6.2.1(e) - microorganisms in biotechnology
spec points
the use of microorganisms in biotechnological processes
To include reasons why microorganisms are used; economic considerations, short life cycle and growth requirements.
what is biotechnology?
Biotechnology involves applying biological organisms to the synthesis, breakdown or transformation of materials in the service of people.
Exploitation of living organisms or biological processes to improve:-
Agriculture
Animal Husbandry
Food Science
Medicine
Environment
Industry
Most BT involves the use of enzymes in the manufacturing of required products. Enzymes are most stable when inside a whole organism – MOs.
Q) Why use MOs?
Short life cycle results in rapid growth – large numbers of MO can be generated in a short space of time.
Easy to GM/GE (plasmids).
Unaffected by climate so can be grown anywhere.
Huge range of MOs.
No ethical/welfare issues.
Need only optimal growth conditions (cheap requirement):-
Low temp
Oxygen
Nutrients
Waste removed
food production – indirect – microorganisms action on food
Process | MO involved | Steps |
Baking | Yeast | Yeast respire aerobically in dough producing CO2, when heated CO2 bubbles expand and bread rises. |
Brewing | Yeast | Yeast respire anaerobically in a fermenter producing ethanol. |
Cheese Making | Range of bacteria | Bacteria feed on lactose in milk changing the texture and taste of the milk (curds and whey).Bacteria also inhibit the growth of other bacteria that would cause milk spoilage. |
Yoghurt Making | Bacteria – Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus | Both bacteria are added to skimmed milk in a 1:1 ratio. Then incubated (fermented). Bacteria produce polymers that give yoghurt its smooth thick texture. |
All BT food production needs to be done in sterile conditions otherwise the process could culture bacteria that cause mould and food spoilage.
NOTE// - Milk is used as the substrate to make cheese and yoghurt. During the process the milk is:-
Pasteurised – Heated to kill off all natural bacteria.
Homogenised – spun to evenly distribute fat droplets – uniform product.
Food production – Direct
Any Mushrooms eaten.
Mycoprotein (SCP) – Quorn made directly from Fungus ‘Fusarium’.
