chapter 12 and 14: nervous system
osmosis video: overview of cns
central nervous system (cns)
brain
spinal cord
peripheral nervous system (pns)
somatic
autonomic
afferent
sensory information
outside → central nervous system
visual, auditory, chemoreceptors and somatosensory (touch)
efferent
motor info → periphery
contraction of skeletal muscles
movement through somatic nervous system
contraction of smooth muscle
activity of internal organs through autonomic nervous system
types of cells
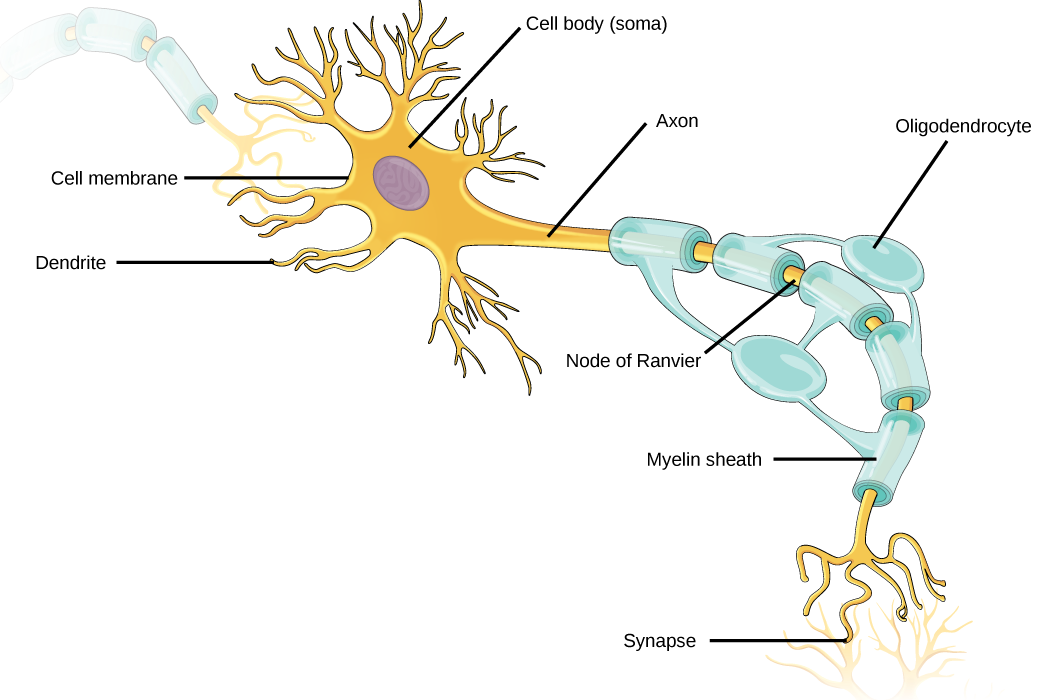
neurons
cell body
organelles
group of cell bodies (in cns) → nucleus
group of bodies (outside cns) → ganglion
dendrites
axon
glial cells
oligodendrocytes
cns
schwann cells
pns
astrocytes
cns
structure and metabolic support
resident immune cells
nourish blood-brain barrier
myelin comes from the glial cells
the brain
cerebrum
right
receives afferent fibers
sends efferent fibers to left side
left
receives afferent fibers
sends efferent fibers to right side
cross section of cerebrum
outermost area
gray matter
billions of neurol cell bodies
innermost area
white matter
axons
cerebral cortex
frontal lobe
movement and executive function
parietal lobe
sensory information
locates where we are
guides movements in 3d
temporal lobe
hearing
smell
memory
visual recognition of faces and language
surrounds and communicates with hippocampus
send info from short term → long term memory
occipital lobe
vision
white matter
internal capsule
highway that allows info to flow through neurons going to and from cerebral cortex
basal ganglia
pallidum
striatum
caudate nucleus
goes around pallidum and putamen
putamen
goes around pallidum
striatum receives input from cerebral cortex about desired movement → sends output signal to other basal ganglia → control smooth movement → inhibiting undesired movements
diencephalon
thalamus
collection of nuclei
nerve cell bodies
process sensory info
body → cerebral cortex
motor info
cerebral cortex → body
hypothalamus
regulate body temp
sleep and wake cycle
eating and drinking
regulates release of endocrine hormones
sends info to pituitary gland
anterior and posterior
cerebellum
coordinate movement, precision and balance
spinal cord and brain work together
fine tune motor activity → muscle memory (ex riding a bike)
brain stem
midbrain
vision, hearing, motor control, sleep/wake and consciousness
pons
facial expression/sensation
body equilibrium and posture
medulla
blood pressure, breathing, swallowing, coughing, vomiting and digestion

spinal cord
extends from brain stem to lumbar region of back
info travels up spinal cord by afferent (sensory) fibers
info travels down spinal cord by efferent (motor) fibers
for test
ch 12
know differences in neurons
know different types of glia
know ch 12 diagrams
difference between oligodendrocytes and swan cells
know resting potential vs acting potential
neurotransmission
amines, amino acids and neuropeptides
NOT on hormones
ch 14
cranial nerves
ch 13, 15, 16 and 17 will be tested later
neuroscience powerpoint
introduction
rhythmic activities
sleeping, waking, hibernation, breathing, walking
cerebral cortex: range of electrical rhythms depending on state of consciousness
gray matter, no myelinated sheath
eeg: classical method of recording brain rhythms from cerebral cortex
circadian rhythms: change in physiological functions according to brain clock
electroencephalogram
eeg
measurement of generalized cortical activity
noninvasive, painless
diagnose neurological conditions such as epilepsy, sleep disorders, research
recording brain waves
electrodes to scalp, low resistance connection
connected to banks of amplifiers and recording devices
eeg records small electrical field generated by synaptic currents in pyramidal cells
sleep
readily reversible state of reduced responsiveness to and interaction with the environment
sleep deprivation is devastating
one third of lives in sleep state
3 functional brain states
awake
non rem
rem sleep
 Knowt
Knowt