1.introduction in to haloalkanes and haloalkenes
The replacement of hydrogen atom(s) in an aliphatic or aromatic hydrocarbon by halogen atom(s) results in the formation of alkyl halide (haloalkane) and aryl halide (haloarene)
Haloalkanes contain halogen atom(s) attached to the sp3 hybridised carbon atom of an alkyl group
haloarenes contain halogen atom(s) attached to sp2 hybridised carbon atom(s) of an aryl group.
Many halogen containing organic compounds occur in nature and some of these are clinically useful: -
They are used as solvents for relatively non-polar compounds and as starting materials for the synthesis of wide range of organic compounds.
Chlorine containing antibiotic, chloramphenicol, produced by microorganisms is very effective for the treatment of typhoid fever.
Our body produces iodine containing hormone, thyroxine, the deficiency of which causes a disease called goiter.
Synthetic halogen compounds : chloroquine is used for the treatment of malaria
halothane is used as an anaesthetic during surgery.
Haloalkanes and haloarenes may be classified as follows:
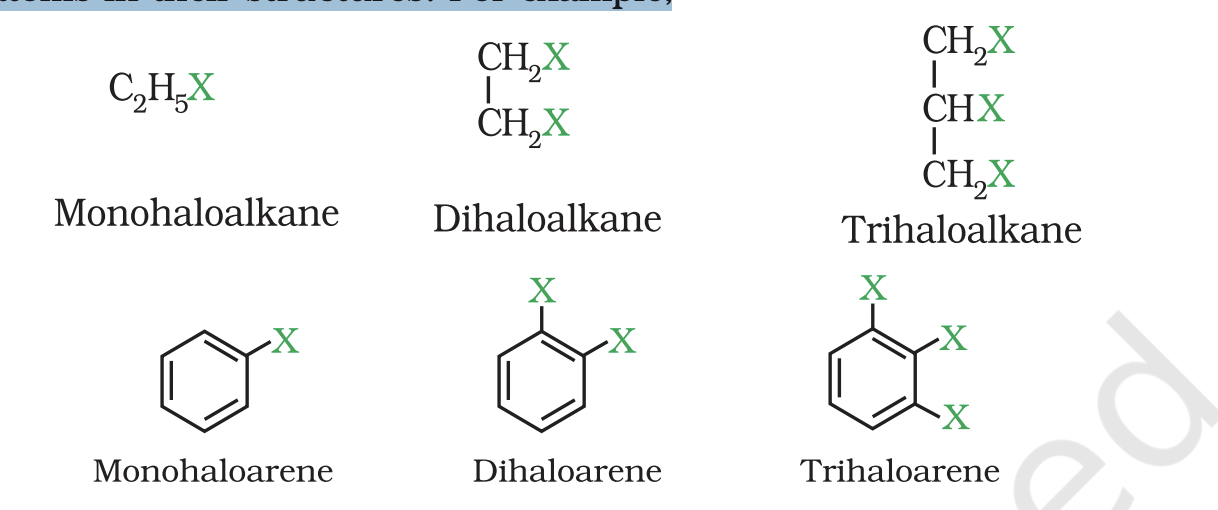
These may be classified as mono, di, or polyhalogen (tri-,tetra-, etc.) compounds depending on whether they contain one, two or more halogen atoms in their structures.
Monohalocompounds they are classifies as 😄
(a) Alkyl halides or haloalkanes (R—X) In alkyl halides, the halogen atom is bonded to an alkyl group (R).
They form a homologous series represented by CnH2n+1X.
They are further classified as primary, secondary or tertiary according to the nature of carbon to which halogen is attached.
