Unit 2 - 2D Kinematics
Vector - a physical quantity with both magnitude and direction
Resultant - the sum of two or more vectors
Resolving a vector into components - replacing a vector with scalers
Horizontal Free Fall
Projectile motion - the motion of an object projected in a gravitational field, such as from Earth's surface, and moving along a curved path
when an object starts freefall, nothing changes the horizontal axis unless a force acts on it
if one object is dropped horizontally and the other vertically from the same height, both objects will land on the ground at the same time because they have the same vertical velocity
vertical velocity determines the time they reach the ground, while the horizontal velocity determines how far the horizontally thrown object travels on the x-axis
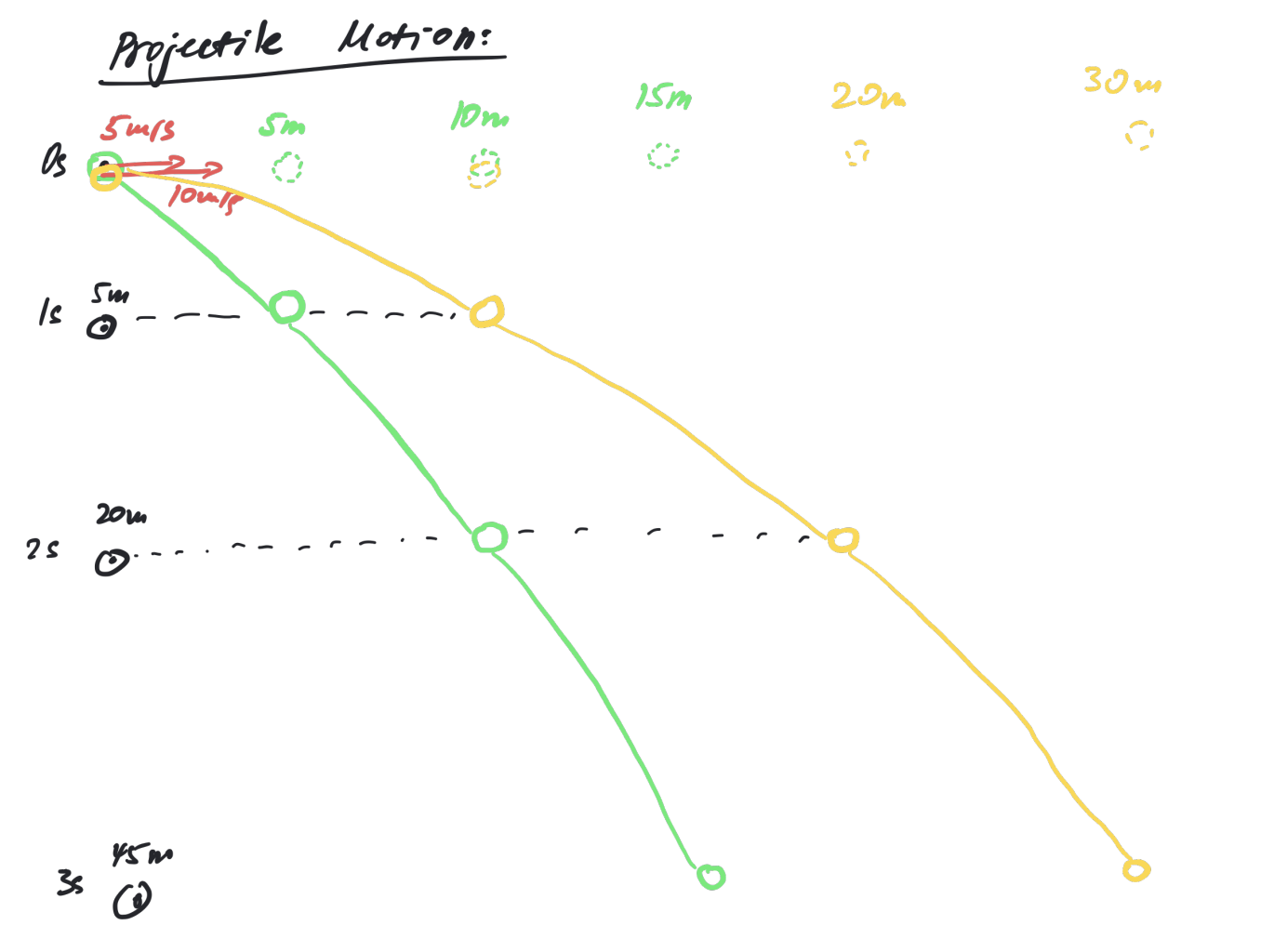
Parabolic Motion
completely symmetrical movement of the object thrown
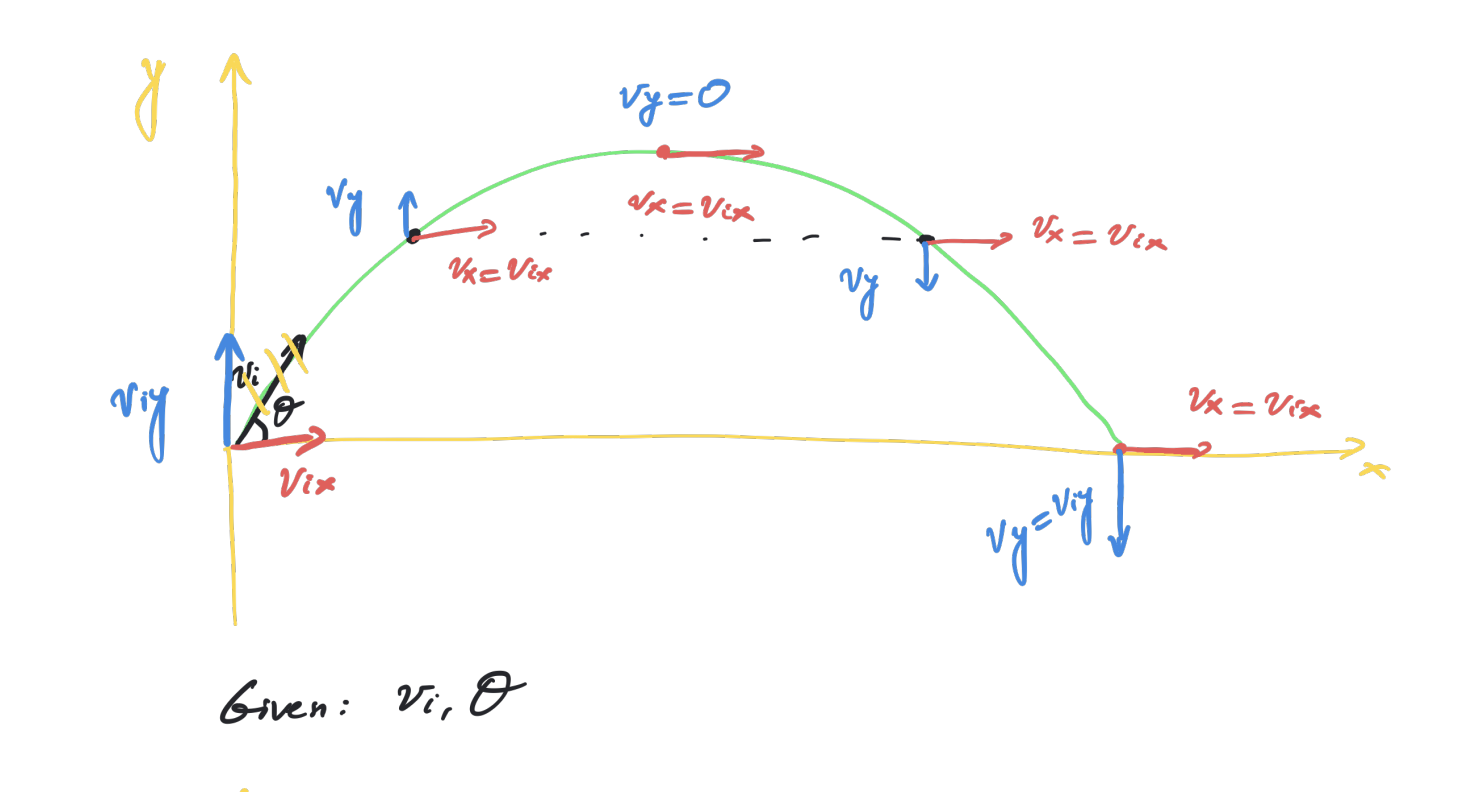
velocity, x, and y are always changing so x and y are described seperately
as the horizontal velocity increases the free fall stretches more
vix = vicosθ
viy = visinθ
horizontal velocity never changes
vertical velocity before it hits = -viy
GOAT vids