Module 1
SI Units- International system of units
Length/Distance- Meter (m)
Mass- Kilogram (kg)
Time- Second (s)
Metric Conversions
Kilo- 10³
Hecto- 10²
Deka- 10
Deci- 10⁻¹
Centi- 10⁻²
Milli- 10⁻³
Micro- 10⁻⁶
Nano- 10⁻⁹
Scientific Notation Rules
All non zero digits are significant
112 → 3 sigfigs
All zeros between non-zero digits are significant
303 → 3 sigfigs
All zeros to the right of a decimal point are significant:
10.0 → 3 sigfigs
Whole numbers with zeros to the left of a decimal point may be significant with appropriate information
42,100 → 2 sigfigs
100. → 3 sigfigs
Exactly 100 → 3 sigfigs
In decimals smaller than 1, the leading zero is not significant
0.00234 → 3 sigfigs
In scientific notation the zeros are always significant
2.00 × 10⁶ → 3 sigfigs
In performing multiplication/division, the number with the least number of sigfigs determines the sigfig of the final answer
When converting units the conversion factors are exact and don’t determine the number of sigfigs of the answer
Comparing different values
Percent difference- used when comparing any two numbers
| value A - value B| / average)
Percent error- used when comparing a number to an accepted value
|True Value - Measured Value| / True Value × 100%
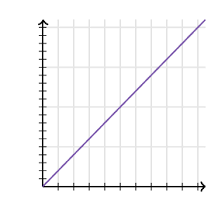
Four Common Graphs
Linear graph
Equation- y=mx+b
Slope- Δy/Δx
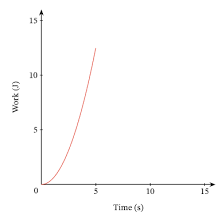
Power graph
Equation- y=axᴷ
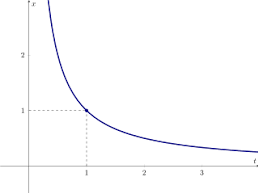
Inverse graph
Equation- y= 1/xᴷ
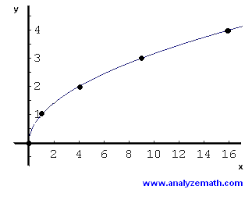
Root graph
Equation- y= k root x
Lab related info
Diameter vs Circumference
Have a positive linear slope
Pi is their slope
Area of a Circle
Area and radius squared have a positive linear slope of Pi
Area and radius have a power relationship