Fusarium grown in huge fermenters with glucose syrup.
Grows into a mycelium (fungal body).
Mycelium combined with albumen (egg white) and processed into food product.
advantages v disadvantages
Advantages of using microorganisms to produce human food Disadvantages of using microorganisms to produce human food | |
Microorganisms reproduce fast and produce protein faster than animals and plants. | Some microorganisms can also produce toxins if the conditions are not maintained at the optimum. |
Microorganisms have a high protein content with little fat. | The microorganisms have to be separated from the nutrient broth and processed to make the food. |
Microorganisms can use a wide variety of waste materials, including human and animal waste, reducing costs. | Need sterile conditions that are carefully controlled, adding to costs. |
Microorganisms can be genetically modified to produce the protein required. | Often involve GM organisms, and many people have concerns about eating GM food. |
Production of microorganisms is not dependent on weather, breeding cycles, etc. – it takes place constantly and can be increased or decreased to match demand. | The protein has to be purified to ensure it contains no toxins or contaminants. |
No welfare issues when growing microorganisms. | Many people dislike the thought of eating microorganisms grown on waste. |
Can be made to taste like anything. | Has little natural flavour – needs additives. |
Microorganisms – medicines and bioremediation
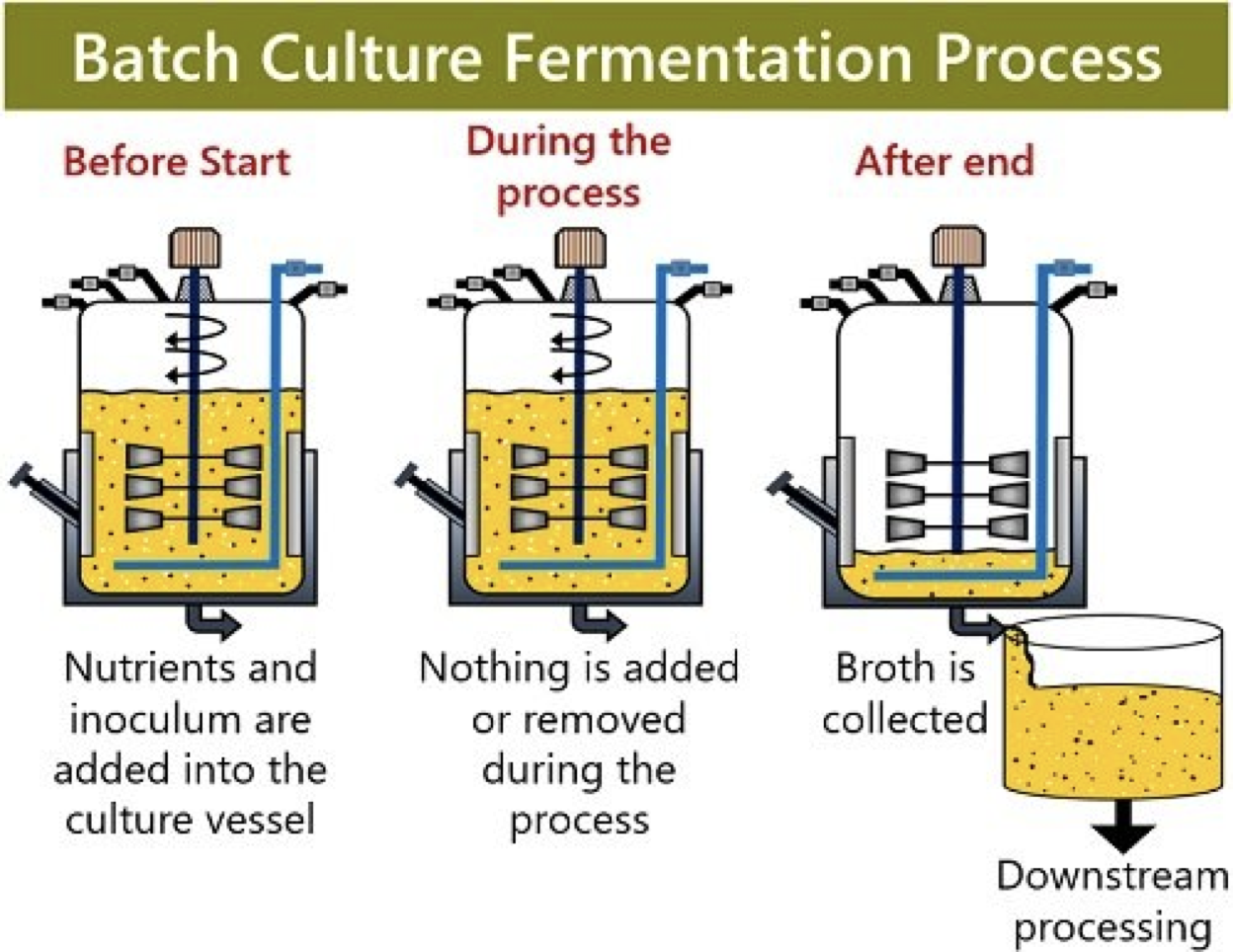
1) Antibiotic production – Penicillin:- produced commercially in small scale fermenters by ‘Batch Culturing’ of the Fungus – Penicillium.
Penicillium requires specific conditions in the fermentation process to include:-
High oxygen levels.
Rich nutrient medium to grow well.
Specific temp (25-27◦C)
Specific pH – 6.5 (use buffer).
Penicillium cultured and Antibiotic Penicillin extracted and purified.
Microorganisms – medicines and bioremediation
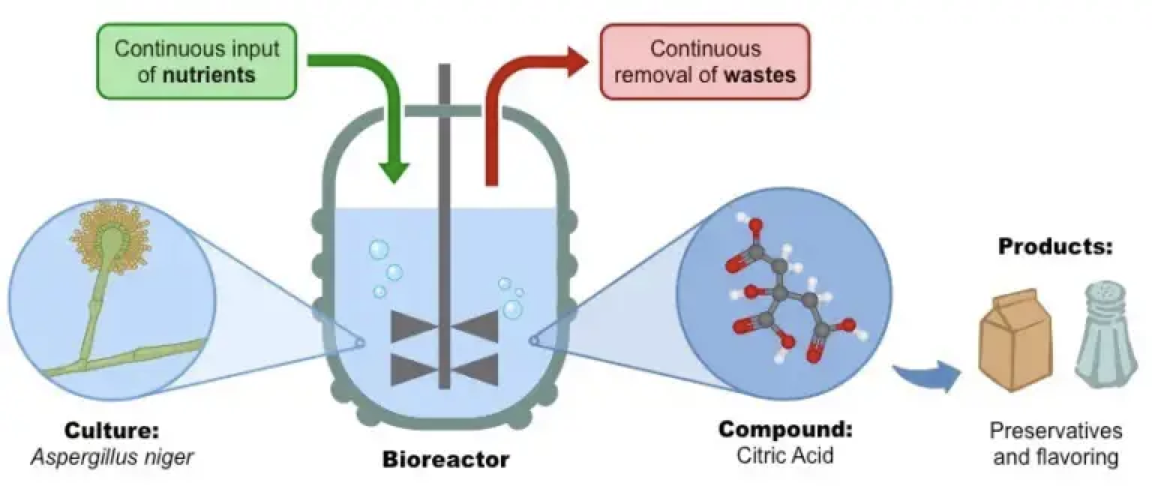
2) Insulin production – E.Coli genetically engineered to make human insulin in ‘Continuous Culturing’ in fermenter.
GM bacteria – production of Insulin
Early GM used bacteria because of their simple genetic structure.
