chapter 4: tissues
what are the 4 tissues of the body
epithelial tissue (covering)
covers exposed surfaces
lines internal passageways
forms glands
connective tissue (support)
fills internal spaces
supports other tissues
transports materials
stores energy
muscle tissue (movement)
specialized for contraction
skeletal muscle, heart muscle and walls of hollow organs
neural tissue (control)
carries electrical signals from one part of the body to another
key concepts
tissues are collections of cells and cell products that form specific, limited functions
4 tissues - epithelial, muscular, connective and neural
epithelial tissues
epithelia: layers of cells covering internal or external strands, thin
glands: structures that produce secretions
characteristics of epithelia
cellularity (cell junctions)
polarity (apical and basal surfaces)
attachment (basal lamina)
avascularity
regeneration
functions of epithelial tissue
provide physical protection
control permeability
provide sensation
produce specialized secretions (glandular epithelium)
microvilli: increased absorption or secretion
cilia: moves fluids
free surface and attached surface
polarity
apical and basolateral surfaces
effective barriers
integrity maintained by
intercellular connections
attachment to basal lamina
maintenance and repair
intercellular connections
support and communication
large connections
cams (cell adhesion molecules)
transmembrane proteins
intercellular cement
proteoglycans
hyaluronan (hyaluronic acid)
glycosaminoglycans
cell junctions
tight junctions (sealed)
gap junctions
desmosomes (buttons) + hemidesmosomes (1/2)
basal lamina
lamina lucida
thin layer
secreted by epithelia
barrier to proteins
lamina densa
thick fibers
produced by connective tissue
strength and filtration
repairing and replacing
epithelia are replaced by division of germinative cells (stem cells)
near basal lamina
classes of epithelia
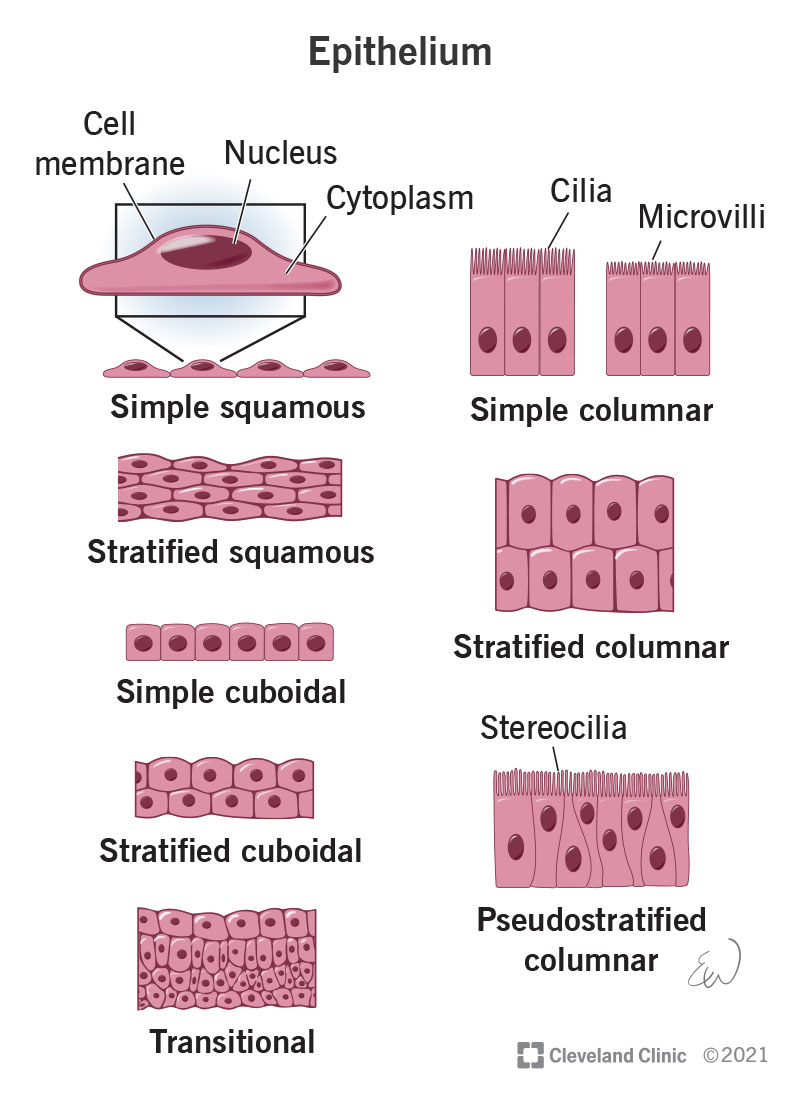
squamous epithelia
