Topic 1
==1.1 Anthropometrics==
Anthropometrics - The measurement of the human body regarding the size, strength and physical capacity
Types of Data:
Static - measurements of the subject while they are in a fixed position (ex. sitting in a chair)
Dynamic - measurements of the subject while they are in motion (ex. driving a car)
Primary - Data collected by the designer. Primary research is used to collect data that does not exist, is dated, and most commonly to cross-reference secondary data.
Secondary - data collected from other sources
Range of Sizes - A selection of sizes a product is made in that caters for the majority of a market.
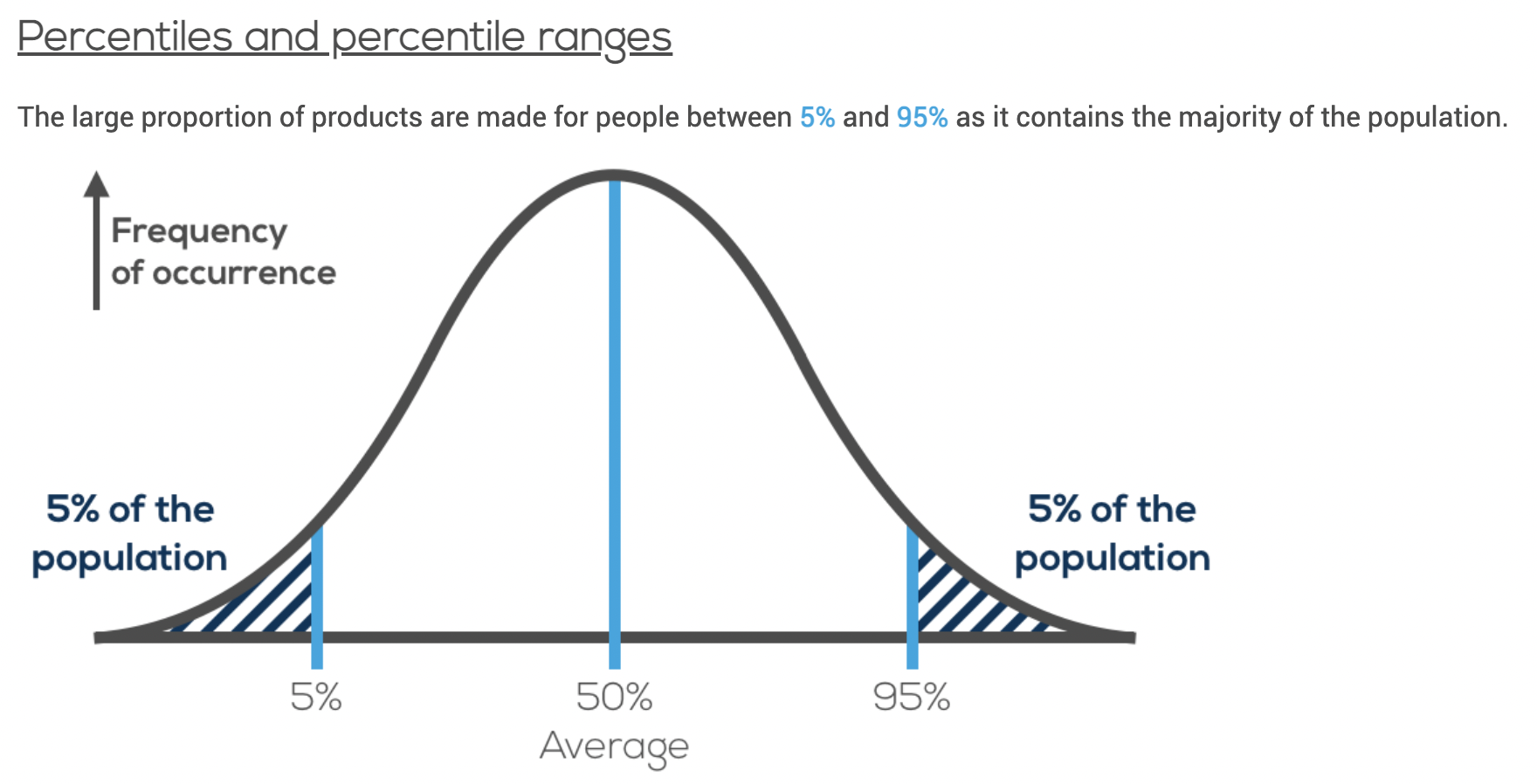
| Percentile | On what type of product it should be applied to |
|---|---|
| 5% and bellow | People at the 5% should be able to have an easy reach on/to/in a product because if they are able to reach then everyone else would be able to as well (ex. computer mouse). |
| Average | Average people should be able to comfortably use the product, as it applies to the people on either side of the graph (ex. chair). |
| 95% and higher | People at the 95% should be able to have a comfortable clearance on/to/in a product because if they have enough clearance everyone would as well (ex. door). |
Ergonomics - The science of refining the design of products to optimize them for human use
- Shape, form, color, texture
- Ease of use
- Comfort in use
- Mapping and user interfaces
- Affordance and logic of the user
- User experience.
