Global dimming and breathing problems
Unbranched hydrocarbons = particulates — global dimming
Sulphur Dioxide
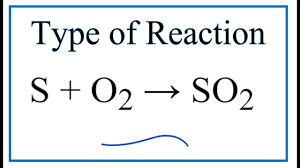
Combustion of sulphur impurities in fuel.
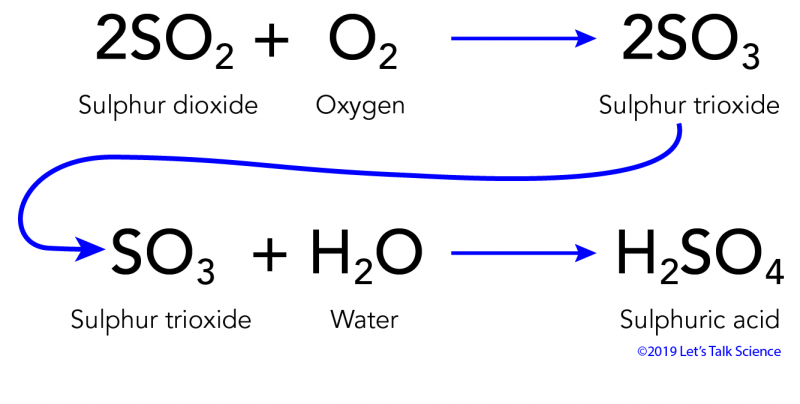
Sulphur dioxide dissolving to form acid rain
SO2 + CaO → CaSO3
Global Warming
CO2, H2O and CH4 all absorb IR radiation
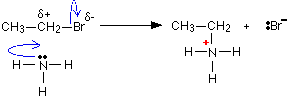
Elimination Mechanism


Alkane + Ammonia Mechanism