Chapter 18- Speed of Reaction
Different reactions take place at different rates. For e.g. fermentation is very slow while precipitation reactions are very fast.
The speed of reactions can be measured by measuring any of the following per unit time: amount of reactant used up, amount of product obtained, volume of gas produced.
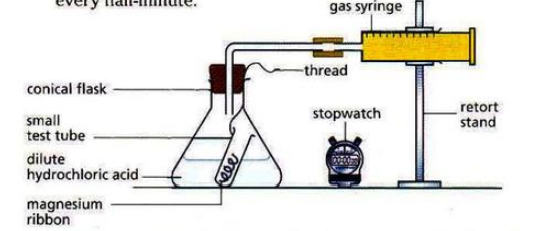
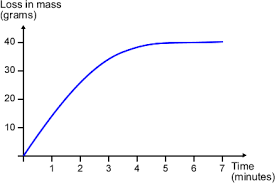
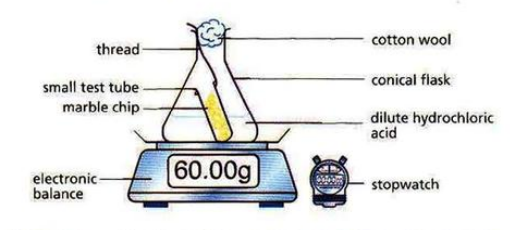
For any reaction to occur, the particles must collide with each other with sufficient activation energy (minimum energy to start a reaction). The collisions that result in formation of product particles are called effective or successful collisions.
FACTORS AFFECTING SPEED/RATE OF REACTION
- Concentration of the reactants (directly proportional to the speed of reaction): When the concentration of the reactants is more, there are more particles per unit volume which increases the frequency of collisions.
- Pressure of gaseous reactants (directly proportional to the speed of reaction): When the pressure of the reactants is more, there are more particles per unit volume which increases the frequency of collisions.
- Particle size (directly proportional to the speed of reaction): When the particle size is smaller, more surfaces are exposed, increasing the surface area to volume ratio which in turn increases the frequency of collisions.
- Temperature of the reaction (directly proportional to the speed of reaction): When the temperature of the reactants is more, the particles gain kinetic energy and collide more frequently.
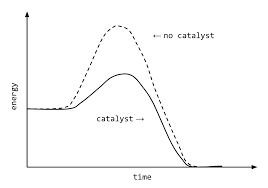
CATALYSTS
Catalysts is a substance which increases the speed of the reaction while remaining chemically unchanged itself.
A catalyst is needed in only a small account, increases the speed but not the yield, is selective in its action, is not used up during the reaction, and may be effected by impurities, heat and pH.
Enzymes are biological catalysts which are sensitive to pH and temperature.
Catalysts speed up the chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy for a reaction or providing an alternate pathway.