APES Notes
Unit 1- The Living World: Ecosystems
Module 1
symbiosis- two species living in a close and long term association with one another in an ecosystem
community ecology- study of interactions among species
Ecosystem are not easily defined
Biosphere is from deepest ocean bottom to highest mountain peak 12 miles
Competitive exclusion principle- principle stating that 2 species competing for the same limiting resource cannot coexist
commensalisms- one species benefits, other is neutral
mutualism- both species benefit
Module 2
Terrestrial biomes defined by dominant plant growth
Temps below 41 f - Tundra and Taiga
Temps between 41 and 68 f- temperate
Temps above 68 f- tropical
For every 10 c increase in temp, plants need 20mm of precipitation to grow
deciduous trees have leaves that fall off yearly. Coniferous trees have needles or scales that do not fall off.
taiga threat- mining and oil extraction
Module 3
Rapids allow water and air to mix, increasing oxygen in the water
Lake Layers- Little Liars Prank Boys
Littoral- Top layer where algae grows
Limnetic- open water as deep as sunlight penetrates
Profundal- no sunlight reaches
Benthic- Muddy bottom
phytoplankton- floating algae
oligotrophic- low nutrients, mesotrophic- moderate fertility, eutrophic- lots of fertility
Freshwater wetlands- very productive, help reduce flooding
Estuaries- where river water mixes with ocean
Coral bleaching- when algae in corals die, from lower ocean pH and high temps
Ocean layers- photic- with photosynthesis, aphotic zone- no photosynthesis so no plants, but there is bacteria that make energy from methane and hydrogen sulfide (Chemosynthesis)
Module 4
Biogeochemical cycle- movements of matter within and between ecosystems involving cycles of biological, geological, and chemical processes
Carbon cycle- C02 is exchanged between atmosphere and water- Largest carbon reservoir is the ocean
Steady state- input = output so no change
Carbon taken by photosynthesis ends up in soil
Nitrogen is often a limiting nutrient
Nitrogen is most held in atmosphere
Nitrogen fixation- turns N2 into nitrogen that plants can use- done by bacteria (ammonium) or lighting and combustion (nitrate) that then goes to earth via rain
Nitrification- conversion of ammonium to nitrite and then nitrate by bacteria
Assimilation- plants/algae incorporate nitrogen into their tissues
Mineralization- after organisms die, fungi and bacteria turn organic compounds back into ammonification
Denitrification- Turning nitrate into nitrous oxide and then plain nitrogen via bacteria in anaerobic conditions.
Nitrogen use in fertilizers can kill off plants that can survive in low nitrogen conditions
Module 5
Phosphorous main reservoir is rocks- no gas phase- limiting nutrient especially in aquatic ecosystems
Assimilation + Mineralization- Plants and animals take up inorganic phosphorus, assimilate it as organic, and upon their death, bacteria mineralize it into inorganic phosphate
Phosphate undergoes geological uplift, it is not easily leached so it has little runoff
Human use of fertilizers causes algal bloom which takes up oxygen so the water become hypoxic and becomes a dead zone- Gulf of Mexico
Household detergents have phosphate
Leaves releasing water- transpiration
Harvesting trees reduces evapotranspiration by less biomass
Module 6
Producers do both photosynthesis and cell respiration
Primary Productivity- rate of converting solar energy into organic compounds over a period of time
Gross PP- Total amount of solar energy captured by photosynthesis in a time frame
Net PP- Energy captured by producer minus the energy they respire
Measure GPP via C02 produced during photosynthesis- C02 taken up in sunlight plus CO2 produced in dark
NPP= biomass production over time frame
Biomass present at a certain time- Standing crop
Only 1% of solar energy that hits producers undergoes photosynthesis (GPP) 60% of that is lost to respiration while 40% supports growth of producers (NPP)
NPP is only 25 to 50% of GPP
Different wavelengths of light move differently through water- blue light goes deeper
Swamps+ Marshes are most productive aquatic ecosystems
Module 7
Detrivores- organisms that break down waste into small particles
Matter only cycles through and ecosystem- its never lost
Second law of thermodynamics- when one organisms consumes another, not all the energy in the consumed is transferred to the consumer.
Trophic level energy transfer is 10%
Ecological efficiency- proportion of consumed energy that is transferred through trophic levels
Unit 2- The Living World: Biodiversity
Module 8
Population bottleneck- if most species die, when it rebounds there will be low genetic diversity
Types of diversity lowest to highest- Genetic, Species, Habitat, Ecosystem
High species diversity- high productivity and resilience
Biodiversity quantified by species richness (# of species) and evenness (proportion of species)
Estimates for species on earth 5-100 million, likely around 10 million. (2 million named currently)
Module 9
Ecosystem services- provisions (Goods that humans use directly), Regulating (regulating environmental conditions), Support (helping processes that would cost humans a lot) Cultural (Economic benefit to humans)
Global ecosystems are estimated (via replacement method) to contribute over $125 trillion per year, twice the global economy
pesticides can kill bees
intrinsic value of an ecosystem- value separate of any human benefit
Module 10
Island biogeography- study of how species are distributed and interacting on islands
Species area curve- more land area=more species
Slope of SAC lines are usually between .2 and .35
In caroni river Venezuela, large islands species survived
Model of Island Biogeography curve- Orange line going down for colonization, Blue going up for extinction- equilibrium is where the two values are equal/offset
This is because when an island has less species, there will be less competition so less extinction, but plenty of species will colonize it
Large and near islands have more rightward points on the curve
Island species are often specialists
Module 11
ecological tolerance/fundamental niche- range of abiotic conditions in which a species can survive, grow and reproduce
realized niche- range of abiotic and biotic factors that a species actually lives in
geographic range- areas where species live
carbon dating- examining how different carbon types (isotopes) change over time to date sediment layers
99 percent of all species that have lived on earth are extinct
Species may move to a different habitat to survive if conditions change
5 mass extinctions in earths history, biggest one 251 million years ago- metorite
We are currently experiencing a 6th max extinction
Module 12
Natural disruptions can be periodic (regular), episodic (somewhat regular) or random
Environmental disruptions rarely hit the same place 2 times in a row
ecosystem resistance- how much a disruption can effect matter and energy flows
ecosystems have increased CO2 absorption to match C02 increases
Measuring changing climates- looking at concentration of greenhouse cases in air bubbles in ice
Scientists use composition change of foraminifera in sediment layers to find temp
Heavy oxygen found in warmer temperatures of ice
Increase of C02 leads to warmer temperature
When oceans warm they cannot hold as much C02
Humans interfering with natural fire can cause fire adapted species to face more competition and increase fire intensity
Intermediate disturbance hypothesis- ecosystems experiencing intermediate disturbance will favor a higher species diversity than those with high or low disturbance levels
Low disturbance favors best competitors, high disturbance favors generalists
Module 13
microevolution- evolution at population level
macroevolution- evolution that gives rise to new species
cell recombination can help defend against invading organisms
negative pesticide cycle can happen
adaptation- trait that improves an individual’s fitness
Evolution by random processes- genetics are altered overtime without a difference in fitness
Mutation, gene flow (mixing populations), Genetic drift( Random mating, failed mating for certain genes) Bottleneck, Founder effect(founders of population are only genes present there)
Allopatric speciation (geographic separation)
Sympatric speciation (evolution of two species without geographic isolation)- often caused by polyploidy mutation (more chromosome sets)- means they cant breed with diploid relatives
fitness is dependent on speed of adaptations
Module 14
Ecological succession- predictable replacement of one species by another over time
primary succession- first stage that occurs on bare rock, has pioneer species that survive with little or no soil
secondary succession- occurs in disturbed areas that still have soil- rapid colonization via grass and wind-borne seeds
climax community- succession final stage
succession happens in aquatic places too- river and intertidal are fast while lake is slow, it becomes land
Succession originally raises species richness, biomass, and productivity
Keystone species- necessary but not abundant species
Indicator species- species that shows a particular ecosystem characteristic- They have quick responses to changes
Endemic species- species that only live in a very small area of the world
Hotspots qualified if it has at least 1500 endemic plant species and if it has lost more than 70% of vegetation that contains the plant species
Unit 3- Populations
Module 15
Population growth rate in a time period= # of offspring individual can produce minus deaths of the individual or its offspring
Carry capacity- upper limit of individuals that are supported (K)
r species experience rapid overshoot and dieback
Survivorship curves- 1 (K spec. and whale) 2- (squirrel) 3-(r spec. sunflower)
Module 16
Density dependent factor- factor that has different impacts based on pop. size. Density independent factors do not
Population growth model- math equation that can find population at any time
fecundity: ability to produce a ton of offspring
exponential growth model- estimates future pop. size after a given time based on biotic potential and # of reproducing individuals in pop. this is ideal, not realistic
EGM makes j shaped curve with time on x and pop. size on y
exponential is density independent
Logistic growth model shows populations limit by carrying capacity- first exponential then slows down- makes s curve
LGM is for density dependent factors
Gause showed density dependent factors
Carrying capacity can be reduced by overuse- can also be caused by predators
Module 17
Earth’s carrying capacity is unknown
Major human increase with agricultural revolution 400 years ago
Malthus- Population will exceed food supply
Global Pop. Growth rate (CBR-CDR)/10 (CBR = # of births per 1000 individuals.
Net migration rate (immigration-emigration)
National pop. % growth rate= ((CBR+immigration)-(CDR+emigration))/10
Infant mortality= # of deaths under 1 year of age for 1000 live births
Child mortality= # of deaths under 5 years of age for 1000 live births
Environmental justice- show of environmental hazards to disadvantaged people
Different types of age structure diagrams- pyramid (developing) medium or top heavy- developed
population momentum- continued population growth after birth control methods
TFR- avg. # of children a women will bear in reproductive years
Replacement level fertility- total fertility rate to keep current population size (2.3) High for developing countries, lower for developed
Likely only 10 billion humans before pop. decline
Module 18
Adequate nutrition leads to pop. growth in developing countries and pop. decline in developed countries
High infant mortality leads to pop. decline
70/growth rate % = pop. doubling time
5 bil people expected to live in urban areas by 2030
Demographic transition model- birth and death rate start high with pop. low, then death rate decreases first, followed by birthrate as pop. increases
Theory of Demographic transition: as the transition from high to lower birth a death rates in a country or region occurs, that country moves from a pre-industrial to an industrialized economic system
Stage 1= CBR=CDR due to poor living conditions
Stage 2= slighty modern, CDR declines but CBR stays high
Stage 3= CBR decreases and growth rates slow
Stage 4= Pop. declines
Developing countries growing faster than developd
IPAT= impact= population x affluence x technology
Unit 4- Earth Systems and Resources
Module 19
Lithosphere: Rigid outer layer composed of the crust and uppermost mantle, responsible for tectonic activity. Around 100 m/ 60km thick
Asthenosphere: Semi-fluid layer beneath the lithosphere that allows for the movement of tectonic plates.
