AP Bio ch 2
Matter - anything that takes up space and has mass - everything around us
Element - Substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by
Chemical reactions - 92 naturally occurring
Compound - Substance of two or more different elements combined in a fixed ratio
IE - NaCl or steel
Essential Elements - carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen compose 96% of living matter.
Phosphorus, sulfur, potassium, calcium, sodium, and other trace elements compose the remaining 4%. Trace elements still necessary for life.
Atom - smallest unit of matter that still retains the properties of the element.
Subatomic particles:
Proton - positive, circa 1 Dalton, located in nucleus
Neutron - neutral, circa 1 Dalton, located in nucleus
Electron - negative, circa 1/2000 of a Dalton, orbits
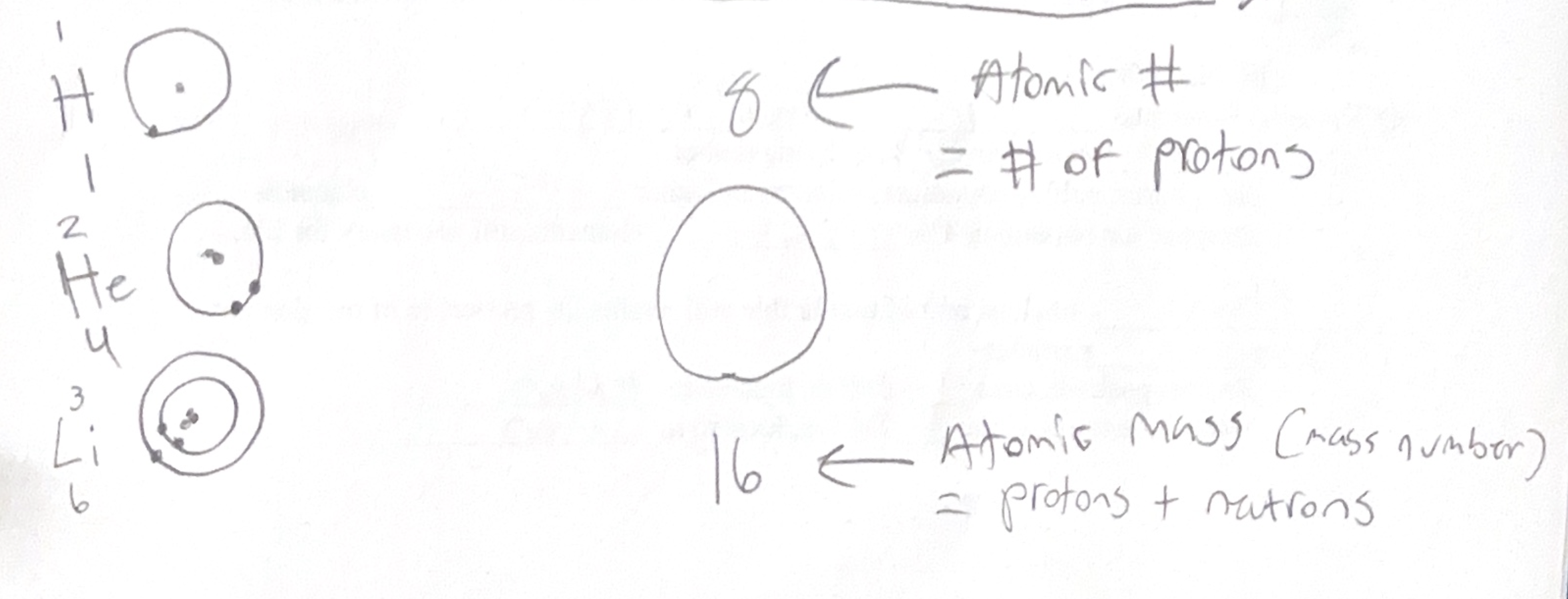
Atomic number - number of protons (if neutral atom, the proton number = electron number)
Mass number (atomic mass) - Protons + neutrons. Mass number will be greater (or equal to, in the case of hydrogen) that atomic of neutrons.
