5.7 Classification & Dichotomous
Scientific Classification
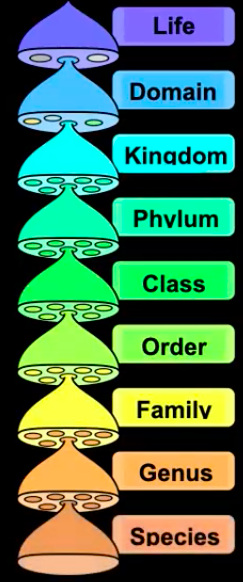
Domains
The 3 domains are: Archaea, Eubacteria, and Eukaryote
older systems do not include domain
 Binomial Nomenclature
Binomial Nomenclature
Binomial Nomenclature, meaning how organisms are named, is determined by the Genus and Species. When writung names using Binomial Nomenclature, the names must be underlined or italicized. Genus must be capitalized species.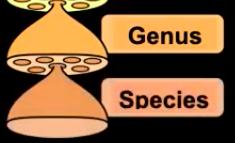
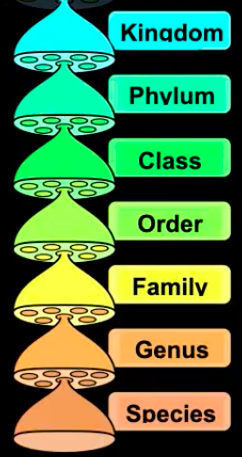
Mnemonic for Remembering the Order of Scientific Classification
Dumb
King
Phillip
Came
Over
For
Good
Soup

Dichotomous Key
This is a method used by taxonomists to identify unknown organisms based on their characteristics. It is made up of a series of numbered couplets, defining one of two group that the organism could fall into. Couplets begin with general characteristics and become successively more specific, as you get closer to identifying the species.
An example couplet:
a) Has a backbone: go to 2
b) Lacks a backbone: go to 10
Plant Phyla
There are 10 plant phyla
Bryophyta (mosses)
Includes mosses, hornworts and liverworts
No true leaves or roots
No cuticle
Reproductive structures are called sporangium which are on long stalks with capsules on end
Reproduce using spores

Filicinophyta (ferns)
A non-woody, vascular plant
Have roots and stems
Have divided leaves with veins
Reproduce using spores
Most produce spores on underside of leaves

Coniferophyta (conifers)
A woody, vascular plant or shrub
Needle-like, waxy leaves
Use cones to reproduce
Male cones produce pollen
Female cones contain embryo

Angiospermophyta (flowering plants)
Vascular trees, shrubs and bushes
Flower bearing plants
Flower produces pollen and ova

Animal Phyla
Porifera (sponges)
Mouth/Anus | Symmetry | Skeleton |
no | no | internal spicules |
|
Cnidaria (jellyfish, corals, sea anemones)
Mouth/Anus | Symmetry | Skeleton |
1 | radial (symmetry for the center of organism) | soft (except corals) |
|

Platyhelminthes (flatworms)
Mouth/Anus | Symmetry | Skeleton |
yes | bilateral | none |
|

Annelida (ringed worms)
Mouth/Anus | Symmetry | Skeleton |
yes | bilateral | fluid under pressure |
segmented body parts
most have closed circulatory system

Mollusca (snails and clams)
Mouth/Anus | Symmetry | Skeleton |
yes | bilateral | most have hard shells |
the mantle is folded to form a cavity
open circulatory system
shell is secreted by mantle
Arthropoda (insects, spiders, crustaceans)
Mouth/Anus | Symmetry | Skeleton |
yes | bilateral | exoskeleton made of chitlin |
they have a head, thorax and abdomen
segmented body

Chordata (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals)
Mouth/Anus | Symmetry | Skeleton |
|---|---|---|
yes | bilateral | endoskeleton (vertebrae) |
a notochord
a dorsal hollow nerve cord
a post-anal tail
pharyngeal slits