Outer Core: Liquid layer composed primarily of iron and nickel, generating Earth's magnetic field through convection currents.
Inner Core: Solid, dense center of the Earth, primarily made of iron, and extremely hot.
Mantle: Solid Upper Mantle, Asthenosphere, and Magma
Theory of Plate Tectonics: A scientific theory explaining the movement of the Earth's lithosphere, which is divided into tectonic plates that float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere beneath. Led by Alfred Wegener’s theory of Pangea
Evidence of drifting continents: Fossils and Rock Formation
Hot Spot: where molten material from mantle reaches lithosphere, volcanoes form when plates move over them: shows movement of plates through volcanic activity
Richter Scale: Measures earthquake force, for each unit increase the force is multiplied by 10
Continental Plates- less dense with iron so rises above oceanic plates
Oceanic Plates- more silicon dioxide and more dense then Continental Plates
Divergent Boundary: area below ocean where plates move away from each other and magma forms new crust (seafloor spreading)
Convergent Boundary: area where one plate moves towards and collides with another
Subduction: When an oceanic plate edge goes under a continental plate at a Convergent Boundary
Island Arcs: island chain formed by volcanoes as a result of subduction
Collision Zone: When two continental plates collide and the crust is pushed up to form mountains
Transform Boundary: area where plates move sideways past each other, often causes faults (fractures in rocks caused by crust movement)
Plate Speed- 1.4 inches/ 36 mm per year
Human Impacts: earthquakes cause collapsed structures, contaminated water, and death
Nuclear power plants shut down if ground movement exceeds their withstanding
85% of volcanoes occur on plate boundaries
Ash damages airplane engines
Module 20
Igneous rocks (Granite) formed by heat (magma)- Balsatic (dark) and Granatic (light). Dominant rock in continental plate crusts
Sedimentary rocks (Limestone) formed by pressure (mud, sand, gravel being compressed). Hold fossil records
Metamorphic rocks ( Marble) formed when any of the three rock types are subjected to high heat and pressure
Rock cycle- cycle governing formation, alteration, and destruction of rock material from tectonics, weathering, and erosion
Physical Weathering: mechanical breakdown of rocks and minerals (Freeze-thaw and roots)
Chemical Weathering: breakdown of rocks and minerals through chemical reactions and/or dissolving of chemical elements from rocks (Lichens that produce acids, water that contains acid touches rocks)
Acid Rain: Rain high in sulfuric an nitric acid
Human impacts on chemical weathering: sulfur emitted from fossil fuel combustion causes acid rain
Erosion: physical removal of rock fragments from landscape/ecosystem ( Wind/ice/water with gravity or organisms burrowing)
Deforestation, Road building, overgrazing causes more erosion
Soil forms from parent material, climate, topography, organisms, time
Soil helps plant growth and water quality
Young/Immature soil: less organic matter and nutrients due to it being mainly fragments of parent rock and less time for organic matter to accumulate
Old soil: nutrient poor due to plant and water leaching
Parent material: Rock material that underlies soil and provides inorganic components
Climate: Temp, humidity, water. (no developed soil in freezing temps- Cold areas have undecomposed organic material)
Topography: Slope and arrangement of landscape ( Soils subject to erosion less deep then those at bottom of slopes)
Organisms: Plants remove nutrients, Animals mix soil, Soil organisms recycle organic matter
Time: How long soils have been around
Soil Horizons (O,A,E,B,C)
O horizon: organic matter at the top- includes humus (fully decomposed organic matter)
A horizon: top layer of soil with mixed organic and mineral material (Top Soil)
E horizon: leaching zone, found underneath O or A horizon
B horizon: subsoil, little organic material
C horizon: underneath b, least weathered, basically parent material
Soil is eroded by wind and water, furthered by logging and poor agriculture
Clay (small, 0 slope) Silt (medium, positive slope) Sand (large, negative slope)
Porosity: size of space between particles
Permeability: ability of water to move through soil
Clay used for containing contaminants
CEC (Cation exchange capacity) ability of a soil to absorb and release cations (positively charged mineral ions)- based on amount and types of clay present
Tradeoff with CEC and permeability
Base saturation= proportions of soil bases (promote growth) and acids (detrimental to nutrition) as a percentage
High CEC and base saturation= high productivity
Bacteria, fungi, and protozoans make up 80 to 90 % of soil organisms- mostly detrivores
Module 21
Watershed- area of land that drains into a particular body of water
Watersheds characterized by area, length, slope, soils, vegetation
Mississippi river drains from 1/3 of US
Length of watershed measured from beginning to outlet
Slope (more slope = more speed and sediment in water)
Soil Type ( Sand = less water flow, Clay+ Silt= more water and sediments- can prevent photosynthesis)
Vegetation: More plants= less erosion through roots
Human impacts on watersheds: Dams, mineral mining, impermeable surfaces
Hubbard Brook Watersheds- underlain by bedrock- without trees there is more nitrate that overfertilizes the water
Chesapeake Bay Watershed- 41 mil acres of land- too many nutrients are causing excessive plant growth and too many sediments kill off seagrass, removing habitats for crabs
Module 22
Insolation: Incoming solar radiation- main source of energy on earth
At high latitudes it is colder because, the sunlight loses more energy than at the equator because it is passing through more atmosphere, the solar energy is split over a larger surface area, and snow reflects more sunlight
Albedo: percentage of incoming sunlight that is reflected. Average Earth= 30%. snow = high, asphalt = low
Earths axis of rotation is tilted at 23.5 degrees - 4 big days - March and September Equinox ( Sun is directly overhead equator) June and December Solstice ( Northern hemisphere is maximally tilted toward/away from the sun)
Atmosphere extends to 10,000 km above earth, its composition is : 78% Nitrogen, 21% Oxygen, 1% other (greenhouse gases)
Atmosphere layers:
Troposphere: closest to surface, extending to 16km, most dense, low temp, global warming expands it
Stratosphere: Ozone layer, absorbs suns ultraviolet rays, around 0 temp, 16-50 km above surface
Mesosphere: 50-85 km above surface, low temp, where meteors burn up,
Thermosphere: 85-600 km above surface, blocks X ray radiation, causes northern lights via charged gas molecules, reaches 2000 degrees Celsius
Exosphere: outermost layer, 600-10,000 km, where satellites orbit, 0-1,700 degrees Celsius.
Air circulates in atmosphere due to changing density, water vapor capacity, adiabatic heating/cooling, and latent heat release
Warm air= low density= rises
Cold air = high density= falls
Saturation point: maximum amount of water vapor in the air at a given temp
Warm air has higher capacity for water vapor
Adiabatic cooling: As air rises, pressure on it decreases, causing it to expand, which lowers it’s temperature
Adiabatic heating: As air sinks, pressure increases, causing a reduction in volume, heating it up
Latent heat release: When water vapor condenses into liquid, energy is released as heat- Meaning that when water vapor condenses in the atmosphere, air will heat up and rise
Atmospheric convection currents: Global patterns of air movement that are initiated by the unequal heating of earth
Atmospheric currents: Humid air warms and rises, Adiabatic cooling makes air reach saturation point, Condensation causes clouds and rain, Latent heat release causes air to rise higher, Adiabatic cooling chills air at the top of cycle, Chill air sinks, adiabatic heating warms it as it sinks, it picks up moisture on surface, and the cycle repeats
These currents show up in Hadley Cells ( current that cycles between the equator and 30 degrees north and south, rising at the equator and falling at 30 degrees north and south)
The Hadley Cell causes desert as hot, dry air falls and goes towards the equator
Space where Hadley Cells converge: ITCZ or intertropical convergence zone- dense clouds and thunderstorms, occurs where there is the most sunlight, moves north and south over a year from 23.5 S to N
Polar Cells: Convection current that rises at 60 degrees N and S and sinks at the poles at 90 degrees N and S
Ferrell Cells: convection current lying between 30 degrees N and S and 60 degrees N and S. Caused by warm air from Hadley cells moving towards the poles and cold air from the poles moving towards the equator
Currents are responsible for biome location
Coriolis effect- deflection of an objects path due to rotation ( Throwing a ball towards equator moves west and towards the poles moves east) ( Ball moves faster at equator)
Earths equator moves faster than the poles 1670 km vs 291 km/hr
Hadley causes Northeast and Southeast Trade winds (name is based on origin)
Ferrell causes Westerlies
Module 23
Ocean currents are driven by temperature, gravity, prevailing winds, the Coriolis effect, Salinity, continent location
Due to warm water expanding, the tropical water surface is about 3 inches/ 8 cm higher than mid-latitude waters
Gyres: Ocean Currents that rotate clockwise in the northern hemisphere and counterclockwise in southern hemisphere
Surface currents separating causes upwelling, which increases water nutrients producers that feed fish fish
Thermohaline circulation- oceanic circulation pattern that drives surface and deep water mixing
TC is driven by surface waters with lots of salt, when it evaporates and freezes in the northern Atlantic then it becomes cold salty water that sinks, travels along the ocean floor, and eventually rises and circles back to the northern Atlantic
Global warming could disrupt Thermohaline circulation by melting the glaciers and making the north Atlantic less salty- therefore less likely to sink. This would make west Europe cold as it would lose its transportation of warm water
Rain shadows- humid winds blowing inland meet a mountain range and undergo latent heating and adiabatic heating that results in warm dry air on the other side of the mountains
El Nino causes bad crop production, La Nina reverses it
Unit 5- Land and Water Use
Module 24.
