Chapter 4 (Campbell's Biology in Focus)
Internal Membranes and Functions
==Cytosol== is the semifluid, jellylike substance inside cells
In eukaryotic cells, most of the DNA is found in the ==nucleus==
In prokaryotic cells, DNA is focused in a region called the ==nucleoid== which is not membrane enclosed
The interior of either type of these cells is called cytoplasm
At the boundary of every cell the ==plasma membrane== functions as a selective border that allows oxygen, nutrients, and wastes to service the entire cell
- the plasma membrane consists of a double layer of phospholipids
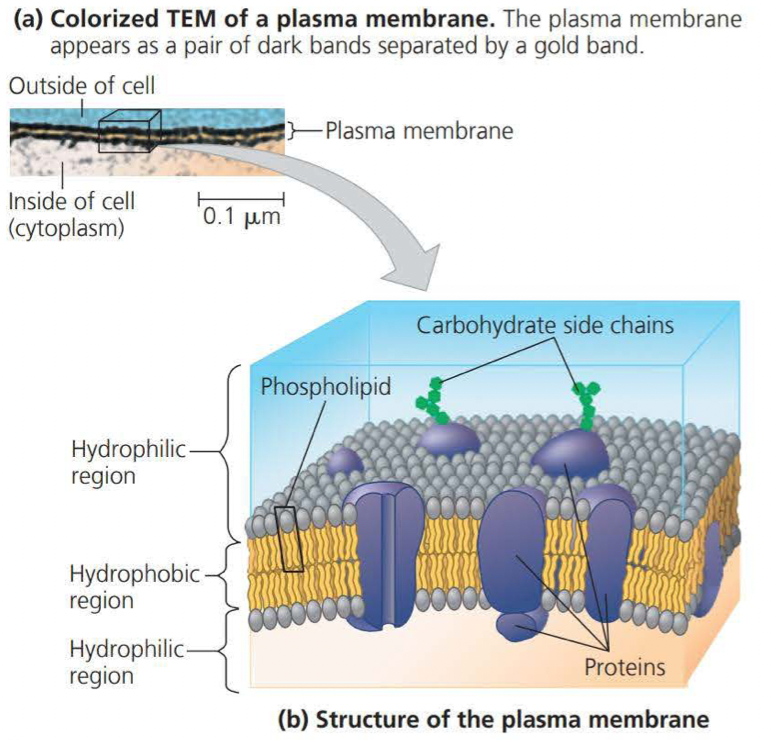
- the plasma membrane consists of a double layer of phospholipids
==Microvilli== increase the surface area of an object due to the crevices
The nucleus contains most of the genes in a eukaryotic cell
The ==nuclear envelope== encloses the nucleus separating its contents from the cytoplasm
- the two membranes are each a lipid bilayer associated with proteins
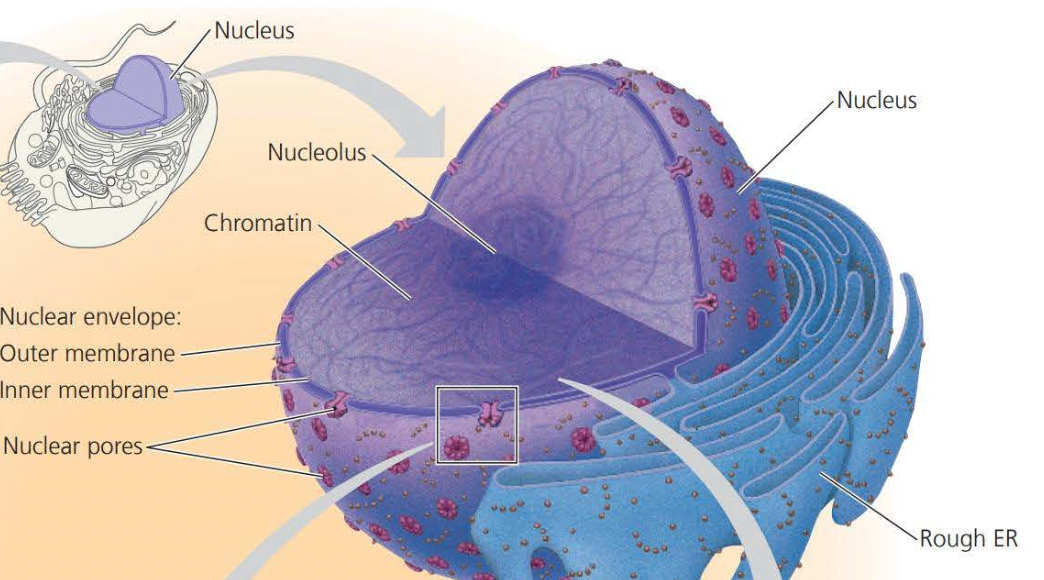
The nuclear side of the envelope is lined by the ==nuclear lamina==
DNA is organized into discrete components called ==genes==
The complex of DNA and proteins making up chromosomes is called ==chromatin==
A prominent structure in the nondividing nucleus is the ==nucleolus== (plural of nucleoli) which is a mass of densely stained granules and fibers adjoining part of the chromatin
==Ribosomes== are complexes made of ribosomal (RNA) proteins
- They carry out protein synthesis
Endomembrane System
Many of the different membrane-bounded organelles of the eukaryotic cell are part of the ==endomembrane system,==
- the endomembrane system includes the
- nuclear envelope
- endoplasmic reticulum
- Golgi apparatus
- lysosomes
- various kinds of vesicles and vacuoles
- plasma membrane.
