DigestionNutrition Review clinical medicine
Name:_____KEY__________________
Clinical Medicine I
Digestive System Reading Questions
Answer the following questions using the Digestive PowerPoint, lecture notes and your Anatomy and Physiology textbook Ch. 16.
- What does the digestive system do?
Takes complex foods and breaks them down into simple nutrient molecules so that those simple nutrients can be absorbed into the bloodstream
- What are the names used for the digestive tube?
GI tract, Gastrointestinal Tract, Gut, Alimentary canal
- List the accessory digestive organs.
Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, Pancreas
- List and describe the different types of diets.
Herbivore plant eater
Carnivore meat eater
Omnivore eats a variety of plants and meat sources
- What is the main difference between a monogastric and ruminant digestive system?
Monogastric is one stomach. Ruminant is one true stomach with 3 fore stomachs for mixing and fermenting
- Define:
- Gastro: Stomach
- Enteric: Intestines
- Enteritis: Inflammation of the intestines
- What are the 5 basic functions of the digestive tract?
Prehension, Mastication, Chemical digestion, Absorption of nutrients and water, and
Elimination of waste
- List the layers of the GI wall. What does each layer consist of?
Mucosa is the lining layer and consists of lining epithelium and some loose connective tissue
Submucosa contains glands and dense connective tissue
Muscle is the thick muscle that allows for peristalsis and segmental contractions
Serosa is the outermost layer that consists of a thin, tough layer of connective tissue
- What is the connective tissue that that suspends the digestive tube in the abdomen called? What does it contain?
Mesentery. Connective tissue and blood vessels
- How does peristaltic and segmental contractions work?
Peristalsis moves ingesta along the tube by waves
Segmental mixes ingesta back and forth in a mixing motion and sections off like a string of
Sausages .
- What are the key structures in the mouth?
Lips, tongue, teeth, salivary glands, hard palate, soft palate, and oropharynx
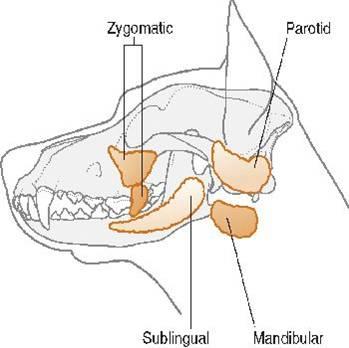
- What are the four pairs of salivary glands called?
Parotid, mandibular, sublingual ( A bonus gland is the zygomatic in carnivores)
- What do digestive enzymes do?
They are proteins that promote (catalyze) the chemical reactions that split complex food molecules
- What kinds of animals have amylase in their saliva? What does amylase break down?
Ruminants, Carbohydrates (sugars)
- What does lipase break down?
Fats or lipids
- Where does the esophagus enter the stomach?
Cardia
- The monogastric stomach is generally divided into how many different areas? What are they?
5, cardia, fundus, body, pyloric antrum (or Antrum) and the pylorus
- What are the three segments of the small intestine in order?
Duodenum, Jejunum, and Ileum
- What is the cecum?
It is a blind pouch of the large intestines between the ileum and the colon. It is more formed in horses since they are hind gut fermenters
- How has the small intestine adapted to increase surface area?
Folds in the walls called villi and microvilli also called the brush border
- Most cases of diarrhea are caused by what?
Lack of segmental contractions in the small intestine so the ingesta flow through too fast
- What is the condition of decreased movement of ingesta called?
Ileus
- What types of nutrients can be absorbed intact into the small intestine wall?
Water, electrolytes and vitamins
- What nutrients must be chemically digested?
Proteins, carbohydrates and fats
Introduction to Nutrition Use your CTVT Chapter 9 and your notes for this section.
- What organization sets the nutritional assessment guidelines?
AAHA
- List the 5 Vital Assessments that were mentioned in class?
Temperature, Heart Rate, Respiration Rate, Pain, Nutrition
- What are the responsibilities of the RVT in regards to nutrition?
To increase the quality of care provided to patients
To help establish a valuable personal and professional bond with clients
To increase profitability for the practice
- What are 2 ways to fulfill the responsibilities of the RVT in regards to nutrition?
Client education; give clear instructions on how to feed, what to feed, how much to feed; discuss therapeutic diets when indicated
- What are the goals of nutrition for companion animals?
Small Animal
Maintain health
Maximize the length and quality of life by reducing nutritional risk factors
- What are the goals of nutrition for large animals?
Large Animal
Maximize meat or milk production
Rapid meat production
Increased quality of milk production
Pays no attention to increasing length of life
- What affects a dog or cats daily nutritional needs?
Species, Age, Activity Level, Purpose of life, Weather, Reproductive Status, Injury
- How does weather affect the daily nutritional needs of dogs and cats?
Their caloric intake should be increased during cold weather to help them have the energy to produce body heat
- Define nutrient.
A substance that provides nourishment to an organism allowing it to carry out its normal functions
Are chemicals that are essential and that a plant or animal obtains from the environment for growth and maintenance of life
- What are the three categories of nutrients?
Water, Macronutrients, Micronutrients
- List the nutrients that are energy producing.
Macronutrients-Carbs, Protein, Fats
- List the nutrients that are non-energy producing.
Vitamins, Minerals, and Supplements
- Explain what essential means.
Cannot be manufactured by the body (at least not fast enough or in quantities needed) and must be obtained from the diet
- Explain what non essential means.
Can be manufactured by the body and does NOT have to be obtained from the diet
- What does conditionally essential mean?
Must be obtained from the diet during certain life stages or disease processes due to the body not being able to produce it well enough during those times
- Label the salivary glands.