Tragedy of the Commons- The tendency of a shared resource to become depleted if it is not regulated in some way- this can happen if the carrying capacity is exceeded and no regulations are made
TotC- no winners- MUST include degradation- shown in global fisheries and with logging
Negative externality (The cost/benefit of a good or service that is not accounted for in purchase price or any other way) causes TotC
How to prevent TotC- Fees/Punishments for overuse- More private land- Government or self regulation
209,000 protected areas in world (3.2 bil. ha or 7.9 bill a)
42% of US land is publicly held
US federal agencies- Forest Service (USFS) Bureau of Land Management (BLM), Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS), and National Park Service (NPS)
if something benefits humans than it is an economic benefit
Alpo Leopold- Land Management guy
Rangeland- grasslands used for grazing cattle- most common use of land in USA
Clear Cutting- harvesting method that removes all or almost all trees in the area- coupled with replanting
CC benefits- easiest, most economical, ideal for fast growing trees,
CC costs- high wind and water erosion, low biodiversity, more CO2, more runoff (harming fish populations), less soil organic matter
CC in heavily forested areas can result in increased habitat diversity
Selective Cutting- removes certain trees, ideal for shade tolerant species,
SC costs- Still has habitat fragmentation, harder and more expensive than CC
Economically Sustainable Foresting- logging technique often without fossil fuels but costly and less yield
30% of commercial timber is produced in USA and Canada
Tree plantation- group of fast growing trees for logging
1969 National Environmental policy act requires environmental assessment of all projects with federal money.
Module 25
2nd Agricultural revolution-- 1600’s-1930’s- mechanization of farming (agribusiness) instead of subsistence farming
Green revolution- 1940’s use of fertilization, irrigation, improved crop varieties
1920- 32 mil ppl (32%) lived on farms in usa, now only 2.6 mil ppl- 1.3%
Norman Borlaug- won Noble Peace prize for contribution to world food supply
Economy of scale- costs of production fall as output rises
Organic Fertilizer- made from organic matter of plants and animals, lower concentrations but CEC for soil
Synthetic fertilizer- commercial produced fertilizer- highly concentrated and reliant on fossil fuel energy, risk of runoff that causes algae and oxygen depletion, quicker
Irrigation turns non-growable land into farmland- can cause waterlogging where roots cant reach oxygen and salinization that traps salt on soil surface through evaporaton
454 mil kg (1 bil lbs) of pesticides applied in USA each year
Monocropping- main agricultural practice in US where single species is planted
MoC benefits- Improved productivity and easier
MoC costs- erosion of topsoil, increased vunerablity to pests
GMO benefits- Increased crop yield and profits- less expensive food, less pesticides
GMO costs- less biodiversity, possible allergic reactions
EU barely allows GMOs, US does
Energy subsidy- fossil fuel and human energy input per calorie of food produced- most for fishing and feedlot beef- least for hunting and gathering
Module 26.
Plowing- (digging deep into soil and turning it (usually 6-8 inches deep)) breaks up soil structure, done right before planting seeds
Tilling (preparation of soil but not to the degree of plowing) buries weeds and done right after growing season.
They both increase CEC and base saturation and loosen soil so roots can enter
They can cause erosion and CO2 emissions and soil compaction (makes soil less porous).
Slash and burn farming/shifting agriculture- land is cleared and farmed until all nutrients are gone. It is overused and causes soil compaction, CO2 emission, and erosion.
***Nitrogen, Phosphorous and Potassium are the most used fertilizer nutrients. Usually 5 percent nitrogen, 3 percent phosphorous, and 4 percent Nitrogen
Nutrients are usually produced from crushed rock that uses extreme amounts of fossil fuels\
Module 27
70% of freshwater consumption in USA is for irrigation
unconfined aquifers- porous rock covered by soil that water can flow in and out of
confined aquifer- covered by impermeable rock or clay that stops water flow
Water Table- Uppermost area at which groundwater fully saturates rock or soil
Groundwater recharge- process in which precipitation percolates in groundwater
Water from aquifers naturally percolates up in the form of a spring
Artesian well- well in confined aquifer
Confined aquifer use is safer but unsustainable
Water footprint (daily per capita use of fresh water) for metric ton of grain is more than 1 mil liters of water
producing beef in USA takes 11x more water than wheat
Furrow irrigation (67% of water available), Flood irrrigation (70-80% of water available), Spray Irrigation (75-90%), Drip irrigation (over 95%)
Largest aquifer in USA is Ogallala aquifer in great plains
When aquifer removal exceeds it’s renewal, then water table drops, there are less springs, and a cone of depression can be caused that takes water away from shallower wells
Water withdrawals peaked in 1980
Non persistent pesticides are not always better for environment as they require more application
Pesticides can kill other things, hurt farm workers, and pollute groundwater
IPM- use of crop rotation, intercropping, use of pest resistant crops, use of pest predators, and less pesticides
Pesticide treadmill is common positive feedback system
No till agriculture relies on herbicides, because no weeds are killed with tilling
Module 28
Concentrated animal feeding operations (CAFOs)- large structure for maximum occupancy of animals and maximum yield meat or dairy yield.
CAFOs are small, efficient, and produce greater yield
CAFOs use a lot a freshwater, nutrients and growth hormones
Overapplied manure has caused pollution along 56,000 km over rivers in 22 states
Manure lagoon- large man made pond lined with rubber to handle manure without groundwater leaking. If leaking takes place or there is overflow than disease outbreaks will occur
anaerobic decomposition in the lagoons causes the release of CO2 and methane
13% of grain grown in world is used to feed livestock
Diet for a small planet- book by frances lappe that encourages eating lower on food chain for less environmental impact
Free grazing is more ethically acceptable and has less antibiotics and contamination, but costs more and uses more land, same as nomadic grazing
overgrazing or over logging can lead to desertification
Eating less meat would result in less Greenhouse gases from CAFOs
Fish production provides over 3 billion people with 20% of their animal protien.
ToC with fisheries due to the fact that countries don’t own migrating fish
Fishery collapse- decline of a fish population by 90% or more- hurts biodiversity and income of fishermen
5 major methods of fishing- Purse seine nets, Bottom trawl, Midwater trawl, Gill nets, Longlines
Nets can hurt ocean bottom habitats and have bycatch that hurts sharks and turtles
Northwestern Atlantic fisheries had to be closed due to depleted stocks of fish
Sustainable fisheries act of 1996- switched goal of sustainable fishery from economic to environmental
Selling fishing quotas with data of total allowable catch can help with overfishing
People can follow seafood watch apps that tell you sustainability of fish
Module 29
Crustal abundance- average concentration of an element in earths crust
Ore-a concentrated accumulations of. minerals from which economically valuable materials can be extracted.
Metal- element that can conduct electric and heat energy
Elements in earths crust with amount Odd (Oxygen) Sticks (Silicon) Attach (Aluminum) Inside (Iron) Massive (Magnesium) Camps (Calcium)
Ores are formed by magma meeting water or deposition of igneous rock, they can be in veins or disseminated deposits (larger)
Lower the concentration and accessibility, more environmental impact
Recycling increases material reserves, and results in less mining with with lesser impacts
A resource is economically recoverable if it can be profitably mined
Surface mining: dust and particulate movement, water contamination and habitat destruction
Strip( removal of overlying vegetation and soil and rock, very susceptible to erosion, used when ore is close to surface)
Open Pit (Large hole, used when resource is close to ground but extends far)
Mountaintop removal (When tops of mountains are blown off, lots of mine tailings)
Placer (Looking in rivers)
Mine Tailings (unwanted waste material left after mining)
subsurface mining: when the ore is over 100m deep then it is drilled down- produces fossil fuels and acid mine drainage and human danger, also may produce methane
Module 30
Urban area- place with more than 1000 people per square mile
Urban populations represent 55% of the human population
Urban living is increasing, and 17 of the 20 largest areas are in developing countries
Urban areas have smaller impacts per person, but still negatively affect the carbon cycle
Rapid urbanization in developing countries leads to poverty
Suburbs surround metropolitan centers while exurbs do not
in the USA 2/3 people live in suburban or exurban areas- which have 2x environmental impact of urban area people
Urban overuse of aquifers result in saltwater intrusion, where a cone of a depression is created and seawater partially fills it
less infiltration means more runoff
Urban sprawl- urbanized areas that spread into rural areas- caused by more highways, better house prices, government policies, and urban blight (lack of support and deterioration of urban communities)
Cycle for urban blight- Increased gas revenues to more highways to more suburbs to more more traffic to longer commutes to more gas back to more gas money
Smart growth uses sense of place and walkable neighborhoods along with natural beauty
Urban runoff pollutes rivers- solutions are rooftop gardens, electric buses (less pollutants), tall buildings, more trees and parks, and permeable pavement
/
Module 31
Ecological footprint is a measure of the area of how much land and water is used to supply the goods and services that individual populations use- developed by professor reese
EF calculated by land for food we eat, water and energy we use, clothing we wear, and structures we occupy
developing countries usually have smaller footprints
Fair Earthshare is 1.6 ha per person
Carbon footprint- direct and indirect- measures carbon released as CO2 and equivilent amount in other greenhouse gases
embodied energy- energy used to manufacture a product
Passenger cars make up 58% of US transportation CF
China emits most CO2
Module 32
MSY- largest quantity of a renewable resource that can be harvested indefinitely- harvesting at this rate keeps population of resource at ½ of carrying capacity
Sustainability q’s: how is resource importance determined?
MSY problems: very hard to calculate, takes years to know if its actually sustainable,
Environmental indicators- Biodiversity, Food production (grain), Avg. global surface temp and atmospheric concentrations of CO2( currently 415 parts per million), Human population, resource depletion,
Outlooks: Biodiversity: extinctions will continue, Food Pro: Unclear, Temp: likely increase, Human Pop. :leveling off, Resource dep. :unknown
Module 33
Crop rotation: moving crops around each year
Intercropping: close spacing of different crops growing at the same time
Biocontrol: using natural predators
IPM does sometimes use pesticides
IPM causes less pesticide use and increased yield, but does cost money to train and extra time
Agroforestry: intercropping trees and vegetables for windbreaks
Strip cropping- planting crops with different spacing and root characteristics for less erosion
contour plowing- plowing with topographic lines of land- may use cover crops (crops planted to prevent soil erosion)
Terracing- turning sloping land into steps to prevent erosion
People want more perennial plants
perennial plants- live for many years and do not need to be replanted (asparagus)
no till causes more herbicide use but less soil erosion
Green manure- plant material grown in a field with the intent of plowing it
As crops are removed, they lose base cations like calcium and magnesium and become acidic- this is fixed with limestone
Organic agriculture: uses ecological principals, works with natural systems, maintains soil, keeps organic matter and nutrients, avoids synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, and reduces adverse affects of agriculture
OFPA establishes standards for production of organic food
Organic farming is small, more costly, and less time efficient, also may use propane or tractors and might not be sustainable
Module 34
Aquaculture is increasing in popularity, it uses four systems
Open pen (salmon)
submerged net (seabass)
pond farm (catfish)
aboveground tanks (many)
Aquaculture is efficient, saves wild fish from fishing
Aquaculture can cause wastewater escape and escaped fish breeding with wild
Sustainable forestry involves regrowth of natural forests, worker training, less fossil fuels and biodiversity goals.
