Enzymes, Exothermic & endothermic reactions (bio review #3)
Vocabulary:
Activation Energy: Minimum amount of energy required for reactants to form products in a chemical reaction.
Catalyst: Substance that speeds up reactions
Enzyme: Biological catalyst for reactions
Substrate: Reactant in enzyme catalyst reaction
Active Site: Enzyme region binding substrate.
Enzymes:
MOST enzymes are proteins; they’re biological catalysts.
Catalysts: Enzymes that can be reused in the reaction
Speeds rate of chemical reactions.
TIP: Enzymes end in “-ase”
Sugars end in “-ose”
E.g. Lactase enzymes, lactose sugar, oil saccharide
Lactase is a disaccharide- two sugar molecules bond together
Lactose can be quickly broken down and digested
Lactase can break lactose
Fights infections
Regulates body processes
Looks like Pacman
(Protein)
Active site: Where items combine
Substrate: Surface on which an organism lives; includes abiotic and biotic material.
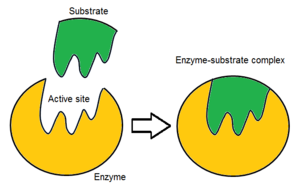
Induced Fit Theory: The binding of a substrate/ another molecule to an enzyme causes a change in the shape of the active site to inhibit its activity.
Cofactors & Coenzymes: Helps enzyme do its job of building up or breaking down substrates into products.
Exothermic & Endothermic Reactions, Energy Diagrams
Vocabulary:
Activation Energy: Minimum amount of energy required for reactants to form products in a chemical reaction.
Exothermic: Releases heat during reaction.
Endothermic: Absorbs heat during reaction.
TIP: exo= external; endo= internal
Exergonic: Releases energy, spontaneous reaction.
Endergonic: Absorbs energy, non-spontaneous reaction.
Exothermic Reactions: Releases energy to surroundings (e.g. bonfire)
Endothermic Reactions: Absorbs energy from its surroundings (e.g. snow melting from heat)
Energy Diagram
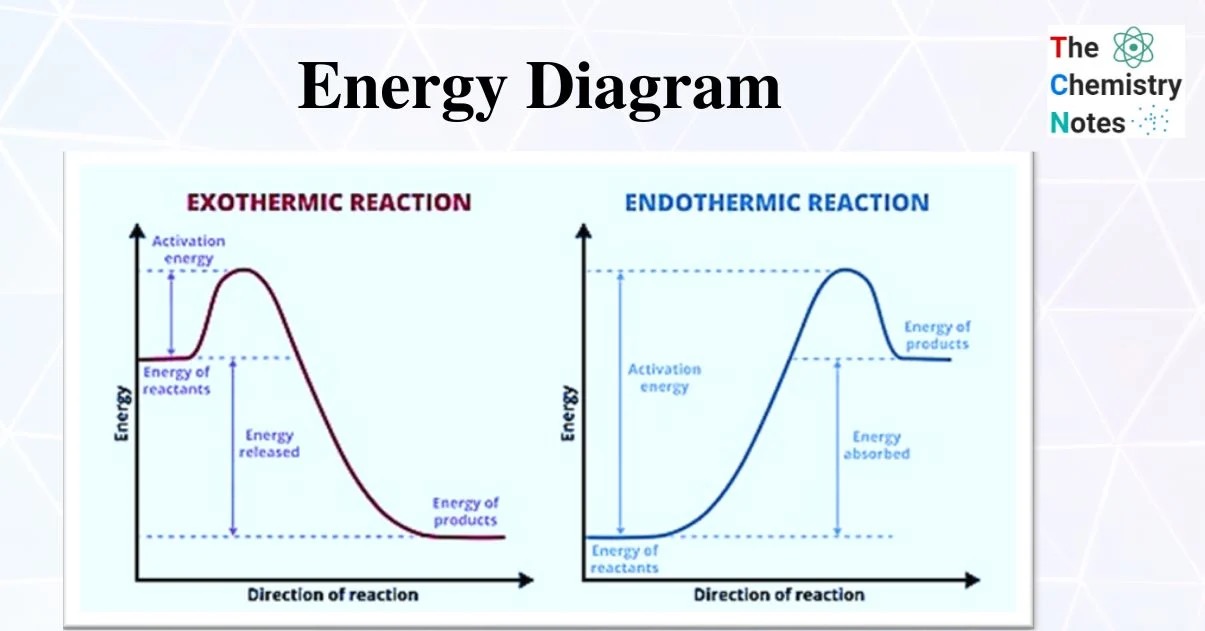
In exothermic reactions energy is released to surroundings, meaning that the energy of the reactants is higher and the energy of the products.
In endothermic reactions, energy is added to the reaction. The energy of the products is higher than the energy of the reactants.