Negative externalities
Neg. Externalities-this occurs when production and/or consumption impose external costs on third parties outside the market for which no appropriate compensation is paid
Negative production externalities examples
Air pollution from factories
Noise pollution from the airline industry
Methane emissions
Negative consumption externalities examples
fly-tipping of house waste
Alcohol addiction
Vehicle pollution
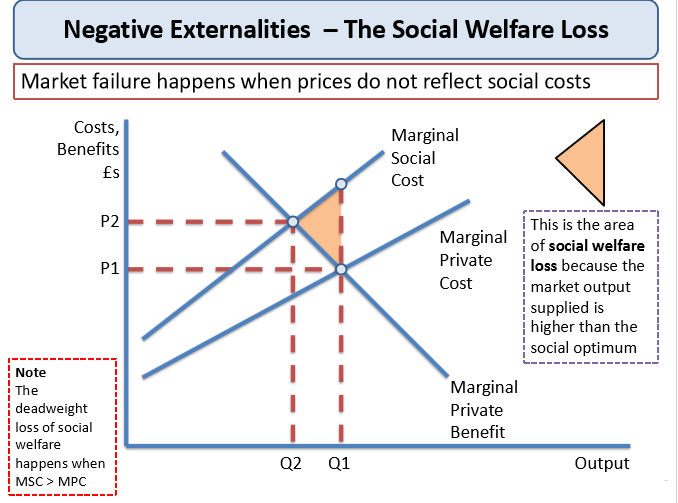
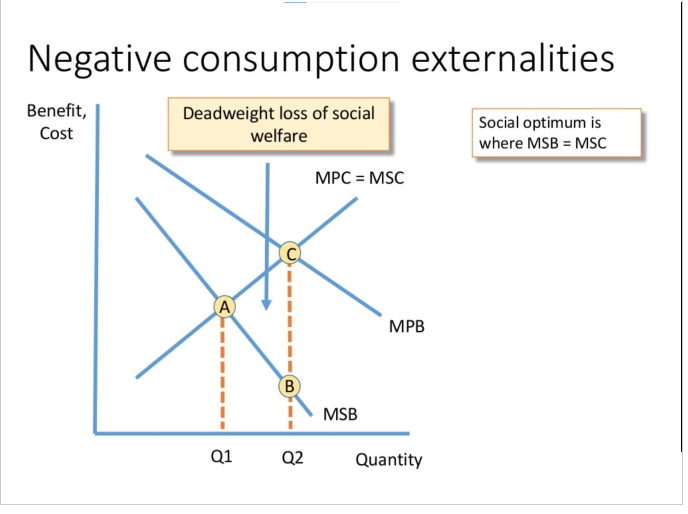
MSC (Marginal Social Cost): The total cost to society of producing one more unit of a good, including both the internal costs and any external costs to others.
MPC (Marginal Private Cost): The cost to a producer for producing one more unit of a good, not including external costs.
MPB (Marginal Private Benefit): The benefit received by a consumer for consuming one more unit of a good, not including any external benefits to others.
MSB (Marginal Social Benefit): The total benefit to society from consuming one more unit of a good, including both the private benefits and any external benefits to others.
Social welfare loss- This is where the market output supplied is higher than the social optimum