Forests certification organizations for sustainability have had scandals with overpricing
Reusing wood is important
Natural predators and prescribed burns sustain forests and prevent major fires
Large fires caused nutrient rich habitat in Yellowstone
Unit 6- Energy Resources and Consumption
Module 35
In anaerobic conditions where decomposers can’t break up all of the dead biomass, it is buried and creates fossil fuels (whose combustion releases carbon)
Joule (J)= 1 W-s (watt-second)
Gigajoule- 1 billion (1×109) joules
exajoule- 1 billion (1×109) gigajoules
Quad(US government’s way to report energy)-1 quadrillion Btu (British Thermal Units)
1 calorie=4.184 J- used for energy expenditure and transfer in ecosystems
1 Calorie= 1000 calories or 4,184 J- used for human food consumption
1 Btu- 1,055 J- used for energy transfer in air conditioners or home water heaters
1 Kilowatt-hour- 3,600,000 J or 3.6 Megajoules-for electrical appliances energy use
Fossil Fuels- large amount of energy in small volume and mass
China and US use the most EJ’s annually
In 2020, each person used roughly 77 GJ that year
developed countries use more than 40% of worlds energy each year
Commercial energy sources- bought and sold, Subsistence energy sources- gathered
US energy sources- Oil, natural gas, coal
Urban Areas use less coal
Energy use follows trends geographically and seasonally
Energy Intensity- energy use per unit of GDP
Fossil fuel supplies are very uncertain
Energy Intensity has decreased in USA past 50 years (more efficient use per dollar)
Crude Oil migrates to the highest point in a formation of porous rock and accumulates there
Hubbert Curve- Represents oil use and projects when world oil production will reach a maximum and when world oil will be depleted.
Hubbert curve uses both upper and lower estimates of reserves
Peak oil- point at which oil extraction and use would increase until roughly half the oil supply had been used up
We may have already reached peak oil
We are running out of conventional oil and gas supplies in next 50 years
Energy efficiency- ratio of amount of energy expended in the form wanted vs the total amount of energy in the system
Energy conservation and efficiency are most cheap and environmentally sound action for maximizing resources
Energy to Mass ratio + energy creation rate makes gas and diesel ideal for vehicles
Second law of thermodynamics- when energy is transformed, its ability to do work diminishes- 2/3 of energy spent on coal burning electricity generation plant ends up as waste heat
Energy return on investment (EROEI)= Energy obtained from fuel/Energy invested to obtain fuel- larger # = more efficient
Nonrenewable resources- Natural Gas, Oil, Coal, Nuclear
Potentially renewable- wood, biofuel
Nondepletable- Wind, Solar, Hydroelectric, Geothermal
Module 36
Sun is ultimate source of fossil fuel energy and most renewable energy
Biofuel- liquid fuel like ethanol or biodiesel created from processed or refined biomass
Biomass- wood, charcoal, manure, solid waste, biofuels, etc.- accounts for 40% of renewable and 5% of total energy consumed worldwide- releases lots of carbon in burning
Modern Carbon- carbon in biomass that was recently in the atmosphere (captured through photosynthesis)
Fossil Carbon- Old carbon contained in fossil fuels
In theory, Burning of biomass(modern carbon) does not increase atmospheric C02 concentrations. Ex: If plants grow back where biomass was just harvested, then the plants will take up equal or more CO2 then was released in the burning of biomass
Carbon neutral- does not change atmospheric CO2 concentrations
Biomass may or may not be carbon neutral
Each fuel has optimal applications
Wood- renewable if regrowth rate = harvest rate. makes charcoal that has 2x energy content of wood per unit mass
Coal- remains from plants preserved 280-360 million years ago, most prominent under wetlands and river deltas
Coal process-
starts with Peat (partly decomposed organic material under soil),
then after compression it becomes Lignite (brown coal- soft sedimentary rock with occasional traces of plant structure, contains 60 to 70% carbon after millions of years),
then after further compression over hundreds of millions of years, it becomes bituminous coal (black or dark brown coal with 80% carbon and bitumen/asphalt, hard but can be hand broken)
After further burial and years of tectonic activity and heat, it becomes Anthracite coal/hard coal (coal with over 90% carbon, highest energy quantity per coal volume, fewest impurities, made after 280-360 million years)
Natural gas is “clean” because its combustion produced smaller amounts of particulates, sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide then oil or coal
Natural gas makeup: 80-95% Methane CH4 and 5-20% ethane, propane, butane
Main Natural gas uses- electricity and industrial processes, sometimes transportation or fertilizer
It is used less for vehicles because it requires transport by pipeline
Liquified Petroleum gas- liquid form of natural gas that is used for heat
Natural Gas and LPG supply 34% of US energy, 24% of global
Crude Oil- mix of hydrocarbons (oil, gasoline, kerosene) and water and sulfur that is liquid both underground and at the surface
Crude oil- used for transportation, can be refined into tar, asphalt, gasoline, diesel, and kerosene
Crude oil distillation- happens in oil refinery where heat causes boiling and separating of crude oil, very costly and dangerous
Boiling points: Butane and lighter products- under 85 F, Gasoline blending components- 85-185 F, Naphtha- 185-350 F, Kerosene, jet fuel- 350-450 F, Distillate (diesel, heating oil)- 450-650 F, Heavy Gas Oil- 650-1050 F, Residual fuel oil- 1050 F
Heavier= higher boiling point, lower= lower boiling point
Tar sands/oil sands- slow flowing, thick deposits of bitumen (degraded crude oil that forms in certain oil deposits) or asphalts- does not flow at room temp.
Tar sand extraction leads to more crude oil, but mining takes lots of energy, contaminates lots of water in dry areas, and requires open pit mining
One barrel of oil= 160L or 42 gallons
Electric hot water heaters have 99% direct efficiency because any lost heat energy to the surrounding areas is captured by the water that surrounds it.
Gas water heater only has 60% direct efficiency
Gas water heaters can have better overall efficiency because the electricity can come from inefficient sources such as a coal-fired powerplant
Look at both fuel appropriateness for task and overall efficiency
Other factors in choosing vehicles- convenience, comfort, style
Smaller cars have less air pollution and better MPG
Self driving car technology may decrease fuel efficiency by 5 to 10%, but it could be made up for by driving with optimal fuel efficiency
Electricity is secondary source of energy- obtained from conversion of primary source- meaning it is an energy carrier (moves and delivers energy in convenient, usable form to end users)
40% of US energy generates electricity, but only 13% of that 40% is available energy for end uses
Electricity is clean at point of use, but not location of production
Energy source that requires fewest conversions to reach end product is likely most efficient
Improvement in gas combustion technology- led to combined cycle natural gas-fired power plant (uses both steam turbine to generate electricity and turbine powered by exhaust gases from combustion to generate electricity)- with 60% efficiency
Power plant capacity- max electrical output
Most power plants don’t operate every day- to calculate plant’s output use capacity factor (fraction of time a power plant operates in a year)
Most power plants have capacity factor over .9
It takes time for nuclear and coal fired plants to reach full capacity, so they are often running at all times, hydro plants are easier to power up so they are not
Cogeneration/combined heat and power- use of fuel to generate electricity and deliver heat to building- leads to greater efficiency as waste heat is used. Can be as efficient as 90% compared to 75% for steam heating and 35% for electricity generation
Natural gas power plants make 40% of all electricity
Module 37
Fossil fuel distribution depends on a region’s geology
Crude oil made from remains of phytoplankton, this and coal material do not decompose like most parts of carbon cycle
Large flame in oil wells- gas flare caused by purposeful burning of excess natural gas to reduce it and avoid explosion
Worldwide petroleum consumption- 4 billion gallons per day, US is 21% of this
Coal Advantages: energy dense, plentiful, low cost of mining, transportation, and refining
Coal disadvantages: lots of mine tailings, as surface coal decreases subsurface mining is needed, combustion results in sulfur and other bad element releases, lots of ash, leakage can be deadly, lots of C02
Oil ad.: convenient use and transportation, cleaner than coal, often used for transportation
Oil dis.: lots of sulfur and trace metals, sulfur removal is costly, need for extraction leaves high risk for leakage or spill, lots of spill in everyday use, oil flaring
Natural Gas ad.: 50% of US homes use natural gas for heating, less impurities, less CO2, lots of natural gas pipelines make it convenient
Despite less CO2, there is more methane
Fracking: uses high pressure fluids to split rocks rocks underground and unearth less accessible natural gas
Good: Fracking causes less cost of natural gas via a surplus, is a domestic energy source and keeps US jobs, and is cleaner than coal or oil
Bad: Fracking takes up lots of water, only a portion of which is removed and then must be treated before it goes back to local water bodies. Chemicals are added to fracking fluid that can contaminate aquifers, natural gas can also contaminate wells and make water flammable- but this may be unconnected to fracking
Fracking releases volatile organic compounds (category of organic compound air pollutants that evaporate at typical atmospheric temps. from both fracking fluid and technology used in fracking) they are a precursor to other types of air pollution
A large amount of escaped natural gas (fugitive gas), may be leaking from fracking and gas extraction and releasing methane that traps heat
Fuel is converted to electricity and releases CO2 and heat energy
In a power plant: Fuel is burned, energy goes to water which becomes steam and rotates a turbine that turns the generator which makes electricity that is transported on the electrical grid. After steam goes through the turbine, it becomes water, which is sometimes cooled or released into nearby water bodies.
