Organic Chemistry
Carbon compounds as fuels and feedstock
Crude oil, hydrocarbons and alkanes
Crude oil is a fossil fuel that comes form the remains of ancient biomass (mainly plankton), and is formed over a billion of years due to the effects of high pressures and temperatures
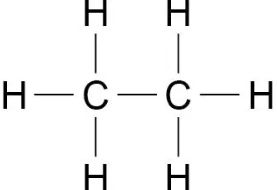
Crude oil is mostly made out of hydrocarbons (substances that only contain hydrogen and carbon) called ALKANES (saturated meaning they only contain single bonds)
the general formula for the homologous series (each member has the same functional group, general formula and similar chemical properties) of alkanes is Cn H2n+2
The first four alkanes are methane, ethane, propane and butane
Fractional distillation and Petrochemicals
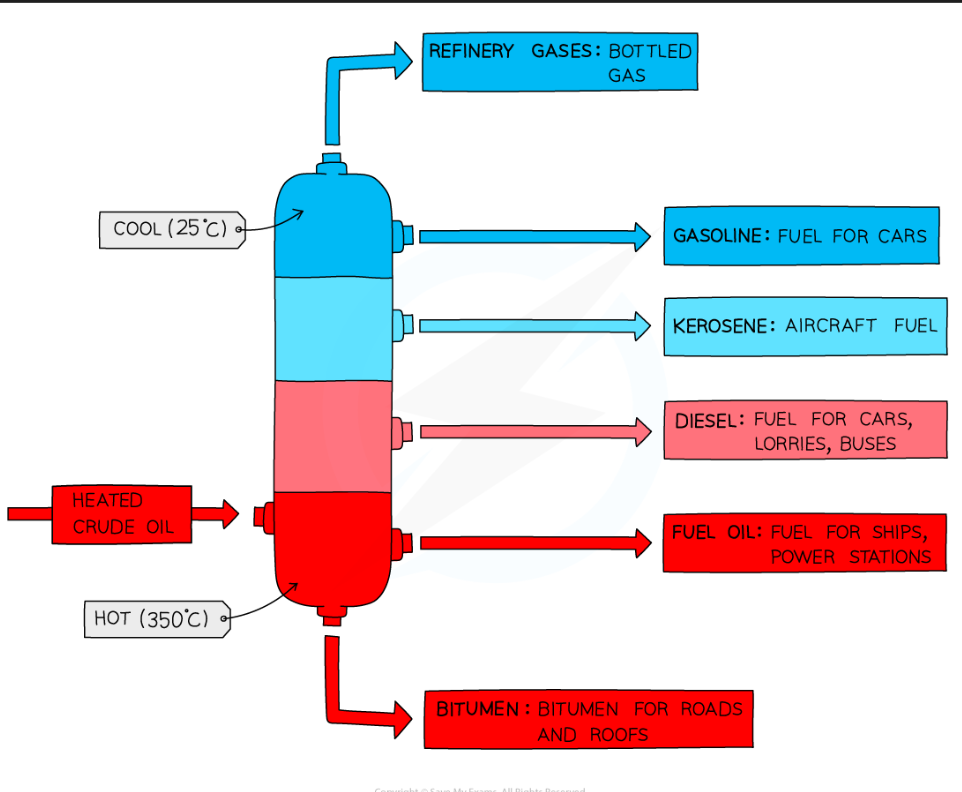
crude oil is seperated into different fractions using fractional distillation, which consists of :
Heating crude oil and waiting for it to vaporise
the vapours of the crude oil enter the fractionating column which has a temperature gradient
The vapours of hydrocarbons with high boiling points condense at the bottom of the column
The vapours of hydrocarbons with lower boiling points rise up the column and condense at the top
A fraction is a group of hydrocarbons of similar chain lengths