ENGLISH REVIEWER 3RD QUARTER
Propaganda - is a form of a communication that is aimed at influencing the attribute perspectives and emotions of people or communities
Types of propaganda techniques
(Can be products, acceot ideas and avail services)
Card Stacking - technique that shows the products best features
Name Calling - the use of names that may evoke fear or hatred
Plain Folks - use common people to sell or to promote a product or service
Glittering Generalities - this is the use of words or ideas that evoke a positive emotional response from an audience
Soft Soap - this is the use of flattery or insincere compliments designed to get the audience on the side of the speaker
Bandwagon - this is a technique that persuades people by showing them that everyone else are doing the same thing (just folllowing a trend)
Testimonial - this is a technique wherein a famous or seemingly authoritive person recommends a product or service
Transfer - this is a technique used in propaganda and advertising known as association this technique of projects positive or negative qualities of a person,entity, or value to another in order to make the second more acceptable or discredit it
Simplification - this is used to reduce crucial issues to basic ideas and packages them with catchy slogans and images
Loaded words - this is a technique uses words in attempting to influence an audience by using emotional appeal or stereotypes that cannot be supported by concrete evidences
Literature
from the latin word litaritura/litteratura which means “writing formed letters”
it pertains to a collection of written, compositions, encompassing poetry, novels, etc.
Types of literature
Fiction - form of literary expression stemming from a writer’s creative mind
Nonfiction - grounded in reality focusing on actual people, places, and events.
Elements of a story
Setting - it refers to the time and place in which the action of the story happens
Plot - it is characterized as a connected series of events within a narrative where each occurrence influences the others demonstrating a cause and effect connection
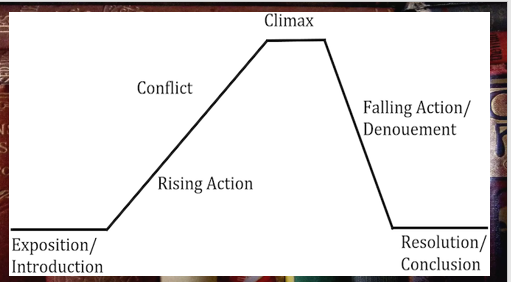
Exposition/initial action - beginning of story
Rising action - tension starts to build
Climax - characters face the major conflict
Falling action - after climax
Resolution/denouement - conclusion of the story
Character - it refers to a person, object, or an animal
Protagonist - it is the main character who does heroic acts in the story
Antagonist - it is also a main character who opposes the protagonist
Conflict - it refers to the problem that the main characters have to face
Man vs man - protagonist vs antagonist
Man vs self - protagonist vs himself
Man vs society - protagonist vs govenment, culutural or societal tradition
Man vs supernatural - protagonist vs gods or supernatural forces
Man vs nature - protagonists vs environment, weather, animals, etc
Point of view - this is the angle of narration or the perspective from which the story is told
First person - the narrator is a character in the story who can reveal only personal thoughts and feelings. it uses the personal pronoun I
Third person - this is when the narrator is removed from the story
Theme - refers to the idea or the message of a story
Issue - significant problem
Common issue
Social
Moral
Economic
Social issue - problem that impacts numerous individuals
Moral issue - disagreements in beliefs
Abortion - termination of pregnancy
Stealing - involves unlawful taking someone else’s property without permission
Corruption - is a criminal act that involves the improper utilization of public authority for personal gain
Economic - scarcity of resources considered inadequate to fulfill human wants and necessities
Inflation - fluctuations of prices for goods
Poverty - lack of basic needs like food, housing, education, and health
Unemployment - lack of jobs