simple squamous epithelium
absorption and diffusion
mesothelium
lines body cavities
endothelium
lines heart and blood vessels
stratified squamous epithelium
protects against attacks
keratin proteins add strength and water resistance
cuboidal epithelia
simple cuboidal epithelium
secretion and absorption
stratified cuboidal epithelium
sweat and mammary ducts
stratified cuboidal epithelia
sweat gland ducts
transitional epithelium
urinary bladder
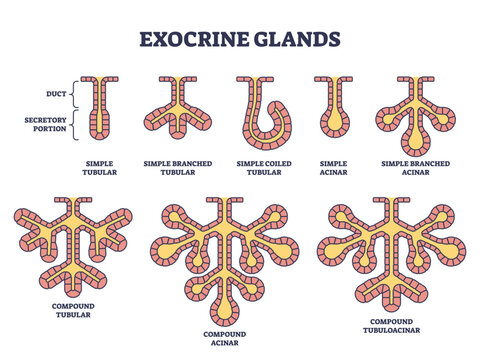
glandular epithelia
endocrine glands
release hormones, no ducts
exocrine glands
secretions through ducts
columnar epithelia
simple columnar epithelium
absorption and secretion, intestinal lining
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
cilia movement, trachea
stratified columnar epithelium
protection, salivary gland ducts
modes of secretion
merocrine secretion
sweat glands, released by vesicles (exocytosis)
apocrine secretion
mammary glands, released by shedding cytoplasm
holocrine secretion
sebaceous (oil) glands, released by cells bursting, gland cells replaced by stem cells
goblet cells: the only unicellular exocrine glands, intestinal lining
connective tissue
functions
forms capsule surrounding organs (serous membrane)
tendons and ligaments
skeletal system
fat storage
cushioning and insulating
transporting
protection
cells of connective tissue
building → -blast → fibroblasts, chondroblasts, osteoblasts
breaking → -clast → osteoclasts
cell → -cyte
loose connective tissue
loose (areolar): protein fibers that form a lacey network with fluid filled spaces
contains: collagen, reticular and elastic fibers
cells: fibroblasts, microphages and mast cells
located: throughout body
function: packing and nourishment
dense connective tissue
thick bundles of collagen fibrils densely packed with little to no extracellular matrix
fibers are oriented in the same direction
located: tendons and ligaments
function: withstands forces with great strength
adipose tissue