Water use in thermal energy generation is a substantial amount of water consumption in US
total efficiency= all efficiencies multiplied- rest of energy is lost as waste heat
Energy quality- ease at which an energy source can be used to do work. High quality has a convenient, concentrated form that does not require much energy for transportation
Gas energy concentration= 44MJ/kg. Wood energy concentration= 20MJ/kg
Module 38
Radioactivity- emission of ionizing radiation or particles caused by spontaneous disintegration of atomic nuclei
Nuclear Reactors use same turbine-style way to generate electricity as fossil fuels, they just use uranium-235 as fuel
Unstable isotopes are radioactive, Radiation contains energy that is heats the surrounding environment
Fission- nuclear reaction where a neutron strikes a relatively large atomic nucleus, which then splits into two or more parts, releasing additional neutrons and energy in the form of heat
Additional neutrons from fission can make more fission, leading to a chain that gives off lots of heat energy
Nuclear reactors harness this kinetic energy to make a self-sustaining chain of fission as fuel
Byproduct of Nuclear: radioactive waste that remains hazardous for many half-lives
1g of 235 U has 2-3 million times the energy of 1g coal
containment structure contains nuclear fuel, which is contained in fuel rods inside of it- there can be hundreds of them
Uranium fuel is processed into pellets that go into fuel rods
heat from fission is transferred to water that loops around and transfers it to other water, creating steam that turns the turbine and powers a generator
control rods- rods in between fuel rods that absorb excess neutrons and can slow or stop fission
Collusions must happen at a controlled speed- water and control rods are used for this to prevent meltdowns and fires
Up to 900kg of uranium ore to produce 3kg of nuclear fuel- uranium is extracted and concentrated- rest is left as mine tailings
suitable nuclear fuel has over 3% uranium 235 (rest is Uranium 238 that doesn’t fission as easily)
Nuclear power A’s: less air pollution (10% of equivalent fuel energy), allows fuel independence in countries without fossil fuels. makes up 70% of energy in France
Nuclear power disad.: public concern, expensive factories, takes 704 million years for U235 radiation to half (half life of 704 mil. years), thermal pollution
Radioactive decay- when parent radioactive isotope emits alpha/beta particles or gamma rays- measured by average rate of decay of radioactive element (usually stated in half life)
Half life allows knowledge of potential danger of elements
radioactive waste- nuclear fuel that is no longer useful in a power plant but still gives off radioactivity
Nuclear fuel waste: high level (used fuel rods), low level (contaminated items like clothing), and uranium mine tailings (residue after uranium ore is mined and enriched)
fetuses and young people are most vulnerable to radiation
Becquerel/bq= measurement of radioactive decay, 1Bq= decay of 1 atom per second
Curie= unit of measure for radiation- 37 billion decays per second
Fuel rods are threat to humans for 10 or more half lives- they are stored at power plant in pool storage or lead-lined dry containers
Nuclear waste must be stored indefinity, away from humans,
US Government wanted to store waste in Yucca Mountain Nevada, they never did
Three Mile Island accident- (1979 PA, caused by lack of cooling water around reactor)
Chernobyl- (1986 Ukraine, caused by test removal of control rods, 31 deaths and radiation spread, contaminating cows, humans, and causing thyroid cancer)
Fukushima- (2011 Japan, caused by earthquake, no deaths by radiation)
Nonrenewable EROIN from most to least: Coal, Natural Gas and Nuclear Energy, Diesel, Gasoline
Module 39
Charcoal has 2x energy per unit of rate then wood
Air pollutants with Wood/Charcoal Burning:
Particulates/Soot: Solid or liquid particles suspended in the air
Carbon Monoxide: Colorless, odorless gas formed during incomplete combustion of most materials
Nitrogen oxides: by-product of combustion of any fuel in the atmosphere
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): Organic Compounds that evaporate easily
CO2: by-product of all combustion-is modern carbon in biomass combustion
Manure fuel risks indoor air pollution
Biofuels- Ethanol (alcohol made by converting starches and sugars from plant material into alcohol and CO2, usually corn) and Biodiesel (diesel substitute made by extracting and chemically altering plant oil, usually soybeans or algae)
US is world leader in Ethanol production
Brazil uses biofuels from sugarcane as sustainable fuel
Ethanol is mixed with gas, Gasohol has high O2 content and less air pollutants
Ethanol doesn’t introduce fossil carbon, but it does cause lower fuel energy content in gasoline, it also causes inefficient use of corn
Biodiesel- more expensive than petroleum diesel, typically B20 (80% petroleum diesel, 20% biodiesel)
Algae produces lots of fuel for biodiesel
Any diesel vehicle can run on straight vegetable oil (SVO), that is obtained as waste from restaurants and filtered to become fuel
Passive Solar- use of sun energy without technology- seen in south facing windows to admit solar radiation in the winter and solar ovens (box cooker)
Solar ovens remove wood as a fuel source, stopping deforestation and extreme travel
Active Solar- use of sun energy captured by technology (solar water heating, photovoltaic solar cells, solar thermal systems for electricity)
Solar water heating systems: Heat energy from the sun heats circulating liquid driven by a pump (active) or natural convection (passive), hot water than goes to hot water tank for use- usually have a backup energy source
Photovoltaic solar cells: systems that capture energy from the sun as light and convert it into electricity. They use semiconductors that generate electric current when exposed to sunlight and convert that current into a higher-voltage alternating current for use.
PSCs: use solar panels and are either tied to electrical grid where extra energy goes, or to batteries to store extra electricity. Effectiveness limited by the sun being visible and less efficient at higher temps when air contains more moisture
Concentrating Solar Thermal Electricity Generation: large scale applications of solar energy to electricity generation. They use mirrors and lenses to concentrate sunlight into a small beam. Best in desert areas, but large amounts can reduce NPP and impact habitats
CST requires lots of land and are ineffective at night
Active Solar A’s: No CO2 or water pollution, most energy produced when demand is highest on hot days, economically feasible to install and makes homeowners money
Active Solar DA’s: expensive to make, can take a long time to get return on investment, manufacturing requires energy, water, toxic metals. Improper recycling is dangerous
Hydroelectricity: energy made by kinetic energy of moving water
China makes most hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity amount depends on flow rate of water and the distance water falls
Water Impoundment systems: storage of water in a reservoir behind a dam, dam operators control opening and closing of gates to control flow rate of water (how much electricity is produced). Uses turbine to power generator. Three Gorges Dam (China) is the largest
Run of the River systems: Hydroelectricity generation where water is retained by small dam or no dam, energy generated when water passes through channel with submerged turbine. It has less environmental impact but is small and can be unreliable
Tidal Systems: use of tidal energy (energy from the movement of water driven by gravitational pull of the moon), they use gates and turbines to convert energy to electricity
Hydroelectricity A’s: No pollution, cheaper electricity, minimal amount of fuel for use, recreational appeal and economical gains from reservoir
Hydroelectricity DA’s: Flooding that causes anerobic decomposition of covered plants (releasing methane), relocation, high heat and low oxygen environment in reservoirs that can kill fish and hold parasites. Downstream removal of sandbars and removal of seasonal water movement that disrupts fish lifecycles. Greenhouse gas release in building and filling reservoir, siltation (accumulation of sediments on reservoir bottom) also happens and can reduce capacity and lifespan of dam)
Module 40
Geothermal energy- heat energy from radioactive decay of elements deep in earth. Convection currents move magma (from radioactive decay) to surface of earth, heating groundwater that either reaches the surface in geysers or can be removed by drilling
Iceland heats 90% of homes with geothermal energy
Heat released by radioactive decay is nondepletable, but the groundwater that it heats can be depleted
Geothermal energy has little growth potential because it is not easily accessible everywhere and can be costly to reach, geothermal plants can also release hydrogen sulfide and methane
Heat exchangers: collect heat by circulating cool liquid underground, where heat from the ground flows to the cool circulating liquid, and then returns to the surface
Direct heat- hot groundwater is pumped directly into a radiator
Ground Source heat pumps- solar energy from heat that is trapped underground- works by fluid being pumped through pipes underground, gives heat in the winter and cool in the summer- uses 30-70% less energy to heat/cool a building than a standard furnace
Hot water heat pump- extracts heat from air in garage or basement and transfers it to water in a domestic hot water tank- similar to heat removers in refrigerators
200-250% of the amount of energy in the electricity used to run the HWHP is transferred to water in the tank because the heat pump takes heat energy from surrounding air
Fuel Cell- an electrical-chemical device that converts fuel, such as hydrogen, into an electrical current, cell never dies as long as it receives fuel
How a fuel cell works- H2 is split into electrons and protons in upper reaction layer. Protons move across membrane while electrons go around (electrical current). O2 molecules are split and combine with protons and electrons to form water in lower reaction layer- only waste products are energy and water (2H2+O2=energy + H2O)
Getting hydrogen is hard because it is rare, explosive, and bonds with other molecules so it requires separation
separation of hydrogen molecules- either use of natural gas hydrogen or electrolysis (electric current applied to water to split hydrogen and oxygen), can be renewable if electricity used is from a renewable source
hydrogen is an energy carrier
Hydrogen is not used on a large scale, but the fuel cells are 80% efficient in conversion and it has only water as a waste product (compared to fossil fuel 35-50% efficient with pollutant production)
Hydrogen DA’s: must find a way to get hydrogen without using more fossil fuels than it’s energy would save, transportation would need larger fuel tanks for hydrogen use than gas, there could be a tank rupture that could cause fire or explosion
Module 41
Wind energy: energy from the kinetic energy of moving air
Wind ultimate source of energy is the sun that drives heating for air circulation
China has largest wind energy capacity in the world
Texas makes 40% of wind energy in US
How a wind turbine works: wind turns blades, which transfers energy to gearbox, which turns the mechanical energy into electricity. Motorized drives turn the turbines to face the wind for maximum efficiency
Larger blades and taller towers increase turbine capacity
Land turbines have capacity factors of 25-40%, Offshore has factors of 40-50%
Turbines are usually in wind farms so there can be less electrical transmission lines
Cape Wind failed due to scenic and regulation issues
Block Island wind farm- first offshore in US, capacity of 30 MW
Wind energy A’s: clean, renewable, only fossil fuel use is in manufacturing and worker transport, can share land with other areas
Wind energy DA’s: rely on batteries that are hard to produce and recycle, bird and bat deaths (turbines are turned off during migration time and painted to reduce this), noise, habitat fragmentation concerns
Phantom loads- electrical demand by a device when it is turned off (cable boxes and gaming consoles)
Ways to save energy- Weatherize, plant landscaping, less hot showers, hybrid vehicle, buy energy efficient devices, use power strip, reduce phantom loads, use laptop instead a desktop computer
Things governments can do to save energy: increase public transport access, high taxes on coal and natural gas, low taxes on hybrid vehicles,
Hybrid electric vehicles are more efficient than internal combustion engines because they capture kinetic energy of braking, which is converted into electricity and back to the motor
HEV- hybrid electric vehicle, PHEV- Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles, BEV- Battery Electric Vehicle
reducing energy during high electrical demand periods- brownout, cutting energy completely- blackout
Peak demand- greatest quantity of energy used at one time, causes there to be backup generators for times of necessity
Ways to diminish peak demand- variable price structure (less cost when demand is less)
When calculating energy saved, add the amount of energy that would have been lost to convert that energy to a useable form
Use florescent and LED lights over incandescent bulbs
Energy Star program- set by EPA, measures efficient standards
Sustainable design- windows on south-facing wall for passive solar, skylight, high efficiency systems, proper insulation, double paneled windows, dark materials on road, building into a hill, green roofs, recycled materials, location close to workplace
Thermal mass- property of a building material that allows it to retain heat or cold
High TM: stone and concrete, Low TM: wood and glass
CA Academy of sciences: uses passive solar, radiant heating, solar panels, green roof, skylights
Sustainable energy: must combine energy efficiency, energy conservation, renewable and nonrenewable energy resources.