The ==endoplasmic reticulum== is a large network of membranes that accounts for more than half of the plasmic membranes in eukaryotic cells
- ==Smooth ER== lacks ribosomes
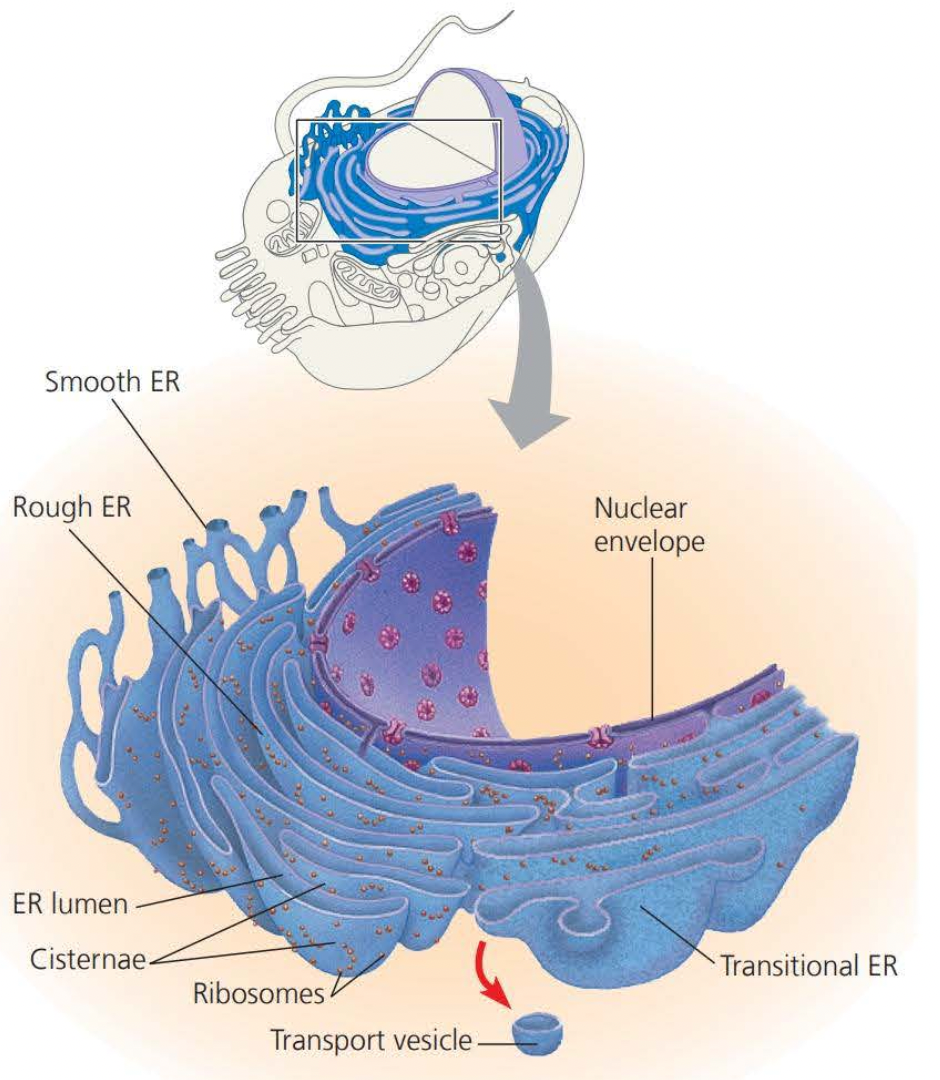
- ==Rough ER== is studded with ribosomes on the outer surface of the membrane
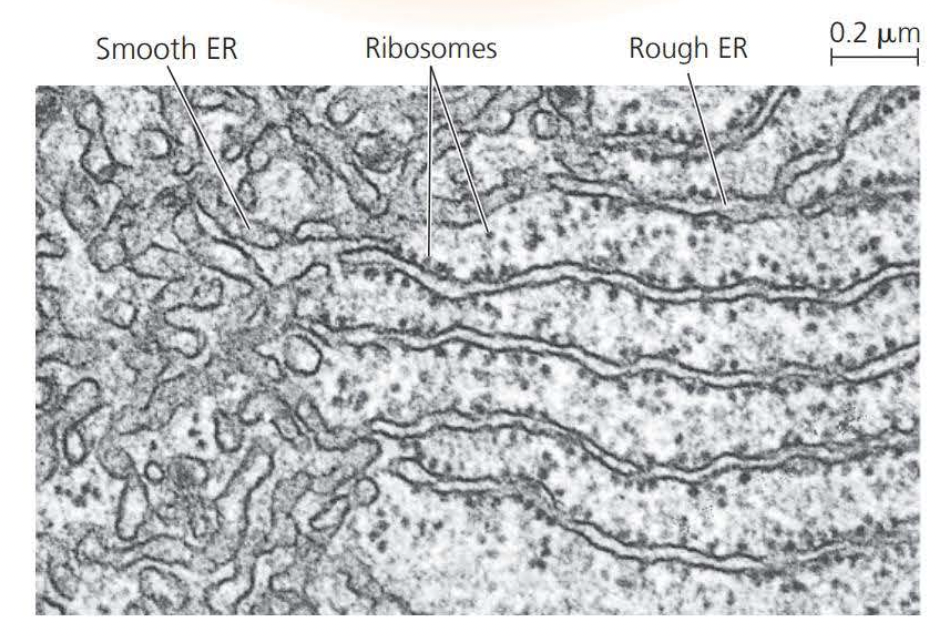
- ==Smooth ER== lacks ribosomes
Functions of Rough ER
- Most secretory proteins are ==glycoproteins==
- ==Transport Vesicles== are vesicles in transit from one part of the cell to another
The Golgi Apparatus: the shipping and receiving center
After leaving the endoplasmic reticulum in transport vesicles, they head to the Golgi Apparatus
- The ==Golgi Apparatus== is like a warehouse for receiving, sorting, shipping, and some manufacturing.
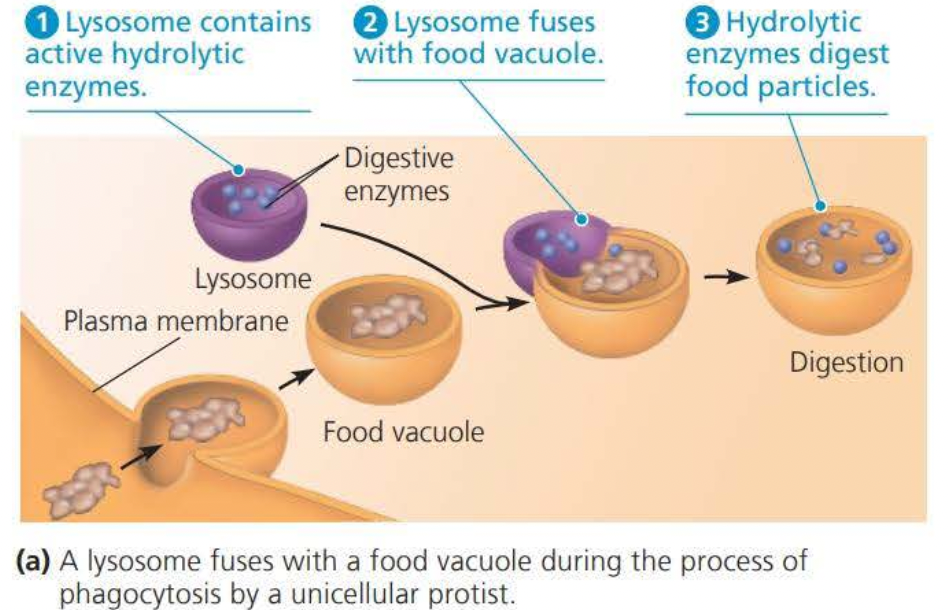
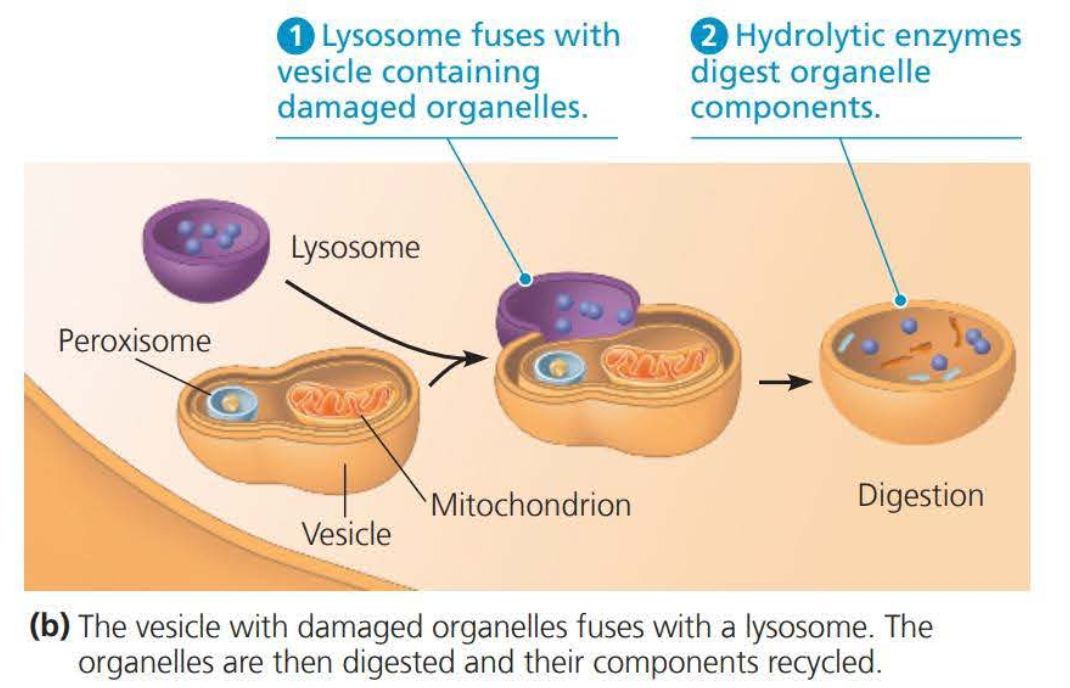
A ==lysosome== is a membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes that many eukaryotic cells use to digest macromolecules
