[Development in EAST ASIA] 1.1: The Song Dynasty
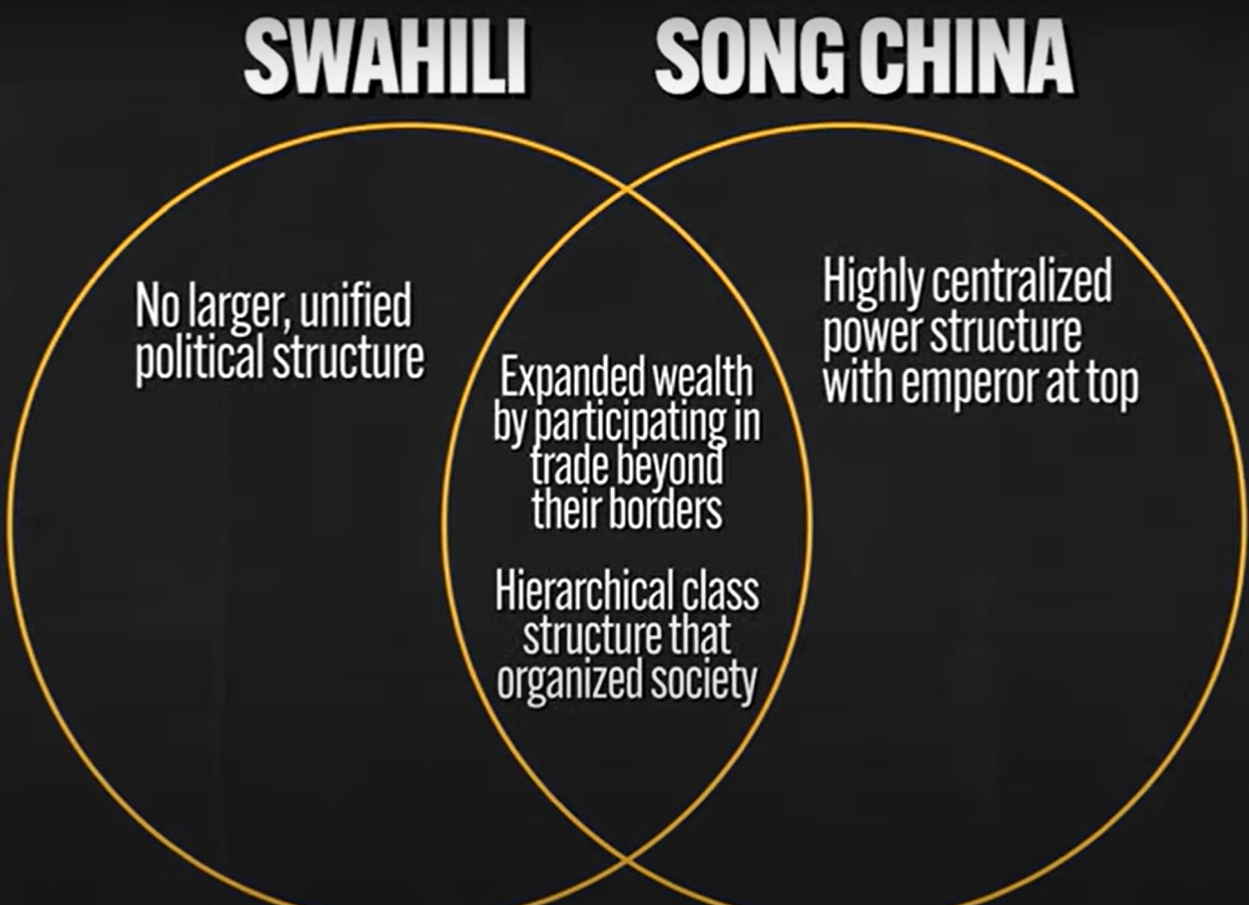
Power of SONG CHINA
How did the Song Dynasty maintain and justify its power?
Confucianism
A philosophy that taught human society is hierarchical by nature, which is to say, society was composed of unequal relationship
The greater entity should treat the lesser entities with concern and benevolence while the lesser entity should suck it up.
If everyone lived according to their rules - Harmony
Key Ideas:
Filial Piety: The practice of honoring one’s ancestors and parents
Starting the Tang Dynasty, Confucianism experienced a revival, and was carried into the Song Rule
Neo-Confucianism - What made it new was the influence of Buddhist and Daoist philosophical ideas
Women were relegated to the subordinate position in the hierarchy.