cells are full of lipids, little extracellar matrix
location: subcutaneous areas, mesenteries, renal pelvis
function: packing material, thermal insulation, energy storage, protection
blood
vascular tissue
blood cells surrounded by non living fluid matrix (plasma)
fibers - only visible during clotting
atypical connective tissue
8 cell types of connective tissue proper
macrophages
large amoeba like cells in immune system
eat pathogens and damaged cells
fixed stay in tissue
free migrate
adipose
fat
mesenchymal cells
stem cells that respond to injury or infection
differentiate into fibroblasts, macrophages and more
melanocytes
coloration
mast cells
stimulate inflammation after injury or infection
basophils are mast cells carried by blood
lymphocytes
specialized immune cells in lymphatic system
microphages
phagocytic blood cells
respond to signals from macrophages and mast cells
loose connective tissues
areolar
least specialized
open framework
elastic fibers
holds blood vessels and capillary beds
adipose
white fat
most common
stores fat
insulator
brown fat
more vascularized
breaks down fat
produces heat
adipocytes do not divide but mesenchymal cells divide and differentiate
reticular
support
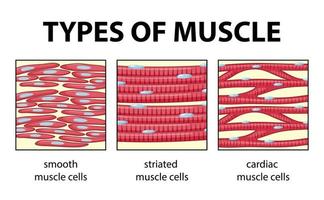
muscle tissue
contracts and shortens, responsible for movement
ex striated skeletal, striated cardiac, non-striated smooth
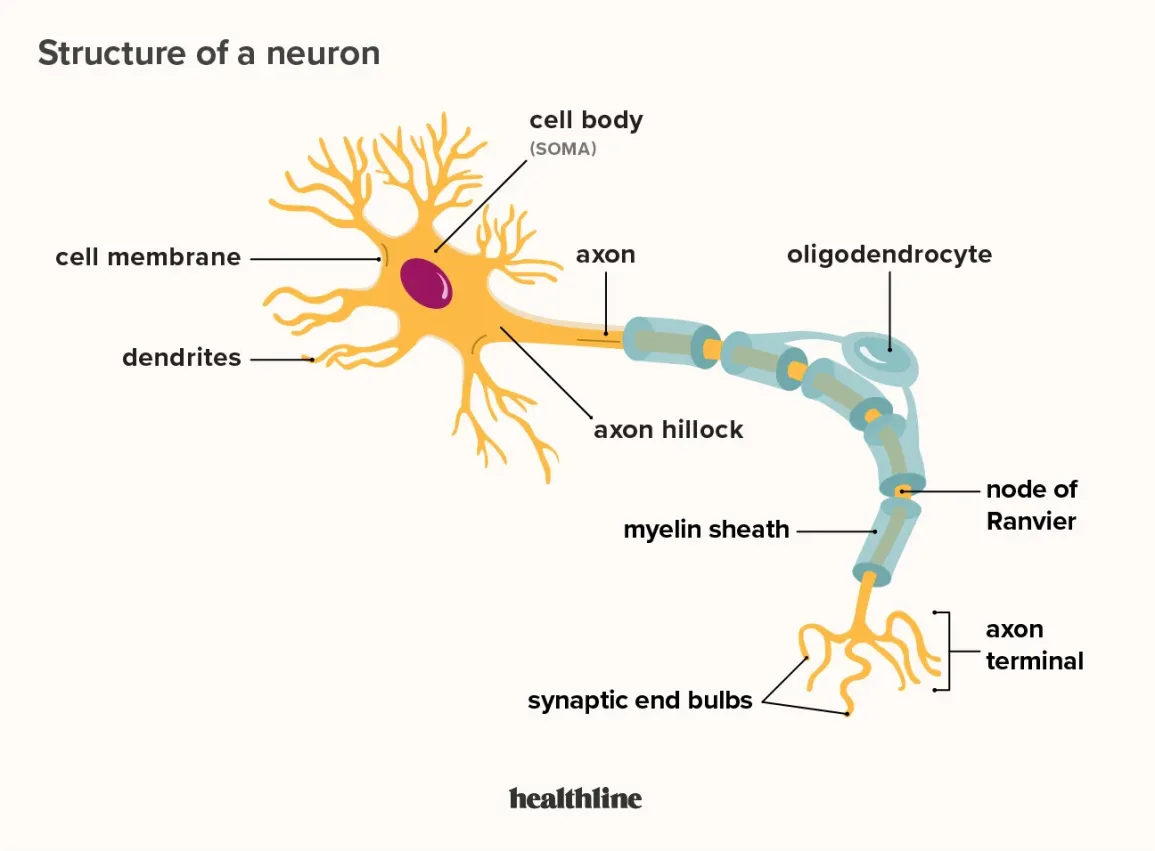
nervous tissue
neural tissue
can see neurons
ability to conduct electrical impulses
2 types of cells
neurons - communication among neurons in brain
conscious and unconscious though processes
info relayed by frequency and pattern of impulses
neuroglia or glia cells
support/repair/supply nutrients
neuron
tissue repair
tissue injuries and repair
tissues respond to injuries to maintain homeostasis
cells restore homeostasis with 2 processes
inflammation
caused by body releasing histamine
tissue’s first response to injury
regeneration
heparin is a blood thinner