Mechanisms and Characteristic of Nerve Trauma
- Trauma
- Physical injury or wound that is produced by an external or internal force
- Mechanical Injury - force or mechanical energy is that which changes that state of rest or uniform motion of matter
- When a force applied to any part of the body results in a harmful disturbance in function and/or structure - a mechanical injury occurs
- 5 Types of Tissue Loading
- Compression - shortens and widens tissue
- Tension - pulls or stretches tissue
- Shearing - rubbing (blisters)
- Bending - tension and compression
- Torsion - twisting
- Traumatic vs. Overuse Injuries
- Injuries are either caused by trauma or overuse
- All injuries are acute, if the injury does not heal properly it becomes chronic
- Injuries that result from overuse occur with the repetitive dynamics of running, throwing, or jumping
- Anatomical Characteristics of Muscles

- Muscle → Fascicles → Muscle fibers (cells) → Myofibrils → Thick and thin filaments
- Muscle: Tissue of the body which primarily functions as a source of power
- Responsible for moving extremities and external areas of the body are called skeletal muscle
- Muscle Strains
- When a muscle is overstretched by tension or forced to contract against too much resistance, separation or tearing of the muscle fibers occurs.
- A muscle strain can be a stretch, tear or rip in the muscle or its tendon.
- Grade 1: some muscle fibers have been stretched or torn
- Grade 2: a number of muscle fibers have been torn
- Grade 3: a complete rupture of the muscle has occurred
- Muscle Cramps
- Extremely painful involuntary muscle contractions that occur commonly in the calf, abdomen or hamstrings
- Heat cramps is related to excessive loss of water and some extent several electrolytes or ions that are essential elements in muscle contraction
- Muscle Guarding
- Muscle contracting in response to pain
- Body’s defense mechanism to act as a splint
- Muscle Spasms
- A reflex reaction caused by trauma to the musculoskeletal system
- Clonic - involuntary muscle contraction characterized by alternate contraction and relaxation in rapid succession
- Tonic- muscle contraction characterized by constant contraction that lasts for a period of time
- Muscle Soreness
- Pain caused by overexertion in exercise
- Acute onset muscle soreness - fatigue, occurs immediately after exercise
- Delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS) - increased muscle tension, swelling, and stiffness
- causes include small tears in the muscle tissue or disruption in connective tissue that holds muscle tendon fibers together
- Anatomical Characteristics of Tendons
- Tough band of connective tissue that attaches muscle to bone
- Concentrates a pulling force in a limited area
- Because a tendon is usually double the strength of the muscle it serves, tears commonly occur at the muscle belly, musculotendinous junction or bony attachment

- Tendinitis/Tendinosis
- Tendinitis- inflammation of the tendon
- Moves or slides on the other structures around it whenever the muscle contracts, if the movement is performed repeatedly the tendon can become irritated and inflamed
- Crepitus - a crackling feel or sound that occurs by tendon’s tendency to stick to the surrounding structure while it slides back and forth
- Tendinosis - breakdown of a tendon without inflammation (degeneration)
- Tenosynovitis - inflammation of a tendon and its synovial sheath (thin layer of tissue)
- Contusion
- Compression of soft tissue that results in bleeding into surrounding tissue
- Ecchymosis - bluish-purple discoloration of the skin
- Joints
- A point where two bones interest
- Necessary for all types of movement in the body involving bones
- The force generated by muscles is used to carry out movement through various joints
- Synovial joints
- Articulations of two bones surrounded by a joint capsule lined with synovial membrane
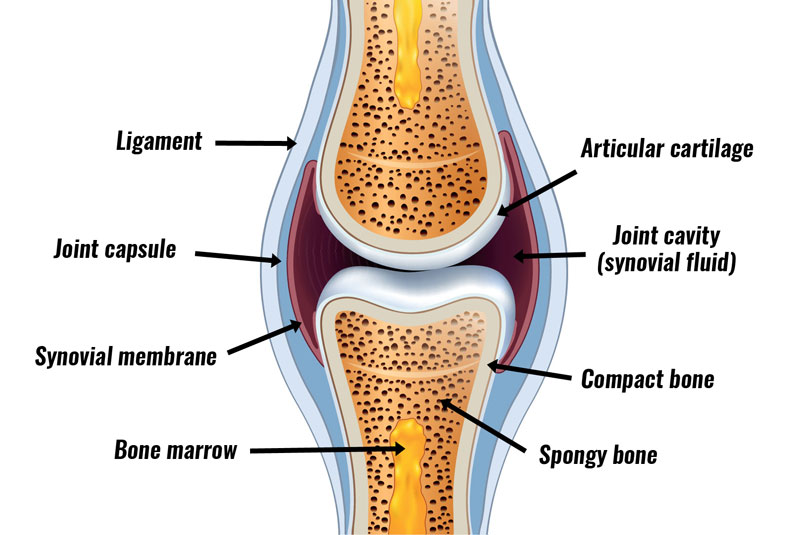
- Bursitis: inflammation of bursae (pieces of synovial membrane that contain a small amount of fluid) at sites of bony prominences between muscle and tendon
- Dislocations and Subluxations
- Dislocation occurs when at least one bone in a joint is forced completely out of its normal alignment
- Subluxation is like a dislocation except that a bone comes partially out of its normal articulation then goes right back into place
- Anatomical Characteristics of Ligaments
- Ligaments are composed of dense connective tissue arranged in parallel bundles of collagen composed of rows of fibroblasts
- Ligaments connect bone to bone

- Ligaments Sprains
- Occur when stress is applied to a joint that forces motion beyond its normal limits or planes of movement
- Grade 1 Sprain - stretch or separation
- Grade 2 Sprain - tearing and separation with instability
- Grade 3 Sprain - total tear of ligament which leads to instability of joint
- Classification and Load Characteristics of Injuries