Women’s legal rights were restricted and property became their husbands and no remarried
Foot binding
Imperial bureaucracy
A governmental entity that carries out the will of the emperor.
During the Song Dynasty, the imperial bureaucracy grew in scope and help maintain their rule
Civil Service exam: heavily based on Confucian classics
The bureaucracy was staffed was only the most qualified men - awarded by merit
China Influences its neighbors
Korea empires were independent politically because they were able to maintain a tribute relationship with china
Korean court used a similar civil service examination to staff their bureaucracy
Korea adopted many Confucian principles which organized their family structure
Korea went even further than China in marginalizing the role of women.
Heian Japan adopted cultural trait voluntarily
Vietnam was independent politically but participated in a tribute relationship
Elite members of Vietnam society adopted:
Confucianism
Buddhism
Chinese literary techniques
Civil service examination system
But they did not marginalize their women
Buddhism in Sing China
Originated in South Asia → China
Buddhist beliefs
Four Noble Truths
Life is suffering
We suffer because we crave
We cease suffering when we cease craving
The eightfold path leads to the cessation of suffering and craving
Eightfold Path
OUtlines the principles and practices that Buddhist must follow
A moral lifestyle and the practice of meditation
Theravada Buddhist
mainly restricted to monks
Mahayana Buddhist
Emphasized that Buddhist teachings were available to all, and not just a select few
Emphasized compassion
Made the Buddha into an object of devotion
Tibetan
Same basic doctrines as the other, with a few additions
Emphasized more mystical practices
Lying prostrate
Elaborate imaginings of deities
Economy in the Song Dynasty
Commercialization of economy
Paper money
Iron & Steel production
Agricultural innovation
Champa Rice → Vietnam
Drought resistant
Harvestable Twice a tear
Effectively doubled agricultural output
Transportation innovation
Grand Canal
Magnetic compass
New shipbuilding techniques - JUNKS
[Development in DAR-AL-ISLAM] 1.2: Islamic Empires
Three Major Religions
Judaism
Ethnic religion of the jews
Originated in the Middle East
Monotheistic: One god
Christianity
Prophet: Jesus Christ
Islam
Prophet: Muhamad
Salvation would be found in righteous action like almsgiving, prayers, and fasting
New Islamic States arise
Abbasid Caliphate
Ethnically Arab
In power during Golden Age of Islam
→ Soon fragmented —> Several new islamic empires began to rise in its place (Made up of Turkic, non Arab people)
Turkic Muslim Empires
Seljuk Empire
Central Asia
Brought in my the abbasid as military force
Mamluk Sultanate
Egypt
Under the leadership of Saladin
enslaved fierce turkic warriors
Delhi Sultanate
South Asia
northern ruled over the Indian population
Continuity in Muslim Empires
Military in charge of Administration
Implemented Sharia Law
A code of laws established in the Quran
Continued Expansion of Islam
Military Expansion
Delhi Sultanate
Merchant Activity
Trade
Muslim Missionaries
Sufis → Sufism: Emphasized mystical experiences
Intellectual Innovations and transfers
Mathematics
House of wisdom
[State Building in SOUTH ASIA] 1.3: SOUTH ASIA & SE ASIA
Belief Systems
Hinduism
Polytheistic Belief system
ultimate goal of believers is to reunite their individual souls to the all pervasive world soul known as Brahman (reincarnation)
Provided the condition for the unified culture in India
Caste system
Islam
Buddhism
Belief Systems Change
Change in religion
Hinduism
Bhakti Movement → Encouraged believers to worship one particular god
Rejected the hierarchy of Hinduism
Encouraged spiritual experiences regardless of social status
Islam
Sufism → movement of more mystical experiences
Buddhism
Became more exclusive
State Building in South Asia
Rajput Kingdom
Vijayanagara Empires
Sea-Based States in SouthEast Asia
Srivijaya Empire → taxes on water route
Majapahit Empire → Tributary
Land-Based States in SouthEast Asia
Sinhala Dynasty
khmer Empire
[State Building in the AMERICAS] 1.4: Human Sacrifice?!