If halogen is attached to a primary carbon atom in an alkyl halide, the alkyl halide is called primary alkyl halide or 1° alkyl halide.
if halogen is attached to secondary or tertiary carbon atom, the alkyl halide is called secondary alkyl halide (2°) and tertiary (3°) alkyl halide
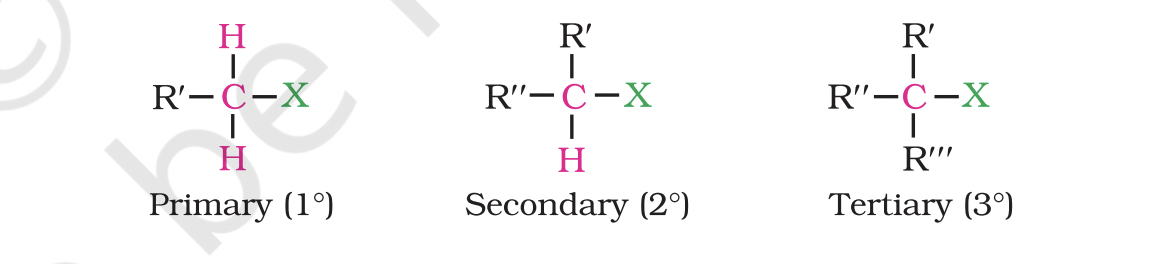
(b) Allylic halides
These are the compounds in which the halogen atom is bonded to an sp3 -hybridised carbon atom adjacent to carbon-carbon double bond (C=C)
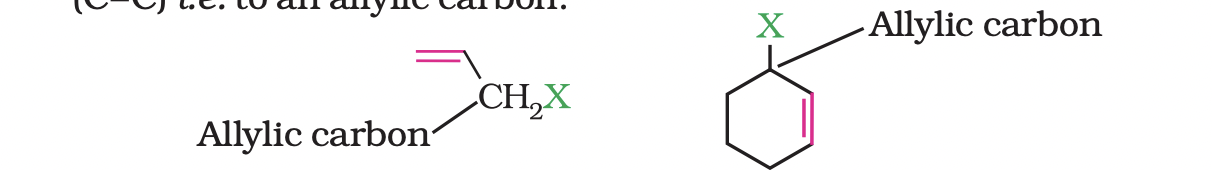 .
.
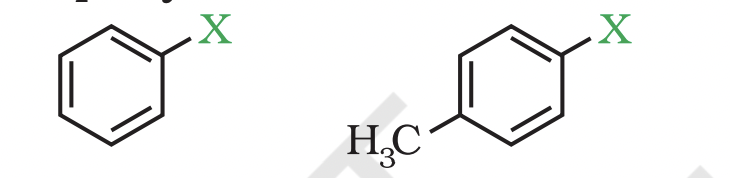
(c) Benzylic halides These are the compounds in which the halogen atom is bonded to an sp3 -hybridised carbon atom attached to an aromatic ring.
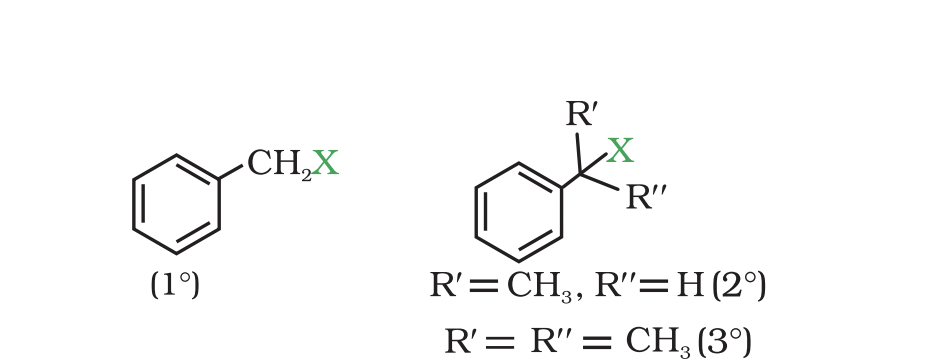
Compounds Containing sp2 C—X Bond
(a) Vinylic halides
These are the compounds in which the halogen atom is bonded to a sp2 -hybridised carbon atom of a carbon-carbon double bond (C = C).
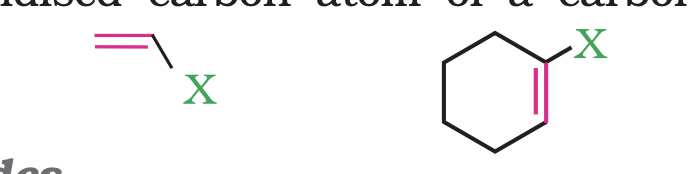
(b) Aryl halides
These are the compounds in which the halogen atom is directly bonded to the sp2 -hybridised carbon atom of an aromatic ring.