AP Psych: Nurture vs Nature
Class Notes 9/20/24
Evolutionary Psychology: the study of evolution of behavior and the mind, using the principles of natural selection
wants to know why humans are alike because of our ancestral path
talks about how our brain became formed due to our ancestral path
Studies the evolution of behavior and mind using principles of natural selection
focuses on sex and survival- sending your genes into the future
Mating Preferences
natural selection has caused males to send their genes into the future by mating with multiple females since males have lower costs involved.
However, females select one mature and caring male because of the higher costs involved with pregnancy and nursing.
Men look for:
physical attractiveness/youthful appearance: associated with fertility
Females look for:
socioeconomic status: needed a male who could provide for offspring
according to evolutionary biology, animals inherit those characteristics which insure that they will transmit as many of their genes to the next generation as possible. It is to both men's and women's advantage to produce as many surviving children as possible. But men and women differ in one critical respect - in order to produce a child, men need only to invest a trivial amount of energy; a single man can conceivably father an almost unlimited number of children. Conversely, a woman can give birth to and raise only a limited number of children; it is to her advantage to insure those few children she does conceive survive.”
Class Notes 9/26/24
Heredibility
the proportion of variation among individuals that we can attribute to genes
Heritability refers to the extent to which the differences among people are attributable to genes.
By age 12, peers can have a stronger influence on an individual’s behavior than their parents.
ie. children of immigrants often adapt the accent of those surrounding them rather than their parents’ accent
R for rat, r for Rosenzweig
Experience and Brain Development
Early postnatal experiences affect brain development. Rosenzweig shows that rats raised in an enriched environment developed thicker cortices than those in impoverished environments.
Dendrites start sprouting up and neural networks begin to form
Experience and Faculties
Early experiences during development in humans show remarkable improvements in music, language, and the arts
Brain Development and Adulthood
Brain development does not stop when we reach adulthood. Throughout our life, brain tissue continues to grow and change.
Cultural Influences
Humans have the ability to evolve culture
Culture is composed of behaviors, ideas, attitudes, values and traditions shared by a group.
Varitation Across Culture
Cultures differ. Each culture develops norms- rules for accepted and expected behavior.
ie. Men holding hands in Saudi Arabia is the norm (closer personal space), but not in American culture.
Environmental influences
personal space: the buffer zone we like to maintain around our bodies
memes: self-replicating ideas, fashions, and innovations passed from person to person
Gender Roles
Gender Identity: means how a person views themself in terms of gender.
Gender-typing: the acquisition of a traditional masculine or feminine role
The Nature and Nurture of Gender
two theories of gender typing
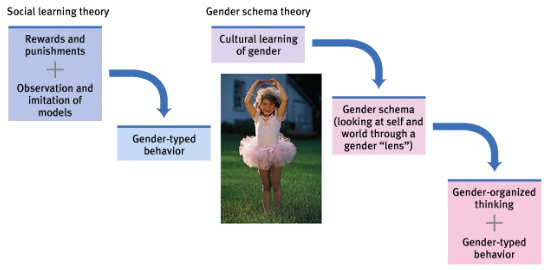
schema: the lens in which an individual looks through and perceives the world
Gender Schema Theory
Social Learning Theory: theory that we learn social behavior by observing and imitating and by being rewarded or punished
Gender Schema Theory: suggests that we learn a cultural “recipe” of how to be a male or a female, which influences our gender- based perceptions and behaviors.
Chapter 4
Behavior Genetics: Predicting Individual Differences
behavior geneticists study our differences and weigh the effects and the interplay of heredity and environment
the study of the relative power and limits of genetic and environmental influences on behavior
Genes: Our Codes for Life
Humans in total have 46 chromosomes- 23 from the mother and 23 from the father
chromosomes are composed of a coiled chain of DNA
chromosomes: threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
DNA: a complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes
genes- the biochemical units of heredity that make up the chromosomes; segment of DNA capable of synthesizing proteins
The 20k to 25k genes can either be active/expressed or inactive
environmental events turn on genes
environment: every nongenetic influence, from prenatal nutrition to people and things around us
when turned on, genes provide the code for creating protein molecules, our body’s building blocks
some small differences between species, even as little as a 1% difference in genomes, affect the behaviors and traits of the species significantly
i.e chimps and bonobos. chimps are aggressive and male-dominated. bonobos are peaceful and female-led.
most traits have complex genetic roots
various traits may be influenced by different genes interacting with a specific environment.
environmental influences interact with our genetic predispositions