==Phagocytosis== is the process of engulfing smaller organisms or food particles
- The food vacuole formed through this then fuses with a lysosome
==Vacuoles== are large vesicles formed by the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi Apparatus
==Food Vacuoles== are formed by phagocytosis
Many unicellular protists living in freshwater have ==contractile vacuoles== that pump excess water out of the cell, thereby maintaining a suitable concentration of ions and molecules inside the cell.
Mature plants generally contain a ==central vacuole==, which develops by the coalescence of smaller vacuoles
The ==endosymbiont theory== states that an early ancestor of eukaryotic cells engulfed an oxygen-using non-photosynthetic prokaryotic cell. Eventually, the engulfed cell formed a relationship with the host cell in which it was enclosed, becoming an endosymbiont.
The inner folds of a phospholipid bilayer are called a ==cristae==
The ==cytoskeleton== is a network of fibers extending throughout the cytoplasm
Eukarya have ==microtubules==, hollow rods constructed from a globular protein called tubulin
In animal cells, microtubules grow out of a ==centrosome==, a region that is often located near the nucleus and is a “microtubule organizing center”
Within the centrosome is a pair of ==centrioles==, each composed of nine sets of triplet microtubules arranged in a ring
- In eukaryotes, a special arrangement of microtubules results in the beating of the flagella and cilia
The microtubule assembly of a cilium or flagellum is anchored in the cell by the basal body
Bending involves large motor proteins called dynein
==Microfilaments== are thin, solid rods. They are also called actin filaments because they are built from molecules of actin.
Thousand of actin filaments and thicker filaments of a motor protein called ==myosin== interact to cause a contraction in a muscle cell
==Intermediate filaments== are named for their diameter, which is larger than the diameter of microfilaments but smaller than that of microtubules