Amory Lovins- suggested that innovation, not resource depletion, moves humans from one source of energy to the next
Delivery of renewable energy sources is hard
5-10% of energy generated is lost during transport on transmission lines,
Smart grid: efficient, self-regulating electricity distribution network that accepts any source of electricity and distributes it automatically to end users. It senses when electricity is needed, and when there is excess capacity- coordinates electricity use with electricity capacity
gas only vehicles always produce carbon monoxide
Oxygenated fuel- fuel with oxygen as part of the molecule
Ethanol produces more of many air pollutants than just gas- due to corn plowing, conversions of forest to farmland, production process using coal or natural gas
Ethanol EROI= 1.3 gas EROI: 15
Ethanol production has caused cropland to move from food to fuel production
Cellulosic ethanol: ethanol derived from cellulose (material that makes up cell walls in plants), can be derived from grass or trees instead of corn,
CE A’s: no fertilizer or plowing for plant growth, can use algae to avoid taking up cropland
CE DA’s: distillation is expensive, large amounts of land needed
Unit 7- Atmospheric Pollution
Module 42
Air Pollution: The introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or microorganisms into the atmosphere at concentrations high enough to harm plants, animals, and materials such as buildings, or to alter ecosystems- usually in troposphere
Air pollution outputs: components of atmosphere or biosphere that remove air pollutants
Things that can alter/remove air pollution: Plant surfaces, soil, clouds, particulates, gases
US Clean Air Act- identified six criteria air pollutants, which EPA uses concentrations of each to decide whether or not an area is clean
CO2 was not an original air pollutant, but SCOTUS ruled that it should be considered one
Most to least pollutant release: Coal, Oil, Natural Gas
Combustion of all fuels in the atmosphere results in the release of nitrogen oxides;
Combustion of all fuels also lead to CO and hydrocarbon release
Carbon monoxide (CO)- problem in developing countries where people cook indoors
Photochemical Oxidants- air pollutants formed by sunlight acting on chemical compounds such as nitrogen oxides. They degrade plant tissue, human respiratory tissue, and construction material. They cause smog, and mainly Ozone is focused on
VOCs- organic compounds that evaporate at typical atmospheric temperatures (strong aromas)- not necessarily harmful
Hydrocarbons- Pollutant compounds with carbon-hydrogen bonds (fossil fuels, lighter and dry-cleaning fluid, oil based paints, perfumes), they become hydrocarbons when they evaporate and enter the air through usage or spillage
Air pollutants can be primary or secondary, or both
Primary air pollutants: VOCs,CO,CO2,SO2,NOx, most hydrocarbons and suspended particles. They come directly from emission sources
Secondary air pollutants: SO3,O3,HNO3,H2SO4,H2O2, most NO-3 and SO2-4. They are primary pollutants that have transformed with sunlight, water, oxygen, or other compounds
Conversion to secondary air pollutants happens more during the day and in wet places
National Ambient Air Quality Standards- specifies concentration limits for air pollutants
All criteria air pollutants in USA have decreased, Lead the most after being removed from gasoline
Module 43
Photochemical smog- Smog dominated by oxidants such as ozone (LA-type smog or brown smog)
Sulfurous smog- smog dominated by sulfur dioxide, sulfate compounds, and particulate matter (London-type smog or gray smog or industrial smog)
In 2021, 40% of Americans were exposed to poor quality air
More hours of sunlight= more photochemical smog
Smog deters tourists and hurts the economy
Brown smog chemical formation process:
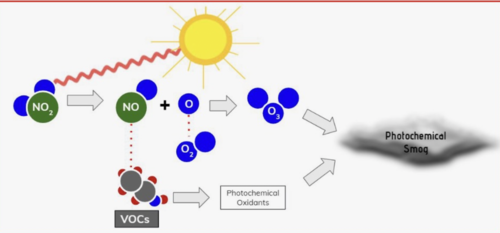
ozone concentration greatest with most sunlight
ozone destruction occurs after sun intensity decreases- O3+NO= O2+NO2
Sublimate- processes of converting a solid to a gas or vapor
formaldehyde- a VOC, natural compound used as a preservative and as an adhesive in plywood and carpeting
Without VOCs, natural cycle of ozone concentration and destruction happens
With VOCs, VOCs combine with NO instead of Ozone, causing less ozone destruction
Reduce nitrogen oxide and VOCs for less photochemical smog
High temp= more smog
Smog can cause burning/itchy eyes, aggravate asthma, emphysema, and bronchitis, and premature death
Long term ozone exposure can cause asthma
Thermal inversion- when warm air at mid altitude covers, cold dense air below, trapping pollutants- causing severe pollution
Inversion layer- layer of warm air that traps emissions in thermal inversion
Conifer trees release terpenes (VOCs)
Natural VOCs led to smog in smoky mountains
SO2 emissions are 30% natural, NO emissions are 44% natural, VOC emissions are 89% natural
Wind moves some pollution
The smaller the particulate matter, the more dangerous as it can travel further in respiratory track
Particulate matter can absorb sunlight, causing haze and reducing photosynthesis
Module 44
CO can cause death by asphyxiation within minutes- it is the most dangerous indoor air pollutant. it does this by bonding with hemoglobin instead of oxygen.
Developed world CO pollution comes from malfunctioning exhaust, Developing world CO comes from cooking inside with improper ventilation
Carbon monoxide detectors are essential
Second hand smoke- caused by being around someone smoking, source of particulate matter
Dead human skin cells, the dust mites that eat them, and their droppings all become dust
Pollen, Dust, Mold, are all Particulates that cause allergies, lung inflammation, and asthma
Asbestos- long, thin, fibrous silicate material with insulting properties that can cause cancer if inhaled. Six different minerals are classified as this
Asbestos is in shingles and insulating material in steam an hot water pipes
Asbestos causes asbestosis (chronic lung condition) and mesothelioma (lung cancer from asbestos exposure). Manufactured asbestos is stable, and not dangerous until it is disturbed
Asbestos removal must be done by professionals, or else the pollution will get worse
Radon 222- radioactive gas that occurs naturally from uranium decay and is an indoor air pollutant
Radon can enter houses through cracks in foundation or groundwater from a well
Radon decays in 4 days into polonium, which also attaches to air particles which cause lung cancer when inhaled
Reduce radon by increase ventilation and sealing basement cracks
formaldehyde is in carpets and pressed wood, sensitivity to it can develop over time
reduce VOCs by using wood flooring or natural fiber carpeting, and reducing perfumes
VOCs inside: detergent, dry cleaning fluid, deodorizers, solvents plastics, fabrics.
lead is in paint chips that can be ingested by young children
outdoor air pollution can cause indoor air pollution from nitrogen oxide and sulfur dioxide if buildings are not properly insulated and air sealed
Indoor air pollution kills 3.8 million people annually
Developed world indoor air pollution- people spend more time indoors, tightly sealed buildings can trap air with pollutants indoors, lots of materials made from VOCs
Sick building syndrome- buildup of toxic pollutants in weatherized spaces, such as newer buildings in the developing world
New buildings often have products made with synthetic materials or glues that haven’t dried, meaning off-gassing occurs and releases air pollution
Reasons for sick building syndrome: inadequate or faulty ventilation, chemical contamination from indoor sources, chemical contamination from outdoor sources, and biological contamination from inside or outside
Developing world indoor air pollution: caused by inside cooking, but ventilation does occur and lessen pollutants if outside air is clean
Module 45
Air pollution fuel prevention: use less fuel, use oil instead of coal, lower sulfur concentration in fuels during refining, replace bituminous coal with anthracite coal- but there will always be a need to control exhaust stream after combustion occurs
Air pollution regulatory practices- requiring vapor recovery nozzles (device that prevents VOCs from escaping into the atmosphere during fueling) at gas stations; restricting evaporation of dry cleaning fluids and use of lighter fluids (VOCs); reduction of wood burning stoves and fireplaces; regulating business emissions
Cars cause air pollution with NOx and VOCs; reduce this by restricting automobile use, expanding public transport, and shutdown industries
Clean air act amendment “Cap and Trade”: institutes buying and selling of allowances for SO2 emissions. each allowance allows for 1 ton of SO2 emissions in a year. Allowances are based on amounts of sulfur that sulfur emitters produced prior to 1990- financial penalties if allowances are exceeded. They are on the open market
Catalytic converter- device that chemically converts air pollutants (NOx, HC, CO) to N2, H2O, and CO2. Inserted before the muffler in car exhaust systems, contains platinum as a catalyst(increases chemical reaction rate without undergoing change its self)
Catalytic converters remove oxygen from nitrogen oxides, creating nitrogen gas, and adds carbon to CO, making CO2, along with treating hydro carbons- very effective
Scrubber: air pollution control device that uses air and lime (dry scrubber) or air and water (wet scrubber) to separate and remove particles and sulfur dioxide from industrial exhaust streams.
In wet scrubber- mist collects particles from air, moves them to sludge disposal system in water, water is moved back to scrubber for reuse.