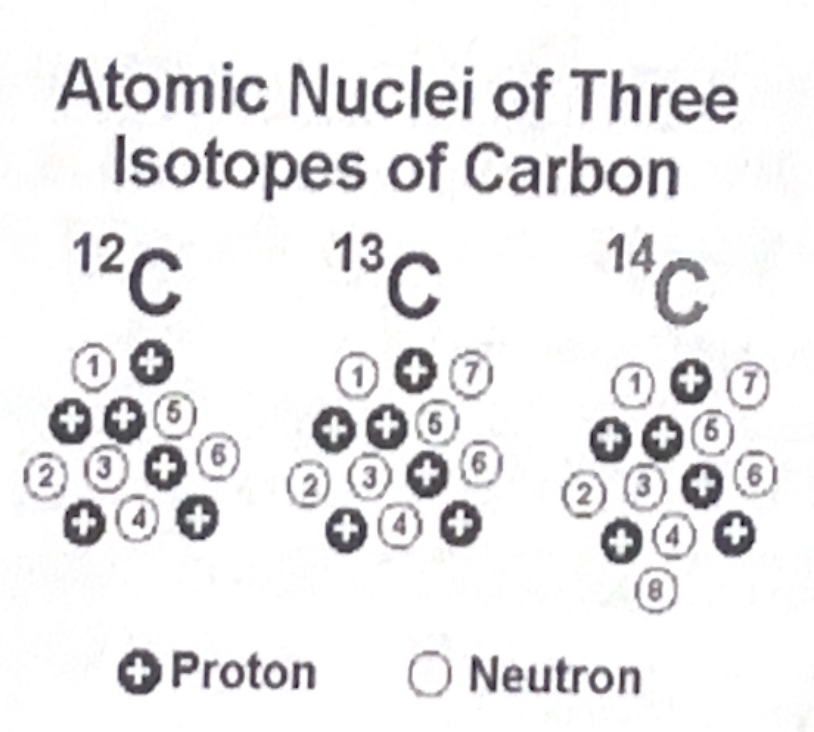
Isotope - Some elements have a differing number of neutrons
Same chemical properties.
EI - Carbon. Exists in three different isotopes, C-12 (99% in nature), C-13 (almost 1%), C-14 (miniscule amount found in nature). C-14 is a
Radio isotope - nucleus decays spontaneously causing radiation. Used as a “tracer” (substance used to track the flow of C in an organism).
Energy levels of electrons - energy is defined as the capacity to cause charge. Electron energy level closest to nucleus is at lowest energy level. Electron energy levels increase in energy as we move away from the nucleus.
- Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell.
Non-reactive if this shell is full (noble gasses)
- Orbitals - First shell can hold 2 electrons (1s), second shell can hold 8 electrons (2s and three 2p’s). Cannot have more than 2 electrons per orbital.

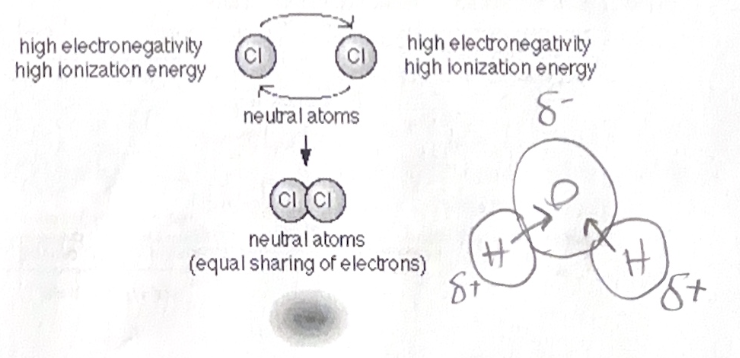
Covalent bonding - sharing of valence electrons. Some of the strongest bonds found in living matter.
H-H (hydrogen to hydrogen) is a single bond, each H is sharing its one electron (structural formula). Can also be written as H2 (molecular formula)
Bonding capacity is based on how many electrons are needed in valence shell, and typically an atoms “valance” = the number of unpaired electrons in the outermost shell.