MesoAmerican Civilizations
Maya Civilization
Urban centers
Writing system
Mathematics
Maya State Building
State structure was basically a decentralized collection of city-states that were frequently at war with one another
Fought to create a vast network of tributary states among neighboring regions
Emphasized Human sacrifices
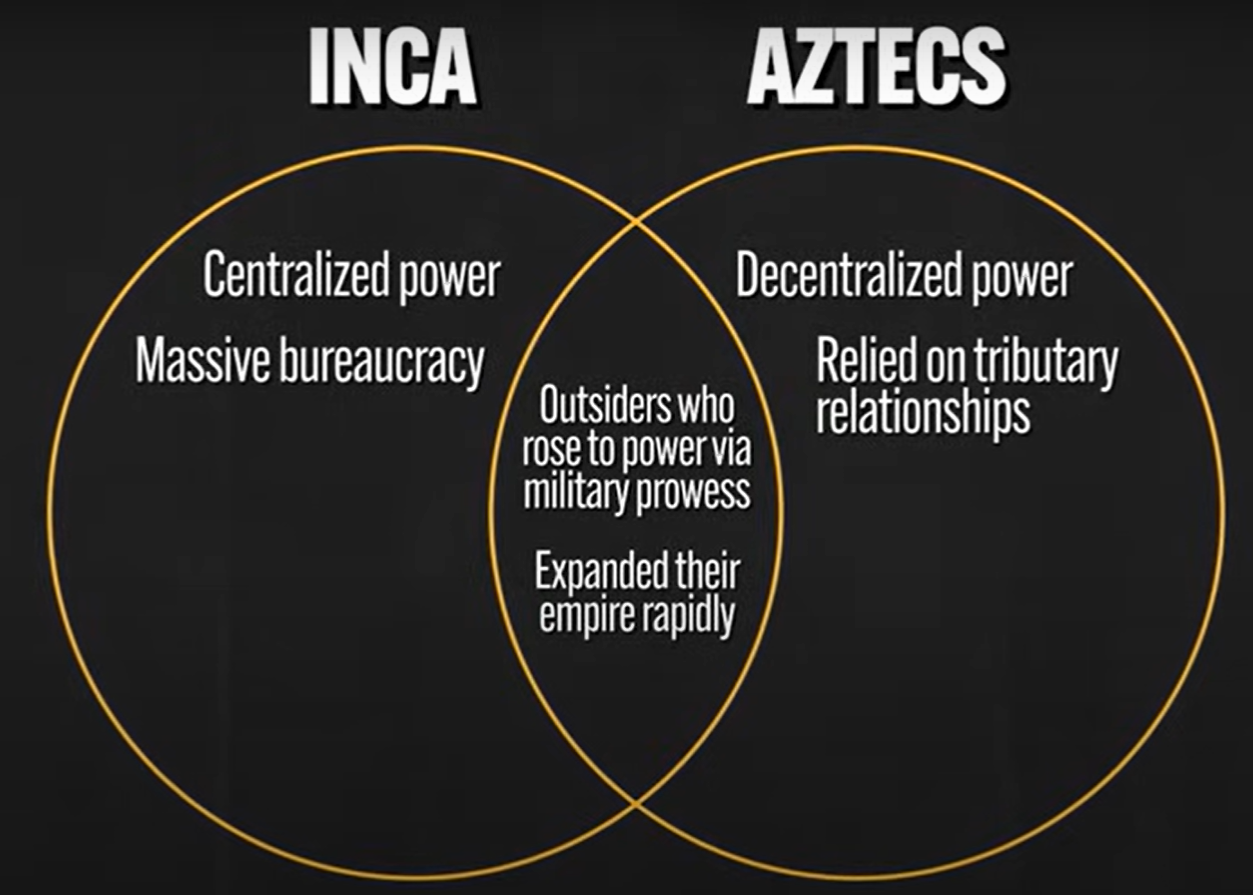
Aztec Empire
(MAYA) Political power → Decentralized power, Tributary system, religious motivation
Andean Civilizations
Inca Empire
MIT’A System
Required the labor of all people for a period of time each year to work on state projects like mining or military service
North American Civilizations
Mississippian Culture
Political structure → powerful chiefs and rules town and extended political power over smaller settlements (hierarchical)
[State Building in AFRICA] 1.5: AFRICA STATES!
