Ecosystem processors
A producer is an organism that makes its food.
A consumer is an organism that eats other organisms to get energy.
Algae vs plants
Algae only live in the water.
Algae are unicellular.
There are no structures in algae.
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is where plants make their food, using carbon dioxide and water to produce oxygen and glucose. Oxygen is the waste product so it is released back into the atmosphere.
Photosynthesis is an endothermic reaction because it takes light in.
The equation for photosynthesis is carbon dioxide + water + sunlight → oxygen and glucose.
1) Water enters the plant through the roots/diffuses into root hair cells.
2) Water travels up from the roots through the stem to the leaves.
3) Carbon dioxide enters the leaf.
4) Carbon dioxide enters the leaf cells/palisade layer.
5) Carbon dioxide and water enter the chloroplasts within the leaves.
6) Carbon dioxide and water react in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll to give glucose and oxygen.
(Photosynthesis mainly takes place in the chloroplasts in the leaf cells).
To measure the rate of photosynthesis, we can measure the number of bubbles produced in a given period using an aquatic plant. We can more accurately measure the rate by collecting the gas in a syringe.
The gas collected will be oxygen because it is a product of photosynthesis. To prove which gas it is, we can see whether it relights a glowing splint.
A limiting factor is the name given to any factor which, when in short supply, affects the rate of reaction.
The four factors affecting photosynthesis.
Light-The more light there is, the faster the rate of photosynthesis.
Water-Too little water slows down photosynthesis.
Temperature-If the temperature is above 40 degrees, photosynthesis is slowed down.
Carbon dioxide-If carbon dioxide levels are increased, and so is the rate of photosynthesis increases, and the growth increases.
How to test a leaf for the presence of starch.
Boil a beaker of water using a Bunsen burner.
Place a leaf in the beaker of boiling water and leave for two minutes.
Turn off the Bunsen burner.
Remove the leaf and place it into a boiling tube containing ethanol.
Put the boiling tube into the beaker of hot water and leave until most of the chlorophyll has been removed.
Remove the leaf from the ethanol and swirl in water.
Spread the leaf on a white tile and add a few drops of iodine.
Leaves
A leaf is an organ.
A leaf’s job is to carry out photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of the leaf.
Chlorophyll is the green pigment, which is why leaves and stems are green.
Epidermis tissue covers both the upper and lower surfaces of leaves.
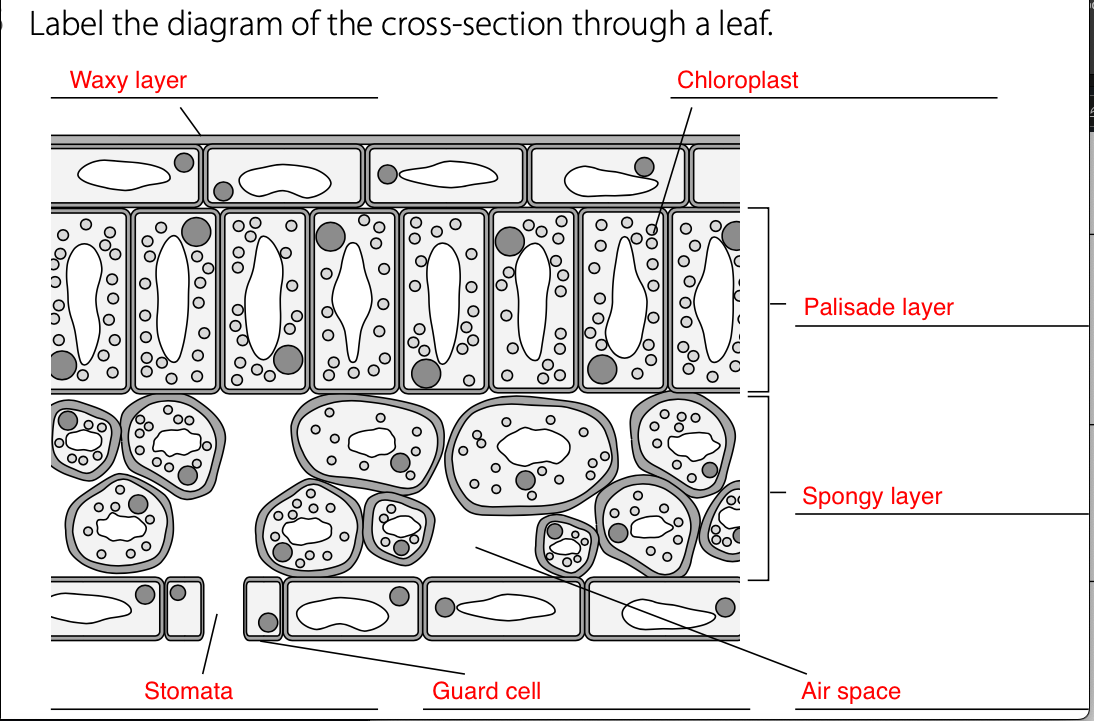
Palisade layer- Cells containing lots of chloroplasts with chlorophyll pigment for absorbing sunlight for photosynthesis.
Leaves have a spongy layer that allows carbon dioxide to diffuse in and oxygen to diffuse out.
Spongy mesophyll- Has air spaces which allow gases to move and be exchanged.
The waxy layer- Prevents water loss. It is transparent, which allows light through.
Guard cells/Stomata- Allow diffusion of gases in and out of the leaf. Guard cells open the stomata during the day and close them at night.