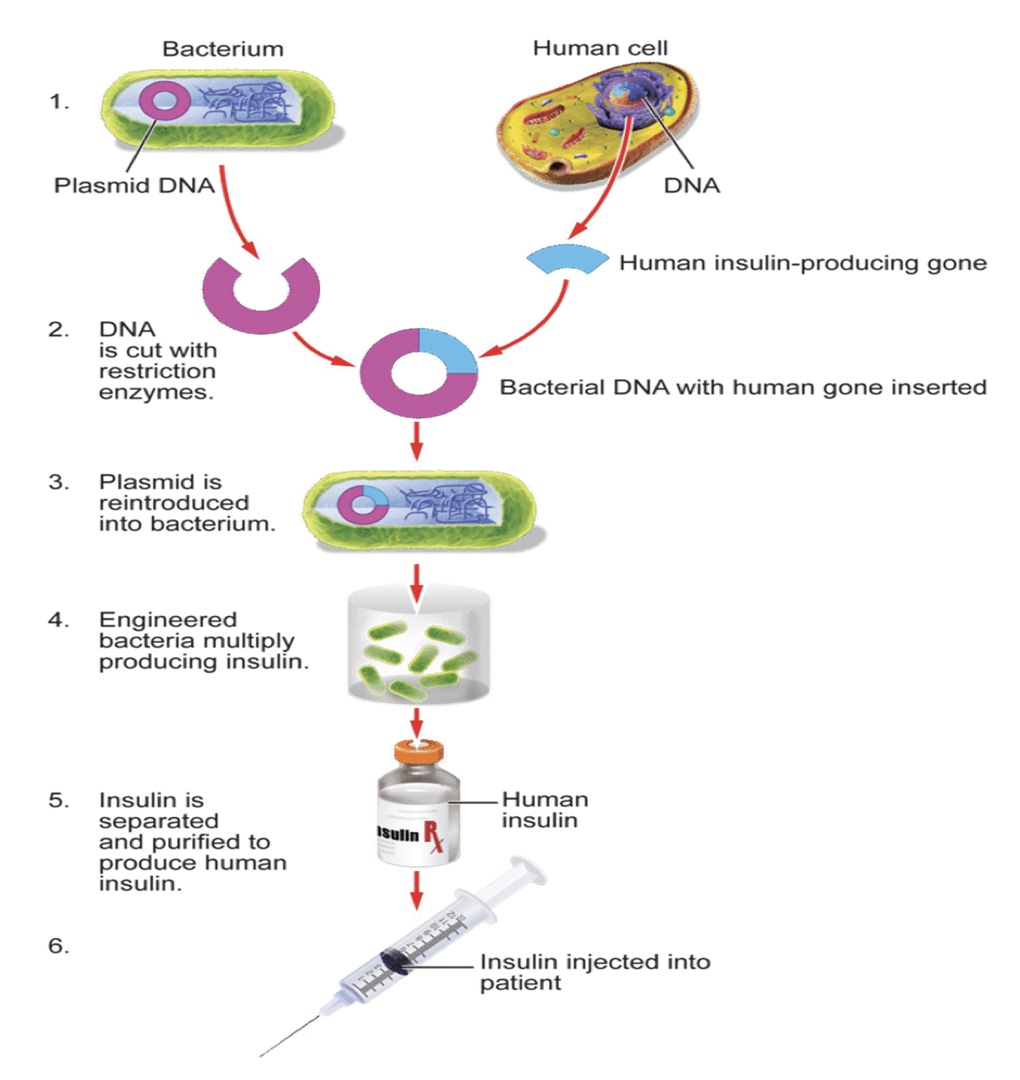
FIRST EXAMPLE – Inserting human gene for insulin into E.coli.
Original source – Pigs (purified/allergy problems).
If bacteria can produce human insulin less problems:-
No rejection/allergy
Less objection from vegetarian/animal welfare groups.
Insulin is a protein hormone – coded for by a gene which makes insulin in protein synthesis.
Bacteria and Plasmids
Bacteria contain PLASMIDS – small loops of DNA (can move between bacterial cells)
Human gene for insulin identified.
Isolation - Cut out of human genome using restriction endonuclease enzymes.
Plasmid removed from bacterial cell.
Plasmid cut open using restriction enzyme.
Using DNA Ligase the Human gene for insulin is inserted into the plasmid and resealed.
Plasmid placed back into bacterium.
Bacterium cultured in fermentation, reproduces and each cell produces human insulin.
Human insulin extracted (purified).
3) Bioremediation- MOs are used to breakdown pollutants and contaminants in soil and water.
Two Types:
Using Natural MO’s:-
E.g. sewage and crude oil are types of organic materials. MO’s breakdown OM releasing carbon dioxide and water and neutralising the contaminant in the process.
E.g. – Add nutrients to an oil spill to increase microbial growth and MO’s breakdown the oil.
Genetically Modified MO’s:
Develop GM bacteria which can breakdown or accumulate contaminants which they would not normally encounter.
E.g. GM bacteria that can remove mercury from contaminated water.
 Knowt
Knowt