State Building in Sub-Saharan Africa
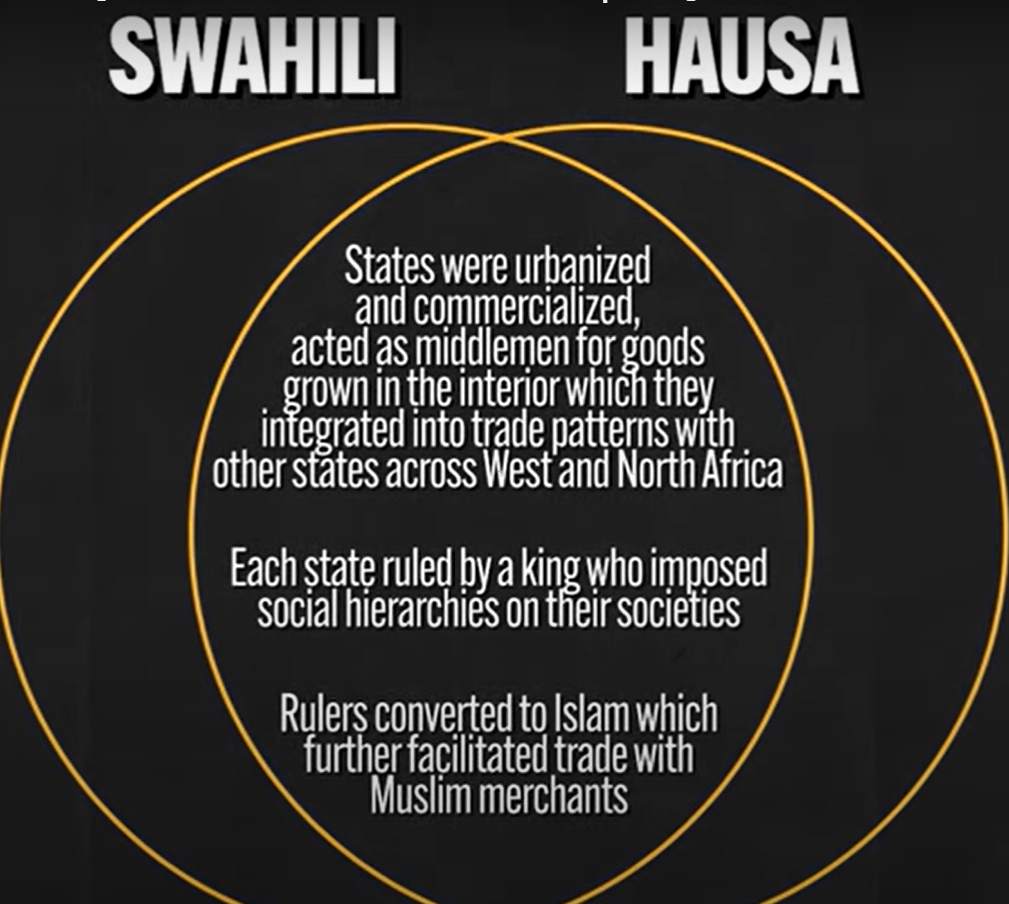
Swahili Civilization (Focused on Trade) → Good importants from farmers
Merchants were interested in:
Gold
Ivory
Timber
Slaves
Islam became a dominant belief
Conversion among the Swahili elite took place voluntarily → connected them to wider economic world of DAR-AL-ISLAM
Great ZimBabwe → Indian ocean trade
State building in West & East Africa
Hausa Kingdoms → Gained power through trade (Trans-Saharan Trade)
 -
-Ethophia → Christianity
Grew wealthy through trade (Indian Ocean Network)
Centralized power
[Developments in Europe] 1.6: Europe = Pretty weak
Christianity dominates Europe
Christianity in Europe
Eastern Orthodox Christianity → helped maintain power
Roman Catholic Christianity
Crusade fought Muslims in distant lands
Political decentralization in the west
No large empires in Europe
Socia, political, and economic order was organized in a system known as feudalism
A system of allegiances between powerful lords, monarchs, and knights
Manorialism: Peasants were bound to land and worked it in exchange for protection from the lord and his military forces
Surfs: Bound to the land
Monarchs in various states began to gain power and centralize their state by introducing large militaries and bureaucracies