Physical
The physical interaction between the person and the object. This includes worksite development, posture, repetitive stress, and more
Cognitive
The effect that objects have on a person's mental processes. This includes memory, perception, reasoning, and more
Organizational
Ways that complex systems can be easily understood by a group of people. This includes communications, work hours management, teamwork, and more
Bio-mechanics - The application of mechanical laws on living organisms
Clearance - the physical space between the objects
Reach - A range that a person can stretch to touch or grasp an object from a specified position.
Adjustability - The ability of a product to be changed in size commonly used to increase the range of percentiles that a product is appropriate for
Organoleptic - The reaction of human senses when exposed to different stimuli
| Stimulus | Factors Affecting |
|---|---|
| Sight | Ease of visibility, readability, computer screen, natural or artificial lighting |
| Hearing | Pitch, frequency, volume, mobile phones, background noise |
| Touch | Texture, grip, friction, temperature, keyboards, dentistry tools |
| Taste | Ingestions of toxins, children’s toys |
| Smell | Aroma, perfume, odor, workspaces, air quality |
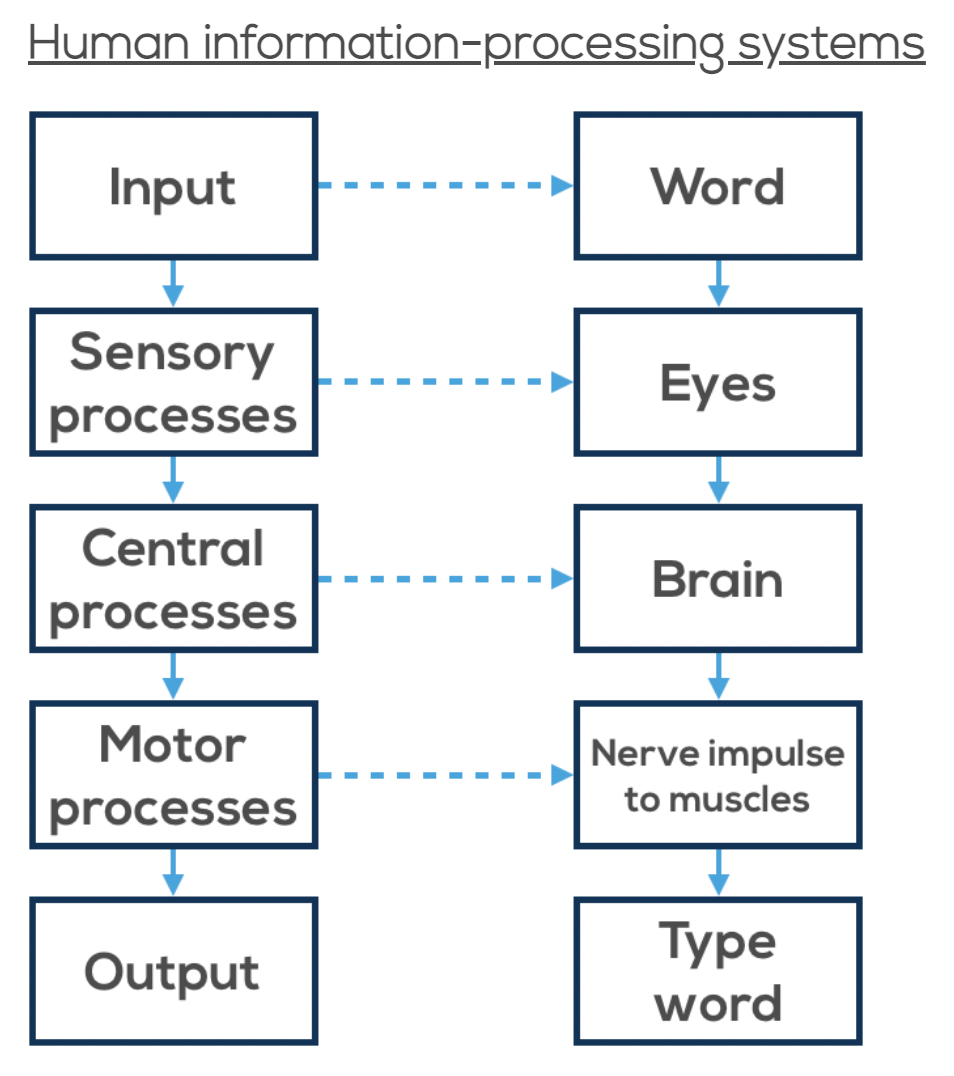
Human Information Processing System Reasons:
- Age – too young and maybe have not learnt the skills (long term memory), too old maybe forget what to do, or too weak to carry out the task.
