the history of life (ch. 25)
age of earth- 4.6 billion years
oldest fossils- 3.5 billion years
stromatolite- a map of prokaryotes, cyanobacteria existing on a thin surface. as the map grows, organic material gets trapped and ultimately a pancake layer is formed. consided to be the oldest life forms. made up of single cells
what do you need to form a cell?
a bag of complex organic chemistry
enclosed in plasma membrane or cell membrane
abiotic synthesis of organic molecules
amino aids, mitrogenous bases, RNA nucleotides
miller- urey, NASA stardust, volcanoes
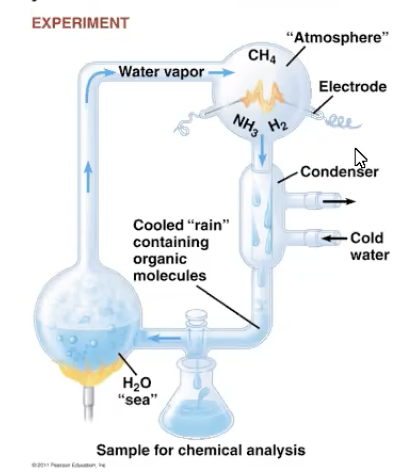
miller-urey experiment: a system that replicted conditions of earth
water source connected to a tube with chemical compounds
condenser where water turned into vapor
nitrogenous bases were found and # of amino acids were greater than what was recorded
nasa star dust mission
a satelite flew thru the wild-2 comet
sample taken were nitrogenous bases and amino acids
small organic molcules to macromolecules
rna nucleotides, AA dripped in sand and clay yield polymers of these molecules
evidence of abiotic synthesis
packaging of molecules into membranes
concentration of organic molecules
a way to keep the chemistry localizd
keeping lipids in water forms vesicles
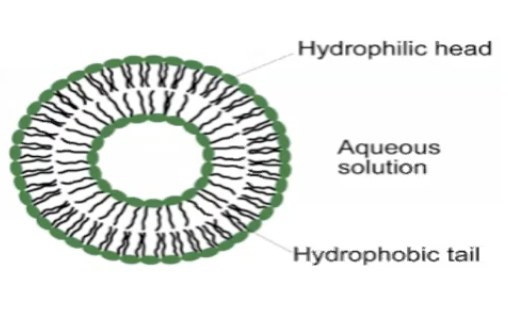
vesicle formation can replicate themselves and continue to grow
can exchange things through the membrane