Scrubbers are used on industrial plants and coal-burning power plants
Fluidized bed combustion- when granulated coal is burned close to calcium carbonate, the calcium carbonate absorbs SO2 and produces calcium sulfate for sheetrock for houses
Ways to filter particulate matter- gravitational, fabric filters that remove particulate matter, electrostatic precipitators (uses electrostatic charge to make particles clump so they can be removed from air)
In electrostatic precipitators, particles collect on collection electrodes, and clean gas exits- common in industrial plants and coal-burning power plant
To reduce NOx, lower temperatures and control oxygen
Air pollution control devices are less optimal than increasing efficiency or switching fuels
Module 46
pH- logarithmic, basic-14, acid-0
acid- a substance that contributes hydrogen oxides to a solution, base- substance that contributes hydroxide to a solution
Rainwater pH- 5.65, acid rain pH- 4, ocean water pH- 8.1
more CO2 in atmosphere- more acidic rain water- more acidic ocean water
Air pollution adds acidity to water
Acid rain/ acid deposition- precipitation high in sulfuric acid and nitric acid
Sources of acid rain- automobile exhaust, stationary fossil fuel combustion, volcanoes
NOx+SO2 turn into nitric acid (HNO3) and sulfuric acid (HNO4) in the atmosphere with oxygen, they then split into inorganic compounds (sulfate, nitrate) and hydrogen ions
Disassociation- when an acid is dissolved in water, it splits into H+(positively charged hydrogen ions) and negatively charged ions
wind causes acid rain to form in places that produce no pollutants, it is hard to regulate internationally
Ways that acid rain harms things- acidifying soil, mobilizing toxic metal
Limestone bedrock reduces the effect of acid rain
Without limestone bedrock, acid rain can mobilize metals that enter surface water and kill species
skin prevents human damage from acid rain
acid rain affects places downwind from sources of pollution
acid rain harms limestone and marble (because it neutralizes calcium carbonate), and paint
Title 4 of clean air covers acid rain and noise pollution
db= 1/10 of a bell, db scale is logarithmic (10 increase in db= 2x loudness)
frequency range of humans: 20-20,000 Hz
Noise pollution measured in loudness and frequency/pitch
decibel A scale- logarithmic scale that measures both loudness and frequency of sound.
noise limits- no more than 85dbA for 8 hours a day
factories can cause noise pollution
wealthy areas have less noise pollution than poor areas
Noise can lead to heart disease, hormonal disruption, distraction, hearing loss
minorities are subject to more air and noise pollution
Noise affects bat hunting, mating and warning signals in birds and amphibians, migration routes, and sonar communication
solution to noise pollution- make ships with quieter propellers
Compound | Symbol | Sources | Impacts |
Criteria Air Pollutants | |||
Sulfur Dioxide | SO2 | Combustion of fossil fuels, volcanoes, forest fires | Respiratory irritant, hurts plant tissue, precursor to acid rain |
Nitrogen Oxides | NOx, NO or NO2 | All combustion in the atmosphere, mainly motor vehicles and stationary fossil fuel combustion, also lightning, forest fires, and microbial activity | Respiratory irritant, ozone and acid rain precursor, overfertilization of ecosystems |
Carbon Monoxide | CO | Any incomplete combustion, and malfunctioning exhaust systems + fires | Interferes with oxygen transport to bloodstream, causes headaches or death |
Particulate Matter | PM2.5 PM10 | Combustion of bio and fossil fuels, road dust, rock crushing, volcanoes, forest fires, dust storms | Can exacerbate respiratory and cardiovascular disease, reduces visibility and causes haze and smog linked to heart disease and lung cancer |
Lead | Pb | Gasoline additive (banned), old paint, | Impairs central nervous system and can make learning and concentrating harder |
Ozone | O3 | Secondary pollutant- formed by sunlight, water, oxygen, VOCs, NOx | Reduces lung function and exacerbates respiratory symptoms, degrades plant surfaces, damages rubber and plastic |
Other Air Pollutants | |||
Volatile Organic Compounds | VOC | Evaporation of fuels, solvents, paint Improper combustion of fuels like gasoline | Ozone precursor |
Mercury | Hg | Fossil fuel combustion and waste incineration, gold mining | Impairs central nervous system, bioaccumulates in the body |
Carbon Dioxide | CO2 | Combustion of fossil fuels, clearing land, respiration | Increases greenhouse gas concentrations |
Unit 8- Aquatic and Terrestrial Pollution
Module 47
Point source (direct source of pollutant) vs. nonpoint source (diffuse area producing pollution- lots of small pollutant contributions in large area.)
Cruise ships can dump waste as pollution- up to 1 metric ton of garbage/day
Living in niche allows for homeostasis (the ability to experience relatively stable internal conditions in bodies)- and for organisms to survive, grow, and reproduce
Low pollutant concentration can impact physiology and behavior- high can impact growth and survival
Pollutant presence doesn’t harm a species, its concentration and tolerance levels do
mayflies are indicator of pollutants because of high sensitivity
Coral reefs suffer from warmer waters and pollutants
Chemical pollutants- heavy metals and synthetic compounds that are naturally and human produced
Heavy Metals- lead, arsenic, mercury
Lead enters water through lead lined pipes, harms fetuses and infants the most- many federal guidelines against use
Lead pollution happened in flint, Michigan when there was no chemical to prevent lead from leaching into water- health concerns at 5 ppb
Arsenic- compound in earth’s crust that dissolves into groundwater- furthered by mining and industrial arsenic uses- causes cancer but can be removed with filtration, 10 ppb limit- problem with arsenic water in India and Bangladesh
Mercury- natural heavy metal from burning fossil fuels and manufacturing cement, also petroleum wells that leach into groundwater- Asia makes most of it
Inorganic mercury isnt bad, but in wetlands/lakes it is converted into methylmercury that harms CNS- most exposure happens from eating fish and shellfish like tuna
Synthetic compounds- pesticides, pharmaceuticals, military and industrial compounds
Pesticides- first synthetic in WWII, kill unintended animals,
Inert ingredients- additives that make a pesticide more effective- not required to be tested for safety- Roundup’s inert ingredient to enter plant leaves, kills tadpoles
Pharmaceuticals- very common pollutant- 90% of streams contain steroids
Military compounds- perchlorates- group of harmful chemicals used for rocket fuel- contaminate soil and then food+ water, which affects thyroid gland and hormone production
Industrial compound dumping caused fire on Cuyahoga river
polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)- group of industrial compounds once used to manufacture plastics and insulate electrical transformers- lethal and carcinogenic
PCDEs- polybrominated diphenyl ethers- industrial flame retardants added to clothing, construction, etc. - detected in breast milk- can lead to brain damage
PFAS- per and poly fluoroalkyl substances- increasingly dumped in water and very pervasive and long lasting- now in almost everyone’s blood- can cause cancer and harm fetuses
Chemical pollutant impacts-
Neurotoxin- disrupts nervous system- insecticides, heavy metals
Carcinogens- cause cancer (cell damage and growth), mutagens are carcinogens that damage cell genetic material- radon, asbestos, formaldehyde
Teratogens- interfere with fetus/embryo development- thalidomide, alcohol
Allergens- cause allergic reactions- chemicals in peanuts, penicillin, codeine
Endocrine disruptors- interfere with normal functioning of hormones (developmental disorders, low sperm counts, breast cancer risk)- wastewater
Wastewater feminizes fish and amphibians
Oil pollution sources-
tanker spills (Exxon Valdez spilled oil off Alaskan coast- still remains two decades later- caused mandated double hull design)
offshore drilling (leaking ~322000 lbs per year in north American waters, Deepwater Horizon- oil pipe break in ocean 20x Exxon Valdez- consequences not yet known)
natural reserves (make up 45% of oil in water worldwide)
How to fight oil pollution-
Plastic barriers are laid to stop oil spreading, then oil is sucked off surface with vacuum or absorbent materials
applying chemicals that break up oil- could hurt marine life
burning oil slicks- causes air pollution and byproduct that harms wildlife
genetically engineered bacteria- occurs naturally, but scientists want to speed it up
sponges
No removal method for underwater plumes
Oil removal onshore- hot water sprayers (also removes marine life), leaving it alone (never really leaves)
Module 48
Levee- enlarged bank on riverside to prevent flooding, largest ones on Mississippi river
Levee use- prevents fertility of surrounding lands- pushes sediments downstream- can cause flooding downstream- can still flood occasionally
Levee failure occurred in NOLA after hurricane Catrina- can either break or water can go overtop and erode it
dikes- structures to prevent ocean flooding- prominent in Netherlands and areas that lie below sea level
dams- barrier that runs across river/stream to control water, creates a reservoir- used for energy, flood control, and recreation- most built for recreation
Three Gorges Dam- large amount of power, prevents seasonal flooding
2/3 of rivers no longer flow freely due to dams
dams are used to prevent seasonal flooding- but seasonal flooding is necessary for species, so humans can recreate it
1300 dams removed in USA- restores natural habitat
Old aqueducts less effective- 55% of water lost
Aqueducts disrupt habitats- water diversion has international problems: Ex: Soviet union damning Aral sea
Desalination: 50% of it done in middle east- Done by distillation(boiling water) or reverse osmosis (salt water forced through semipermeable membrane- cheaper and more efficient- leaves behind brine that is dumped in oceans and can hurt ocean life)
Wetlands harmed by draining, dam construction, agriculture, fishing, disappearing 3x faster than forests
Eutrophication- causes agal blooms/red tides, produces toxins and hypoxic water, eutrophic lakes most susceptible to harmful blooms
Oxygen sag curve- point source pollution causes reduced oxygen at pollution point because bacteria break down sewage and consume oxygen
Sediment accumulation happens when fast moving water dumps sediments into lakes- must be dug up by dredging- can reduce sunlight in water and harm visual predators
Thermal pollution- occurs from logged forests, industrial processes that return hot water to natural water- regulated by EPA- biggest challenge in summer- fixed by cooling towers that use evaporation to reduce water temp
Noise pollution- often caused by US navy activities- can harm whales and animal communication
Module 49
Factors for chemical persistence: temperature, pH, whether it’s in water or soil, whether it can be degraded by sunlight or broken down by microbes
Persistence measured by half life
POPs (persistent organic pollutants)- synthetic carbon-based molecules that break down slowly Ex: DDT
PCBs and PFAS persist in the environment- when PFAS infiltrate groundwater, water filtration systems must be installed in every nearby home or public water lines must be supplied to every home
General Electric dumped 1.3 million lbs PCBs in Hudson river- was forced to remove them but PCBs levels will be high for 15-30 more years
Chemical concentrations in organisms depend on
routes of exposure: (air, water, food, soil, other organisms), usually limited routes per pollutant- pesticides can enter amphibians through skin and snakes as they slither over chemical-contaminated ground
chemical solubility (how well a chemical dissolves in liquid)- water solubility means it runs off into lakes and percolates into groundwater; fat and oil solubility means that they are found more in soils
bioaccumulation (selective absorption and concentration of a chemical within an organism over time)- chemicals stored in fat tissues and build up over time- results in biomagnification