- Strength – too weak to carry out the task
- Skills – do not have the necessary skills yet, may have forgotten he skills, skills needed are too complex
- Health – when mental or physical health is comprised which may lead to not carrying out the necessary tasks.
- Environmental factors – see below for more details
Environmental Factors:
- Air Quality
- Building acoustics
- Lighting
- Worker density
Alertness - The level of vigilance, readiness or caution of an individual
Human Error - slips and mistakes done by people resulted by automatic behaviour or subconsciousness
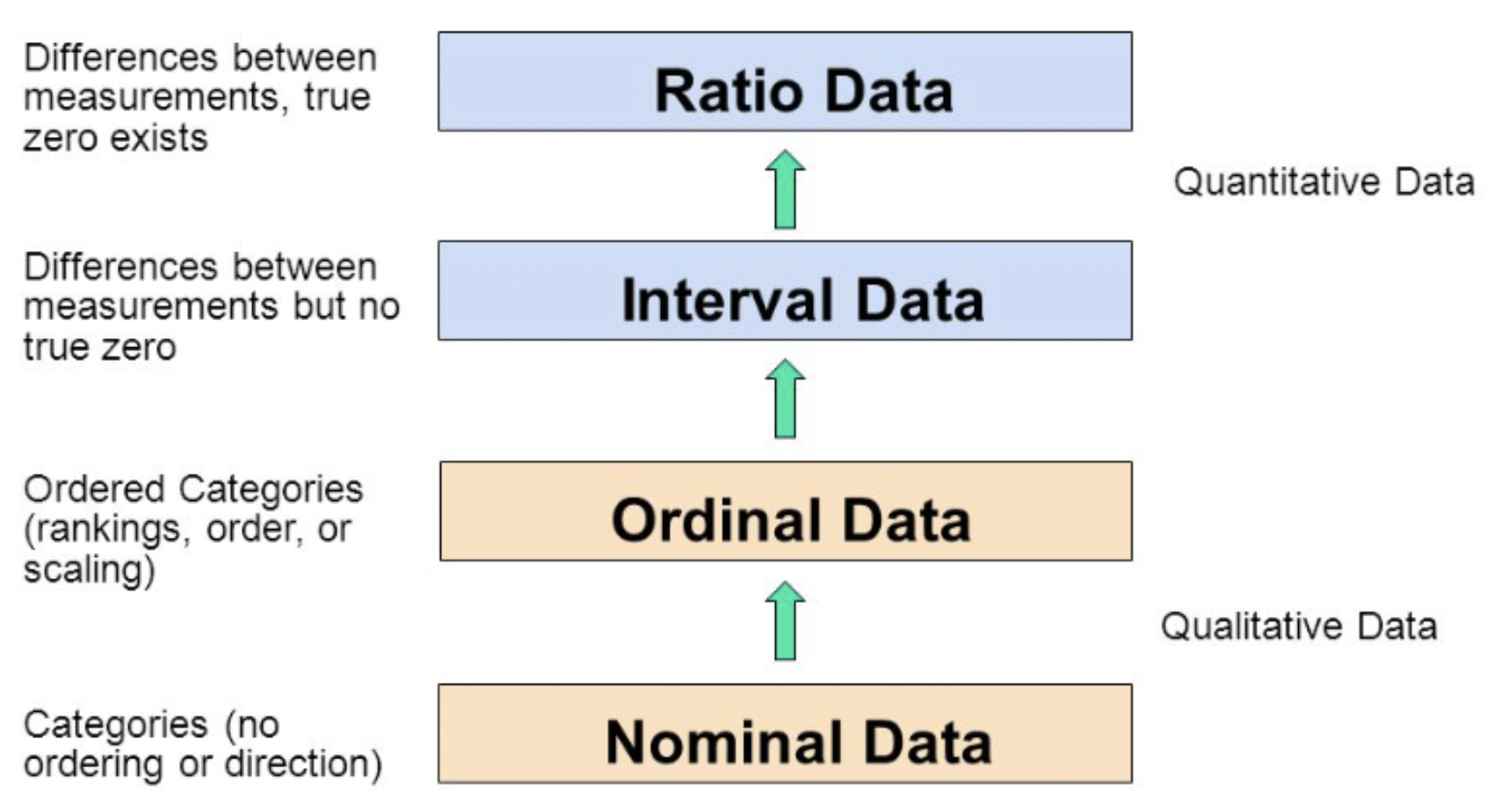
Ways of Measuring:
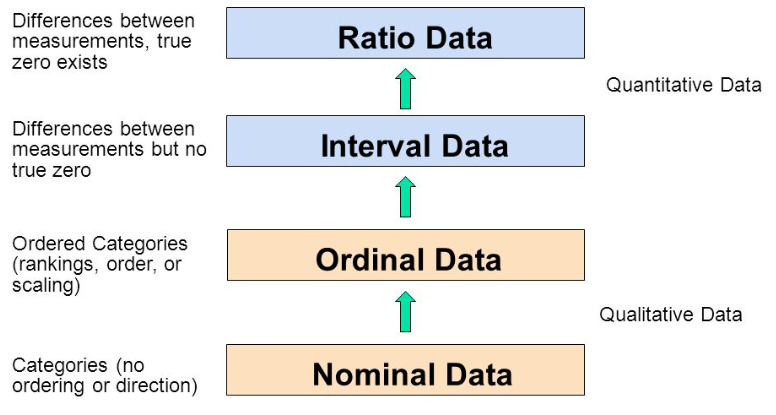
Nominal - listing a student's subjects; can be indexed using a number
Ordinal - preferences like ranking something from 1 - 5
Interval - agreement on a scale 1-5 (from Agree to Disagree)
Ratio - true Zero Point like a ruler
==1.2 Psychological Factors==
Psychological factors - human factor data related to psychological interpretations caused by light, smell, sound, taste, temperature and texture
Examples of Psychological Factors:
Smell
Light
Sound
Text
Texture
Temperature
Value - May be perceived as a function of cost, features, prestige, rarity etc. or a
combination of these factors
Methods of collecting psychological factor data:
Nominal (Data) Scale – Nominal means ‘by name’ and used in classification or division of objects into discrete groups. Each of which is identified with a name e.g. category of cars, and the scale does not provide any measurement within or between categories.