Leaves have/are:
Broad, flat leaves- Large surface area to absorb light.
Veins- Contain xylem tubes, which transport water, and phloem tubes, which transport glucose.
Chloroplasts- Traps light using chlorophyll.
Waxy layer- Stops water from being lost.
Thin-Quick diffusion of gases in and out.
Plant minerals.
Plants need four minerals to survive: Nitrates, magnesium, phosphates and potassium.
Nitrogen + magnesium- Used to make chlorophyll (contains magnesium). -Deficiency can lead to yellow leaves and slower photosynthesis.
Phosphorus- Used for healthy roots. -Deficiency can lead to purple leaves, slower photosynthesis and poor root growth.
Potassium- In the cytoplasm of cells, to helps reactions take place(energy transfer), which makes the leaves and flowers healthy. -Deficiency can lead to slow photosynthesis and poor growth.
Nitrates- Help plants make amino acids. These amino acids are then used to make proteins, which help make up many plant structures and help plants to grow. -Deficiency leads to poor growth and older leaves being yellow.
Fertilisers- Used to prevent plants from suffering mineral deficiency by adding chemicals to replace the missing minerals.
Chemosynthesis.
Chemosynthesis- A reaction performed by bacteria that uses energy transferred by chemical reactions to make glucose.
Methane and Ammonia are examples of chemicals used in chemosynthesis.
Symbiotic relationship- A relationship where both organisms benefit from each other.
The equation for chemosynthesis is Carbon dioxide + water + chemicals→glucose+sulphur based products.
Chemosynthesis occurs in places where light can’t reach.
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells break down glucose (or other nutrients) in the presence of oxygen or without oxygen.
Aerobic respiration.
Humans use oxygen and glucose to make energy.
The waste products, carbon dioxide and water, are also produced.
Aerobic- Uses oxygen in respiration.
The equation for aerobic respiration is glucose+oxygen→carbon dioxide and water(+energy).
The energy released by aerobic respiration helps us to stay warm, move and grow.
Glucose is obtained by cells from the blood.
Oxygen binds to haemoglobin in red blood cells.
Aerobic respiration occurs in the mitochondria, which is in the cytoplasm.
Breathing means taking in gases.
Respiration- A metabolic process where all cells release energy from food(glucose).
Key definition (for respiration).
Surface area -The red blood cells are doughnut-shaped so that they can carry more oxygen.
Mitochondria -The place where aerobic respiration takes place. Also provides energy to the cell.
Cardiac muscle -Where lots of mitochondria are found.
Enzymes -Found in the mitochondria, which help respiration to happen.
Plasma -Glucose is transported around your body in the blood. It dissolves in the liquid part of your blood, called the plasma. The dissolved glucose can diffuse into the cells that need it for respiration.
Haemoglobin -Red blood cells contain this, and when it reaches a cell requiring oxygen, the oxygen diffuses into the cell.
Anaerobic respiration.
Anaerobic respiration- Doesn’t use oxygen in respiration. Your body uses energy from glucose as a substitute when there is not enough oxygen for aerobic respiration to take place.
Anaerobic respiration is not as energy-efficient as aerobic respiration.
It causes lactic acid to build up in the muscles, which causes fatigue and pain.
The equation for anaerobic respiration is glucose→latic acid + (energy released).
In plants, anaerobic respiration makes ethanol.
Fermentation.
Fermentation -An anaerobic respiration process occurring only in certain organisms that produce ethanol and carbon dioxide.
The equation for fermentation is Glucose→Ethanol + carbon dioxide + (energy).
Oxygen debt.
The amount of oxygen needed to break lactic acid back into glucose.
Once the oxygen debt is paid, we no longer feel pain.
Remaining waste products.
Carbon dioxide is toxic to our cells.
It diffuses into our blood and is transported to our lungs, where it is exhaled.
Food chains and webs.
Producer- Makes their food.
Primary consumers eat producers(herbivores).
The secondary consumer eats the primary consumer(consumers).
Apex predator-Carnivore.
Not eaten by anything else.
(The arrow points in the direction that energy is being transferred.)
As energy is transferred along the food chain, much is transferred to the surroundings by heating and waste products; therefore, less energy is available at each level in a food chain.
Food chains vs food webs.
A food chain shows a single, linear path of energy transfer from one organism to another
A food web is a complex network of interconnected food chains, representing all the feeding relationships in an ecosystem/shows linked food chains.
Disruption to food chains and webs.
Interdependence -How living organisms depend on each other to survive, grow and reproduce.
Bioaccumulation -Where chemicals are passed down in food chains as well as energy. Chemicals increase when passed down.
This graph shows what happened to the population of native ocean fish when lionfish (a new predator) were introduced to an area.
Explain the trends shown in the population sizes in the graph.
As the population of the lionfish increases, the population of native ocean fish decreases. Since there is not enough native fish for the lionfish, the lionfish population decreases, and therefore, the native fish population increases due to them not being eaten. The cycle repeats.
Ecosystems.
Ecosystem- All organisms and non-living things found in a particular location and area in which they live.
Co-exist- Where different organisms live in the same place
Habitat- The environment or the location where an organism lives.
Community- A group of populations living and interacting with each other.
Population- All the same plants or animals living in the same area.
Species -A Group of organisms that can reproduce to make fertile offspring.
Niche- A particular place or role that the organism has in the ecosystem.
When organisms have niches that do not overlap, there is no competition, so organisms can live there.