Chapter 20 - Money, price & financial intermediaries
The banking system and the allocation of saving to productive uses
M1: sum of currency outstanding and balances held in checking accounts.
M2: all the assets in M1 plus some additional assets that are usable in making payments but at greater cost or inconvenience than currency or checks.
Commercial banks and the creating of money
Bank reserves: cash or similar assets held by commercial banks for the purpose of meeting depositor withdrawals and payments.
100% reserve banking: situation in which banks' reserves equal 100% of their deposits.
Reserve-deposit ratio: bank reserves divided by deposits.
Fractional-reserve banking system: banking system in which bank reserves are less than deposits so that the reserve-deposit ratio is less than 100%.
Central banks, the money supply and the prices
Velocity: measure of the speed at which money changes hands in transactions involving final goods and services, or, equivalently, nominal GDP divided by the stock of money.
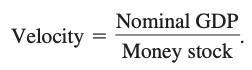
 Note
Note Studied by 65 people
Studied by 65 people Note
Note Studied by 16 people
Studied by 16 people Note
Note Studied by 18 people
Studied by 18 people Note
Note Studied by 21 people
Studied by 21 people Note
Note Studied by 58 people
Studied by 58 people Note
Note Studied by 12 people
Studied by 12 people Knowt
Knowt