may have formed the first membranes, localized it and allowed complex organisms to grow
self replicating molecules
ribozyme - small bit of rna that can self replicate or small pieces
can take genetic materials and make daughter cells
both genetic material and a catalyst
some are self replicating
rna was the first genetic material as it can store and works as a catalyst
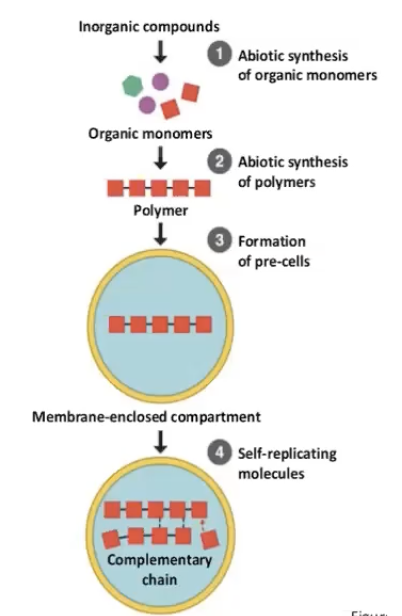
evidence of the first cells- plausible scenario
abiotic synthesis of small organic molecules (AA, N bases)
organic molecules join to make larger molecules macromolecules
packaging of molecules into membranous droplets (protocells)
self replication of molecules allowing for inheritance
replication has potential for reproduction
fossils and the fossil record
preserved remains or traces of a prehistoric organism
tell a story of the history of life on earth
can give record of how life was distributed
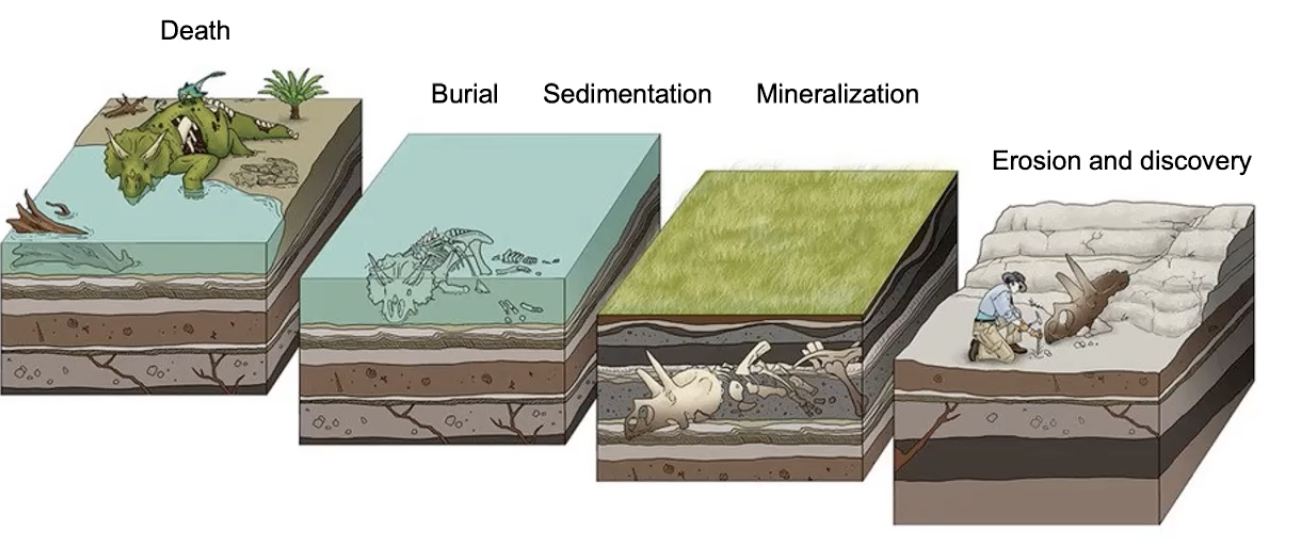
fossil formation
often occurs in sedimentary rock
immediate burial is needed
allows for time to be mineralized
burial slows down rapid decay
bias in the fossil record?
organisms with bones or shells are more likely to leave a record than those that dont
do have fossils of soft bodied organisms
fossils that were more abundant are more likely to be fossilized
animals and plants are more likely to be fossilized than terrestrial things
relative dating- based on position
