Liver
Liver Functions
- detoxification
- Metabolism
- Immune system
- protein synthesis
- blood clotting factor
- production of bile
- Gi anti-microbial
- Blood sugar balance
- storage of glycogen
- Storage of Micronutrients
- production cholesterol
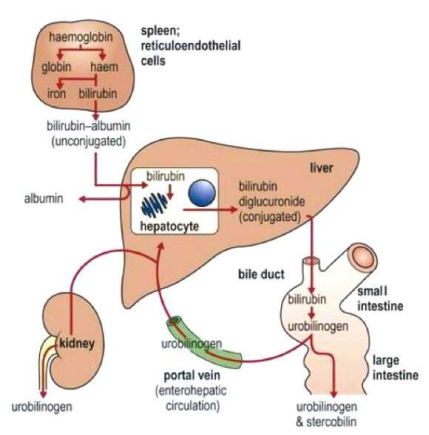
- conjugation: hepatocytes combine bilirubin( produces by red blood cells) with glucuronic acid to make it water soluble
- excretes in the intestine → poop + urine and gives it the color
Symptoms of Chronic Liver Failure
- Encephalopathy → toxification of blood→ body
- build filled belly → ascites
- increased pressure in the portal vein cause fluid to leak from blood vessels into the peritoneal cavity and cause edema → fluid-filled belly
- treatment:
- build a bypass
- paracentesis (removal of the fluid from the abdomen with a needle)
- liver transplant
- increased bleeding
- low platelets and clotting factor
- eyes turn yellow → jaundice → icterus
- hemoglobin breakdown → bilirubin
- first in the eyes because its the whitest and very fatty
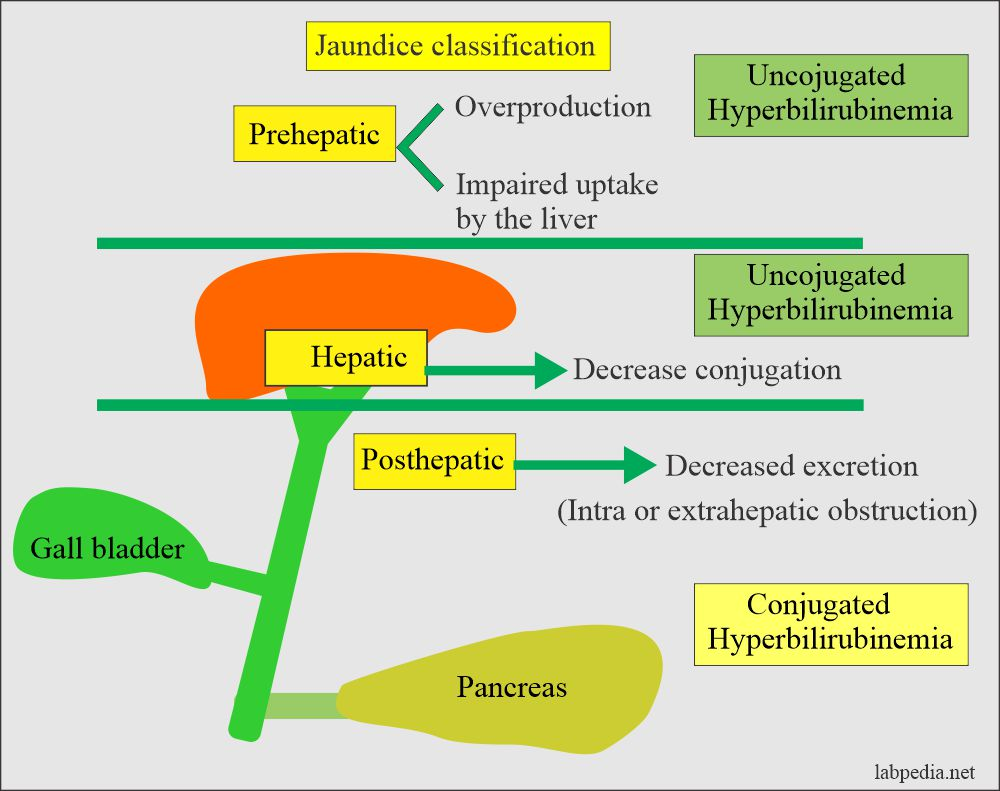
- classification of different types of jaundice
- portal hypertension
- increased blood flow due to resistance (fibrosis)
- variceal bleeding
- due to portal hypertension blood vessels in the esophagus and stomach become enlarged and weakened ( looking like worms) → they can explode
- shunting
- red hand palms
- spider (rashes)
- edema
- bilateral enlargement of breast tissue
- bleeding
- low amounts of platelets because they are stored in liver
- pressure on the venus system
- liver makes clotting factor → less clotting factors in bloody
- too many blood cells
- stones in are in duct
* turn yellow
* the stool is less yellow
- Gynecomastia: bilateral enlargement if the male breast tissue
- in liver failure
- the liver fails to metabolize estrogen, this hormonal imbalance causes the breast development
- Jaundice
- Three types:
- Why is jaundice more common in babies?
- they have higher red blood cells than adults
- the life span of erythrocytes is shorter( different hemoglobin)
- the liver is not as good at conjugation yet
- bowel movements are slower in babies than in adults
- Treatment:
- Phototherapy: UV lights make bilirubin water soluble
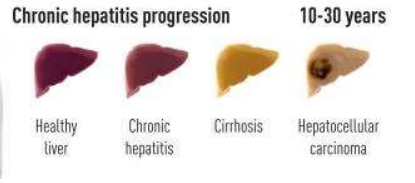
@@Hepatitis@@
- most common cause of hepatitis and progression?
- Viral infection → becoming chronic
- hepatitis a+b+c+d +e
Hepatitis Virus
- symptoms for liver infection?
- → same as liver failure symptoms
Characteristics:
| Hepatitis Virus | %%Type of Virus%% | %%Genetic Material%% | %%Transmission%% | %%Treatment%% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| {{Hepatitis A{{ | HAV | Single-stranded RNA | playground Fecal-oral route, contaminated food or water | No specific treatment, usually resolves on its own“least lethal” |
| {{Hepatitis B{{ | HBV | Double-stranded DNA | Blood, semen, vaginal fluids, and other bodily fluids | Antiviral medications, immune modulators, and/or liver transplant |
| {{Hepatitis C{{ | HCV | Single-stranded RNA | Blood-to-blood contact | Antiviral medications, immune modulators, and/or liver transplant |
| {{Hepatitis D{{ | HDV | Single-stranded RNA | Blood-to-blood contact, can only infect individuals who are already infected with HBV | Antiviral medications and/or liver transplant |
| {{Hepatitis E{{ | HEV | Single-stranded RNA | Playground Fecal-oral route, contaminated food or water | No specific treatment, usually resolves on its own |
==Target Areas for Antiviral Medication==
- Inhibit the virus from invading the host by not letting the virus produce proteins that help them evade the immune system
- prevent viral assembly of proteins by inhibiting viral enzymes involved in the process of replication
- genome replication
- polyprotein processing
- attachment to the cells
- inhibition in the assembly process of virus
- inhibition of molecular structure