Ordinal (Data) Scale – A statistical data type that exists on an arbitrary numerical scale where the exact numerical value has no significance other than to rank a set of data points. Deals with the order or position of items such as words, letters, symbols or numbers arranged in a hierarchical order. Quantitative assessment cannot be made

Interval (Data) Scale – Interval data are based on numeric scales in which we know the order and the exact difference between the values. Organised into even divisions or intervals, and intervals are of equal size.
Ratio (Data) Scale – A ratio scale allows you to compare differences between numbers. For example, use a rating scale of 1-10 to evaluate user responses.
 ==1.3 Physiological Factors==
==1.3 Physiological Factors==
Physiological Factors - encompass the physical aspect of the body
Physical ergonomics - is concerned with human anatomy, and some of the
anthropometric, physiological and biomechanical characteristics as they relate to
physical activity
Human Values:
- quality of life
- improved safety
- reduced fatigue and stress
- increased comfort levels
- job satisfaction)
Key Criterias:
Force
Repetition
Duration - continuous muscular effect
Posture
Fatigue - When people get tired they react in different ways. Fatigue is the temporary
diminishment of performance
Comfort - can be both physiological and psychological and is defined differently depending on the user
Static
Dynamic
Human Factor Design:
- Effectiveness
- Efficiency
- Engagement
- Error tolerance
- Learnability
==Physical Limitations:==
- How the body moves
- Strength, size and stamina
- Visual sensitivity