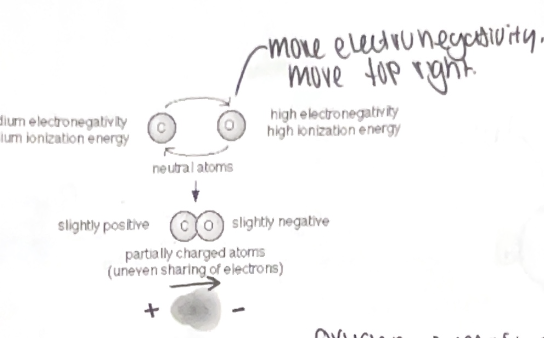
Electronegativity - attraction of a particular atom to the electrons shared in a covalent bond. More electronegative atoms pull harder on the electrons. When electrons are shared equally between two atoms of the same type (IE - Cl-Cl) then it is a non-polar covalent bond. When the electrons are NOT shared equally it is considered a polar covalent bond (IE - H2O) Oxygen is the most electronegative of all 92 elements. Where ever the electrons are being pulled closest to will have a slight negative charge (noted as δ-)

Ionic Bonding: Ionic bonding- The two electrons are so unequal in their attraction to the valence electrons that the stronger of the two strips the electron away from the other atom.
EX- Sodium (11 electrons, single electron in valence) and chlorine (17 electrons, 7 electrons in valence). Chlorine strips the single electron away from the sodium, fulfilling the octet ni the valence shells of both. Because of this donation, the sodium is now positive (has 1 protons, 10 electron) and is called a. Chlorine is now negative (17 protons and 18 electrons) and cation is called an Anion.
-Cations (PAWSITIVE) and anions (onions are negative smells) attract forming this ionic bond. These bonds form what are called "salts".
Oxygen is most electronegative of all 92 elements ( commonly found in an organism)
Weak bonds- Some of the most Important bonds in living matter.
-reversable
hydrogen bonds- H atom that is covalently bonded to an electronegative atom attracts another electronegative atom (usually O or N in living matter)
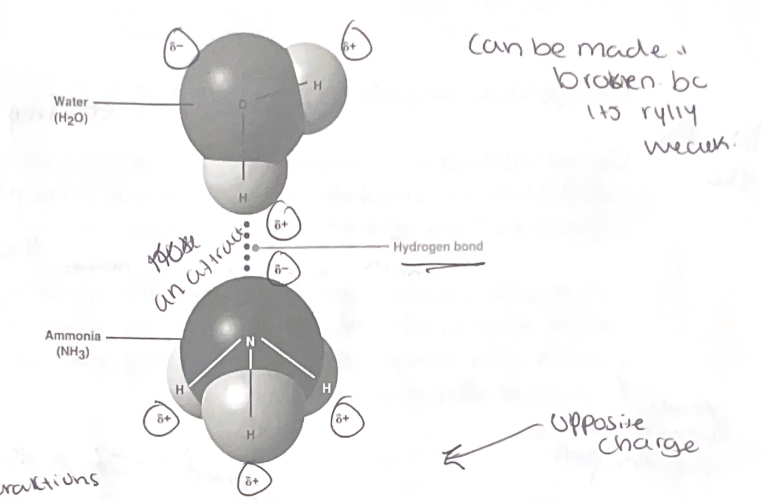
opposites attract!! (slightly positive and slightly negative)
Van Der Waals - "hot spots" of positive charges because of random electron movement (weak bond, negative but strong enough to hold a gecko on a wall!)
Molecular shape and function- When two matching atoms bond it will be a morphine linear molecule. Larger molecules are very complicated and their shape CRUCIAL in recognition, in biological systems.
Chemical reactions- making and breaking bonds. reactants Product(s)
We cannot create or destroy matter, only rearrange it.
photoynthesis- 6CO2 +6H20 —> C6H1206 +602 Some reactions are reversible some are not (said to have gone "to Completion"). If we increase the concentration of reactants. then we will speed up the reaction.


inert is a substance that is not chemically reactive