
Biological Molecules
Protein:
Protein is made of long chains of 20 kinds of amino acids. It functions as most of the structure of living things and enzymes.

There are 20 different amino acids, which join together to form proteins. They can be arranged in any order, thus resulting in many different protein combinations (including haemoglobin, enzymes and ligaments).

Different proteins have different sequences which means that they have different shapes - small changes in amino acid order can completely alter the protein structure. Polypeptide chains can fold in unique ways which is what results in the different types of protein (shape of a protein tells us its function)
Nucleic Acid:
Nucleic Acid is long and short chains of nucleic acid bases, forming DNA, RNA, ATP and GTP. It functions as information storage (only in RNA and DNA), structure, enzymes and energy transfer.
Lipids:
Lipids are made of phosphate, or other charged heads, with long hydrocarbon tails. They function as energy storage, insulation, cushioning, and membranes.
Most lipids are actually made of triglycerides, with their basic unit being one glycerol molecule chemically bonded to three fatty acid chains that vary in size and structure. Lipids are divided into fats (solids at RTP) and oils (liquids at RTP).

Carbohydrates:
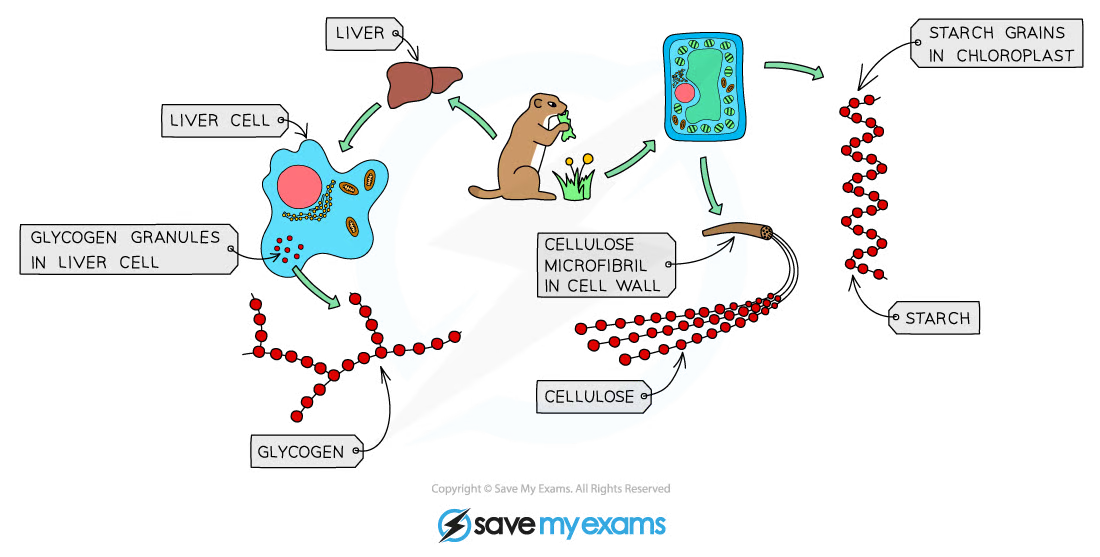
Carbohydrates are made of long and short chains of sugar molecules such as glucose and fructose. They function as energy sources, storage and structure.
Carbohydrates contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. A monosaccharide is a simple sugar (glucose, fructose). Glucose molecules have a lot of energy which can be broken down during respiration by breaking the bonds between carbon atoms. Disaccharides are two monosaccharides joined together. Examples include maltose (two glucose molecules) and sucrose (one glucose and one fructose). Polysaccharides are many monosaccharides joined together. Examples include starch, glycogen and cellulose (all three are many glucose molecules joined). Polysaccharides are insoluble, so they are used as storage molecules.
Small Molecules:
Short Molecules are various molecules, such as hormones, vitamins, neurotransmitters and porphyrins. Their function is to send signals in most cases.
Biological Molecules
Protein:
Protein is made of long chains of 20 kinds of amino acids. It functions as most of the structure of living things and enzymes.

There are 20 different amino acids, which join together to form proteins. They can be arranged in any order, thus resulting in many different protein combinations (including haemoglobin, enzymes and ligaments).

Different proteins have different sequences which means that they have different shapes - small changes in amino acid order can completely alter the protein structure. Polypeptide chains can fold in unique ways which is what results in the different types of protein (shape of a protein tells us its function)
Nucleic Acid:
Nucleic Acid is long and short chains of nucleic acid bases, forming DNA, RNA, ATP and GTP. It functions as information storage (only in RNA and DNA), structure, enzymes and energy transfer.
Lipids:
Lipids are made of phosphate, or other charged heads, with long hydrocarbon tails. They function as energy storage, insulation, cushioning, and membranes.
Most lipids are actually made of triglycerides, with their basic unit being one glycerol molecule chemically bonded to three fatty acid chains that vary in size and structure. Lipids are divided into fats (solids at RTP) and oils (liquids at RTP).

Carbohydrates:
Carbohydrates are made of long and short chains of sugar molecules such as glucose and fructose. They function as energy sources, storage and structure.
Carbohydrates contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. A monosaccharide is a simple sugar (glucose, fructose). Glucose molecules have a lot of energy which can be broken down during respiration by breaking the bonds between carbon atoms. Disaccharides are two monosaccharides joined together. Examples include maltose (two glucose molecules) and sucrose (one glucose and one fructose). Polysaccharides are many monosaccharides joined together. Examples include starch, glycogen and cellulose (all three are many glucose molecules joined). Polysaccharides are insoluble, so they are used as storage molecules.

Small Molecules:
Short Molecules are various molecules, such as hormones, vitamins, neurotransmitters and porphyrins. Their function is to send signals in most cases.
 Knowt
Knowt