Copy of 11.1 The Role of the Nervous System.docx
11.1 The Structures and Processes of the Nervous System
*The PNS can be divided into the afferent system and the efferent system.
- Afferent system: receives input through receptors and
transmits the “input” to the CNS
- Efferent system: carries signals away to the “effectors”
(muscles and glands)
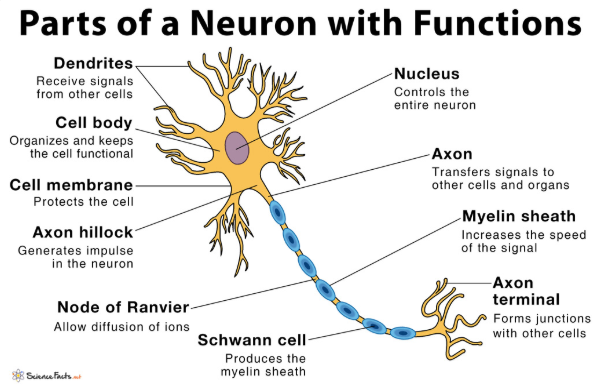
Cells of the Nervous System: (Two main types of cells)
- Neurons: they are specialized to respond to physical & chemical stimuli, to conduct electrochemical signals, & to release chemicals that regulate various body processes
- Glial cells: outnumber neurons by about 10 to 1, they account for about half of the volume of the nervous system. Collectively, they nourish the neurons, remove their wastes, and defend against infection.
Classifying Neurons: Neurons are classified based on their structure as well as their function.
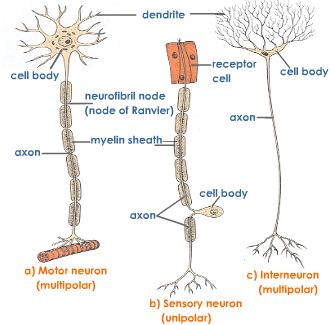
- Motor neuron – transmit information from the central nervous system to effectors (muscles, glands, and other organs that respond to impulses from motor neurons)
- Sensory neurons - sensory receptors, such as those in the skin, receive stimuli and form a nerve impulse. Sensory neurons transmit impulses from the sensory receptors to the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord).
- Interneurons - found entirely within the CNS. They act as a link between the sensory and motor neurons. They process and integrate incoming sensory information, and relay outgoing motor information.
Reflexes – fast, predictable, automatic responses to changes in the
 environment.
environment.
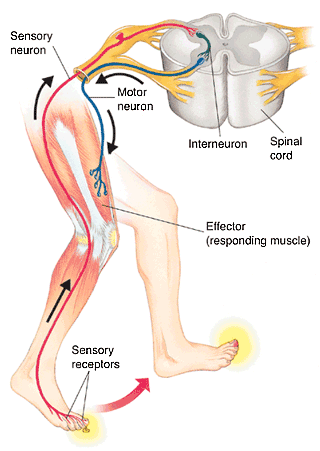
Reflex Arc
- The simplex neural pathway
- Do not require input from the brain
- Allow the body to react quickly to external stimuli
- Involve 5 essential components:
- Sensory receptor-responds to a specific stimulus
- Sensory neuron-propagates the nerve impulse to the grey matter of the spinal cord
- Interneuron-integrates the message
- Motor neuron-propagates (sends) the message out of the CNS to the part of the body that will respond
- Effector-responds to the motor nerve impulse