Sleep and Dreams
What is a Biological Approach?
Main assumptions
Similarities and differences betwen people can be understood in terms of biological factors.
Behavior, cognition, and emotions can be explained un terms of the working of the brain and the effects of hormones, genetics, and evolution.
Background for Dement & Kleitman Study
What is Consciousness?
Consciousness:
Our awareness of ourselves and our environments.
Sleep and Dreams
Circadian Rythm:
Regular bodily rhythms that occur on a 24 hour cycle, such as body temperature, sleep, and wake cycle.
Ultradian Rhythms
Biological rhythms that repeats more frequently than once a day such as heartrate and appetite.
Sleep
Periodic, natural reversibl loss od concciousness.
We measure with the Electro-encephalogram (EEG)
Brain Waves and Sleep Stages (Non-REM)
Beta Waves = Awake
Alpha Waves = Relaxed
Hallucinations = onset of sleep/ false sensory experiebces/falling or rising
Theta Waves = Stage 1 light Sleep
Sleep Spindles = Stage 2 (burst of activity)
Delta Waves = Stage 3-4/ large, slow waves of deep sleep.
Stages in Typical Nights Sleep
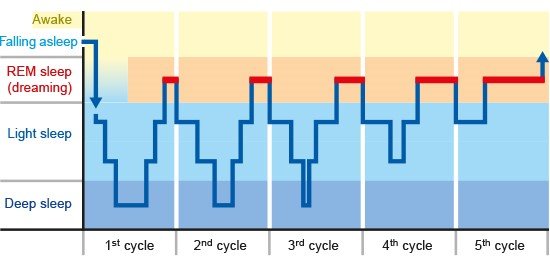
REM (Rapid Eye Movement) Sleep
recurring sleep stage (every 90min)
vivid dreams/lucid dreaming/ nightmare
“paradoxial Sleep”
Muscles are generally relaxed, but other body systems are active.
Sleep Deprivation
Effects of Sleep loss
fatigue
imparied concentration
depressed immune system
greater vulnerability to accidents
Sleep Disorders
Night Terrors
Occur within 2 or 3 hours of falling asleep, usually during stage 4
high arousal - scared but no recall of it
Somnambulism
Sleep halking also in stage 4
Runs in families & affects children more of ten
Ususally due to stress
Insomnia
Persistent problems in falling or staying asleep
Narcolepsy
Uncontrollable sleep attacks
Sleep apnea
Temporary cessation of breathing
Sleeping Paralysis
Occurs during the transition between wakefulness and sleep.