Respiratory System
Respiratory System – consists of specific organs responsible for supplying the blood with oxygen and
expelling carbon dioxide.
==PARTS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM==
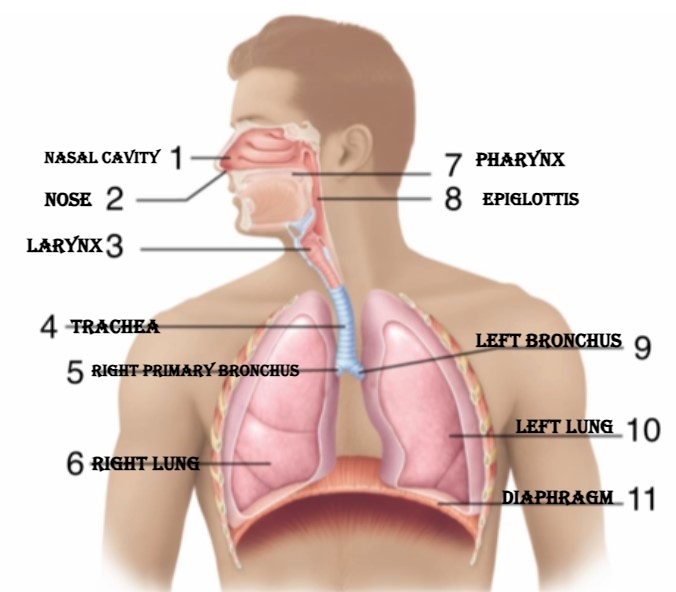
- Nose or nasal cavity - serves as the main entry / exit for air where it is warmed, filtered and humidified to get rid of foreign substances; it has two openings, the nostrils (or nares)
- Pharynx or throat – a muscular tube found behind the mouth and nasal cavity which serves as the passageway for air and food.
- Larynx or voice box – it is formed by several cartilages whose function is to connect the pharynx and trachea and for the production of sound and speech.
- Epiglottis – a flap of tissue that acts as a protective barrier for the lungs.
^^Lower Respiratory Tract^^
Trachea or Windpipe – made up of rings of cartilage making it flexible enough to keep the passageway open for air; Its cilia push mucus and dust particles and bacteria toward the throat.
Bronchi – two tubes that conducts air into the lungs: the left bronchus which is narrower, longer and less straight than the right bronchus.
Bronchioles – tinier branches of the main bronchi going to the air sacs
Alveoli or air sacs – thin-walled bulbs referred to as the sites of respiration
Lungs – main organs of the respiratory system which are large, elastic, spongy sacs.
pleura is a thin membrane covering the lungs
Diaphragm – a dome-shaped muscle separating the chest from the abdomen that aids in respiration