DDT biomagnification- believed to be unharmful, still used to kill mosquitos in some parts of the world, DDT concentration in birds 276000x that of concentration in water, caused thin-shelled eggs in fish eating birds
Humans store chemicals like methylmercury, PCBS and POPs, can lead to cancer, problems in reproductive and nervous systems
Module 50
Solid waste(human-produced waste not in solid or gas form that is not toxic)- increased since WWII- made up by Municipal Solid Waste (solid waste collected from households, small businesses, institutions like schools, prisons, hospitals) and agricultural, industrial, and mining waste
MSW per capita hasn’t increased since 1990, 60% of it comes from households
less MSW in developing countries- but it is increasing with more production
All products enter waste stream-flow of solid waste that is recycled, incinerated, placed in a landfill, of otherwise disposed
MSW make up: 23% paper and paperboard, 22% food, 12% yard trimmings, 12% plastics, and more
Electronic (E-waste)- 2% of waste stream- but greater environmental effects as they contain toxic metals, 38% sent to recycling (which costs more than landfills)- often disposed of without regulation in Asia
MSW fate- 50% landfills, 24% recycling, 14% composting, 12% incinerating
Open landfills ended in US in 1930s- they caused fires and groundwater contamination
anerobic decomposition makes methane, aerobic makes CO2
Leachate- liquid with pollutants as a result of passing through landfill solid waste
sanitary landfill setup- clay/plastic lining at bottom along with pipes to collect leachate (which is recycled back to landfill)- if leachate is too toxic, it is required to be treated as toxic waste- little water is allowed in- compacted waste is held in-between soil layers, and finished with a clay soil cap+ planted with vegetation
Plastic, glass and paper go in landfills, aluminum and metals do not (contribute to leaching and are valuable recyclables), toxic materials do not, food and yard scraps do not (sources of methane)
landfill costs are recovered by a tipping fee: Avg, $55 per ton is US, can cause illegal dumping when fee is a high price
Landfills should be made in loam or clam loam soil far from people and bodies of water, but close enough to have low transportation cost
Landfills often put near poor areas (Fort Wayne Indiana)
leaching occurs at all landfills(overhyped concern), along with greenhouse gas release
Incinerators reduce solid waste to ~25% of volume in ash
Incinerator setup- waste dumped onto platform and sorted, then incinerated, polluted air is filtered out, ash is collected and removed, energy sometimes used to fuel incinerator again (waste to energy system)
Toxic ash has different treatment then regular ash
Acidic gases produced from burning plastics are treated in a scrubber and neutralized
Incineration tipping fee: $70 per ton US avg
Incineration consequences: ash is more concentrated and toxic, incinerators require more waste to run effectively so recycling could be discouraged, may not completely burn all waste due to different properties, environmental justice issues
Solid waste is dumped due to high costs or landfills/incinerators refusing to accept it
Charles Moore found Pacific garbage patch, two in pacific, one in northern Atlantic
garbage dumping in oceans lowered in 1980s
Hazardous waste- waste in any form that is harmful to humans, ecosystems or materials- characteristics: ignitability, corrosivity, reactivity, toxicity
Toxic waste is a category of hazardous waste- means substances that cause harm in chemical ways when ingested or absorbed through skin
US produces 25 million metric tons of hazardous waste each year- mostly industrial but also small scale
Household hazardous waste- paints, motor oil, chemical cleaners- cost much more to dispose of then to buy
Best way to reduce disposal of hazardous waste- less creating hazardous waste
Resource Conservation and recovery act `1976, 1984 (Hazardous and Solid waste amendment)- cradle to grave tracking, no hazardous waste disposal on land
Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act/ Superfund Act 1980- imposes tax on chemical and petroleum industries, uses funds to clean up abandoned and nonoperating hazardous waste sites, authorizes federal government to respond to substance release that could harm human health or environment- EPA maintains National Priorities list for this
Superfunds exist in every state- most in NY, PA, NJ, CA,- major site in Love Canal NY, advocated for by Lois Gibbs
Superfund lacks funding, and does not list all contaminated sites, solely federal government managed
brownfields program- EPA program that works with state and local governments to clean up contaminated industrial and commercial land that doesn’t qualify for super funds- inadequate solution without legal liability controls or management consistency
Module 51
Waste reduction methods (highest to lowest effectiveness)- Reduce, Reuse, Recycle
Source reduction- waste management by cutting waste in the design and manufacturing of a product- ex: using less toxic materials or less packaging
Reuse tactics- milk bottle reuse, eBay and craigslist
Closed loop recycling- product recycled into same product- carpet, paper, aluminum
Open loop recycling- product recycled into something else- plastic bottle to jackets
zero sort recycling- no sorting by residents (more likely to recycle), all sorting occurs at plant with economic returns in mind
Glass and paper markets are volatile- not always financially responsible to recycle them
Compost- break down of organic materials to organic matter (humus)
Optimal carbon to nitrogen ratio for decomposition- 30:1
Layer brown materials (grass, etc.) with green materials (kitchen vegetables)
Turning is necessary for compost
microbe respiration kills pathogens in bacteria
Compost takes up time and space, but also gives nutritional value
Life cycle analysis- can’t determine environmental impact, but can asses economic and energy uses
recycling has lower tipping fee than landfills
Integrated waste management- approach to reducing impact of MSW disposal
Industries with future recycling- carpet and automobile
People should upcycle + follow turtle model
Module 52
Wastewater pollution causes
Oxygen demand- microbes break down waste with oxygen, increasing BOD (biological oxygen demand)
wastewater BOD- 200mg/L oxygen
Nutrient release- decomposing wastewater releases nitrogen and phosphorous
cultural eutrophication- human-caused increase in fertility
>500 dead zones in world as of 2018
Disease causing organisms- wastewater carries pathogens that may cause cholera, typhoid fever, hepatitis, and gastrointestinal illness (dysentery)
¼ of world population- 2.1 bil ppl, do not have access to clean drinking water
fecal coliform bacteria (E. coli)- indicator of wastewater pollution, no human consumption of water if E.coli is present
Rural sewage- septic system- relies on gravity, septic tank split into three layers (top: floating stuff/scum, middle: septage- fairly clear water with bacteria, nutrients, pathogens, bottom: sludge (solid waste from wastewater), leach field to absorb water, turn organic material into CO2+ inorganic compounds, and outcompete pathogens in it, sludge in tank must be pumped out every 5 years
Developed sewage- Primary treatment- filters out large materials, secondary- bacteria breaks down 85-90% of organic matter into CO2+ inorganic compounds, water is aerated and settled particles are disposed of, tertiary- chemicals+ ultraviolet light+ fine mesh removes inorganic compounds and pathogens
Sewage overflow in rainstorms- legal but bad, expensive to fic
Manure lagoons- bacteria breaks down manure for fertilizer, bad if it seeps into underlying groundwater
Module 53
Dose response studies- expose organisms to different chemical amounts and record changes
LD50 is different for different species
when chemical has sublethal effects, researches find ED50 (dose that causes 50% to have a harmful, but nonlethal response)
NOEL- largest concentration with no affect
Scientists test most vulnerable species to represent larger groups- no direct test for reptiles or amphibians due to lack of public concern
Test replacements: mice/rats for mammals, pigeon/quail for birds, trout for fish, water fleas for invertebrates (fish used for aquatic reptiles or amphibians, birds for terrestrial)
safe concentration for animals LD50/10
safe concentration for humans LD50/1000
Risk Analysis steps: Risk assessment, acceptance, management
Risk assessment done by qualitative (no data) and quantitative means
Death probability US- 1/7 (heart disease and cancer), 1/28 (lower respiratory disease)
quantitative risk assessment equation: probability of being exposed to hazard* probability of being harmed if exposed
PCB risk assessment- done by EPA, found that risk from eating contaminated fish is higher than contaminated water or air
risk assessment- EPA standards for environmental hazards= 1 in 1 million
Risk management- acceptable risk- lobbying fought arsenic in drinking water into a compromise at 10 ppb
Innocent-until-proven-guilty principle- potential hazard not considered until data shows that it causes harm. Can bring out beneficial chemicals sooner, but risks long-term contamination- USA
precautionary principle- potential hazard needs actions to evaluate and reduce it. Can slow beneficiary chemical release and reduce financial motivation for research, but is safe for the environment
If asbestos had been under precautionary principal- there would be less deaths and financial cost
Stockholm convention- 2001 agreement among 127 nations banning/reducing 12 chemicals including DDT and PCBs- all endocrine disruptors. In 2017, it listed 32 chemicals in total
In 2007, 27 EU nations made REACH (Registration, evaluation, authorization, restriction of chemicals)- precautionary principle that placed responsibility for environmental risk on chemical manufacturers.
Module 54
retrospective studies- measure people already exposed to a hazard, identify consequences of pollutants like asbestos and sewage water
prospective studies- measure people who might be exposed to a hazard
Synergistic interactions- two risks combined cause more harm then each risk alone
Infectious disease is a disease caused by a pathogen- cause ¼ of worldwide deaths
Common pathogens- viruses, bacteria, fungi, protists, helminths
Risks for chronic disease- developing countries: childhood malnutrition, unsafe water. developed countries: smoking, obesity, high blood pressure
Pathogen causes rapid disease increase- epidemic. epidemic spread large- pandemic
Unsafe drinking water causes cholera+ dysentery( intestine infection that causes diarrhea), and hepatitis (inflammation of liver caused by virus)
Emergent infectious diseases- infectious disease that hasn’t been focused on for 20 years prior. 1 new per year since 1970
Combating disease- developing: better nutrition, sanitation, drinking water, and education. developed: healthier lifestyle choices+ disease education
Increased climate will allow for mosquitos to move towards the poles and spread diseases northwards
Clean water act 1972- maintains and restores chemical, physical, and biological properties of surface waters. Issued water quality standards with pollutant limits and permits for those pollutants. No groundwater, but does include animal feedlots and sewer storm runoff
Safe Drinking Water Act (1974, 1986, 1996)- sets national standards for safe drinking water. EPA sets maximum containment levels (MCL) for 77 different elements and substances in surface and groundwater, but they are subjective and pressured politically+ economically
EPA defines water in terms of uses: aesthetics, recreation, fish protection, drinking water, etc.
47% of wetlands, 46% of rivers and streams, 30% of lakes and ponds, 22% of bays and estuaries fully support designated uses in USA
Nonpoint pollution sources and fracking not covered under existing regulations
More care for water pollution as wealth of a nation grows