2.8 - Network Tools: Professor Messer
Cable crimper

Used to pinch connectors onto a wire - typically coaxial, twisted pair, or fiber.
Metal prongs push through the insulation and clamp the wire onto the plug.
Crimping best practices:
Get a good crimper, cable snips (electrician scissors), and a good wire stripper
Make sure you know the correct modular connector - different cables use different adaptors.
Practice - it won’t take long to be proficient.
Cable stripper
Removes wiring strips from the outside of Ethernet cables.
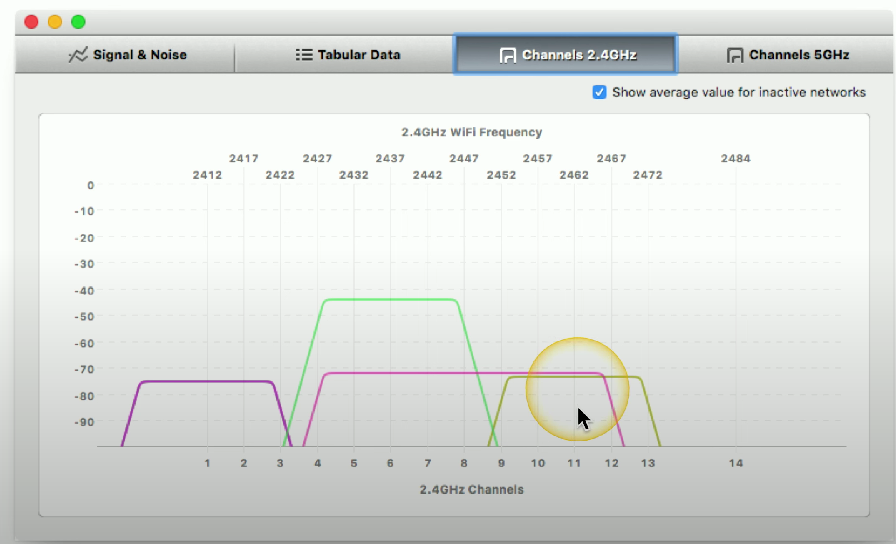
Wi-Fi analyzer
Analyzes Wi-Fi networks to optimize performance and identify interference, typically a purpose-built device or software added to a laptop/workstation.
Toner probe/tone generator
A device used to locate an individual cable in a complicated cabling environment.
Usage process:
Connect the tone generator to the cable you want to trace - can be done via alligator clips or other connection types.
Use the toner probe to detect the signal emitted by the tone generator, allowing you to pinpoint the cable's location among others.
Follow the sound feedback and visual indicators from the probe to accurately trace the path of the cable.
Punchdown tool
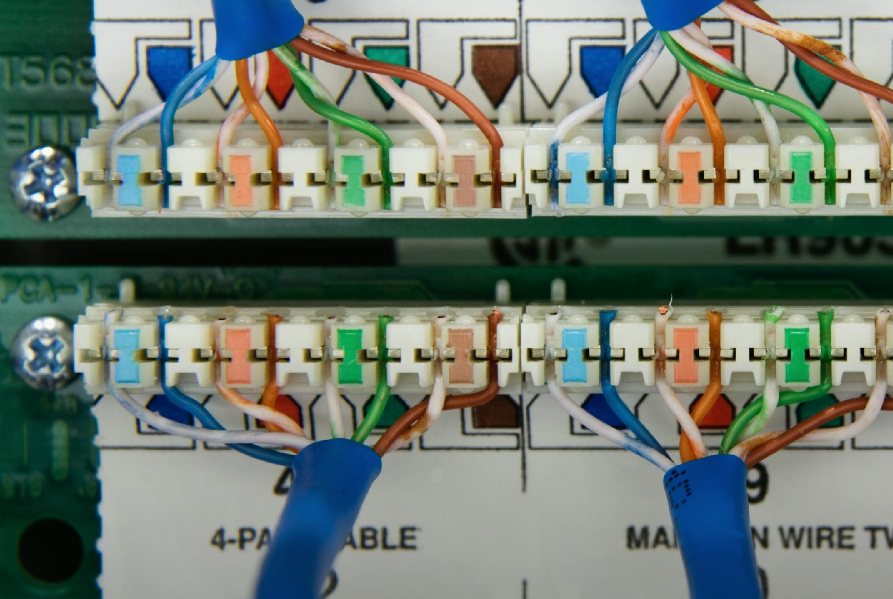
Used to “punch” (add) wires into a wiring block and trims them during the connections.
Different sizes: 66 block, 110 block and others.
Can be tedious - each wire must be individually punched
Best practices:
Organization/cable management is key - record the wires connected to each (typically) numbered block
Maintain the cables’ twists
Document everything - can be done via written docs or cable graffiti
Cable tester
Performs continuity tests for two cables - if a cable is connected properly.
Can identify missing pins/crossed wires.
Not typically used for frequency testing.
Loopback plug
Used for testing physical ports/interfaces
Data is sent from one end of the interface, looping back around, then returning to the same device - if the two values don’t match then there may be a problem with the physical interface.
Used for RS-232 connections (9-pin or 25-pin), or network connections, Ethernet, T1, Fiber
Network tap
Intercept network traffic and send captured packets to a packet capture device.
Can be physical taps: disconnect network links, place a tap in the middle, and forward captured data to an analyzer.
Port mirror: A method of duplicating network traffic from one port to another, allowing a network monitoring device to analyze packets without interrupting the flow of data.