principles in geology
original horizontality- rocks were formed horiontality
principle of superposition- things that are lower in the sequence are older than the ones above
absolute dating
radiometric methods
half life is 2 million years. what is the rocks are is 1/8 of parent material is still present
stratego griffey of earth
rocks in section c are good for radiometric dating

the geologic record
cenozoic= recent life
mesozoic= recent life
paleozoic= ancient life
zoic= sanimals present
proterozoic and below = precambrian
before the cambrian period, early earth, most of earths history
precambrian
the first single celed organisms
3.5+ BYA
procaryotes
photosynthesis and the oxygen revolution
O2 produced by oxygenic photosynthesis produces banded iron formations and continental red beds
the first eukaryotes
1.8+ BYA
eukaryotic features?
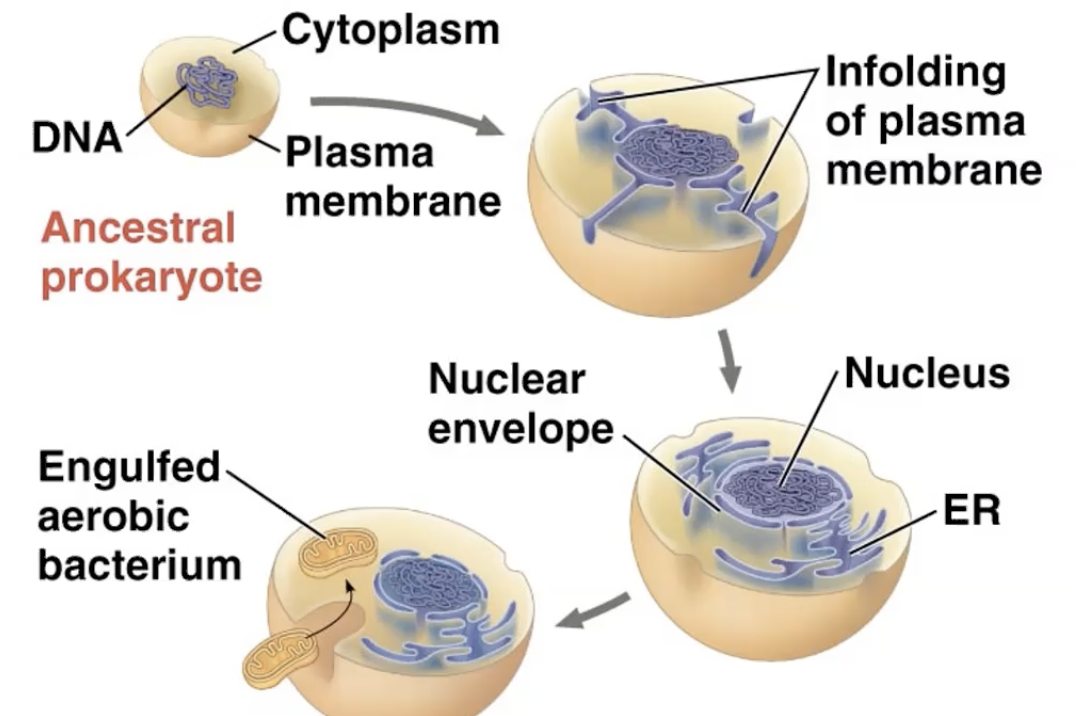
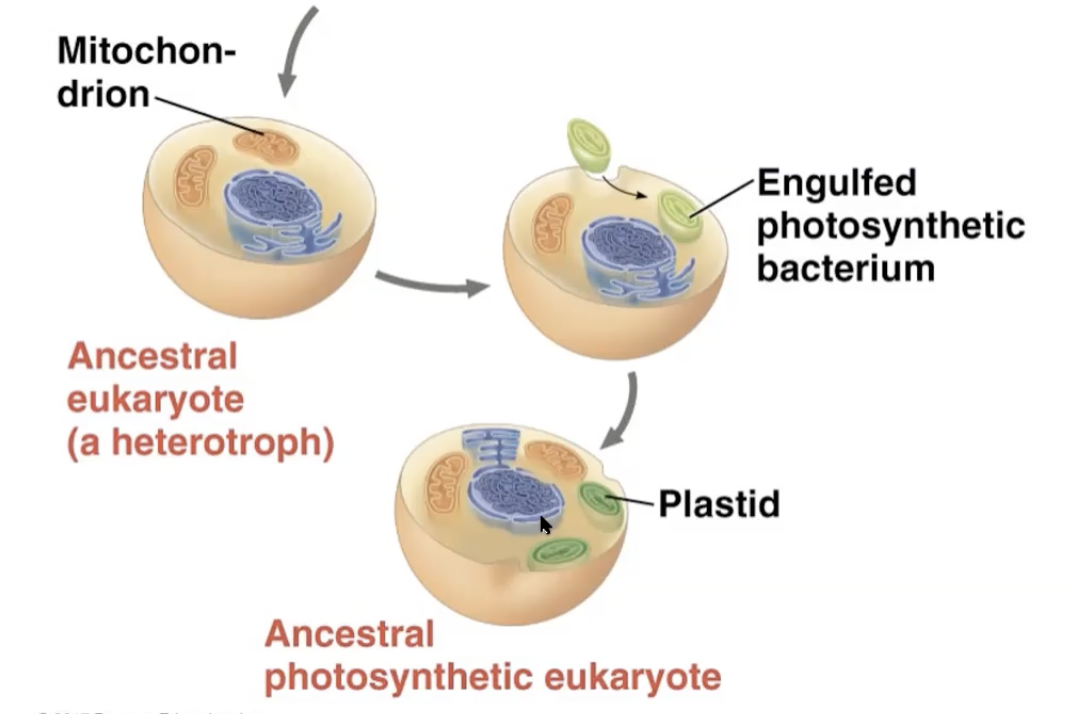
endosymbiosis- model that described the evidence surrounding how prokaryote to eukaryotes
the origin of multicellularity
q.2+BYA
evolved independently in several lineages likely by specialization of cells colonial protists
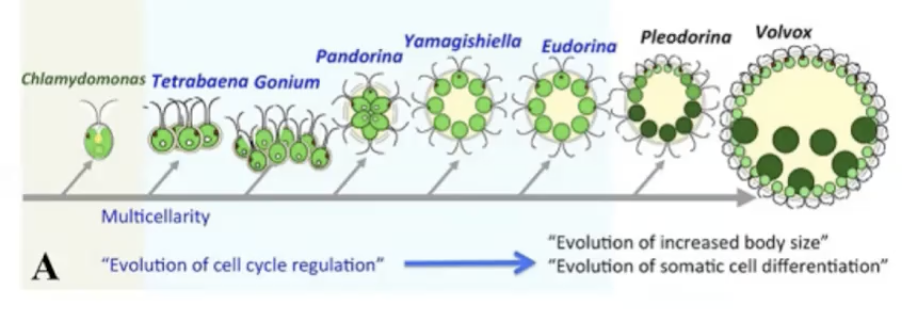
most of life is unicellular
ediacaran fauna
end of precambrian- 600 mya
soft bodied benthic forms
attached to a substrate or the bottom of the ocean
the cambrian explosion
the sudden appearance of fossils resembling modern animal phyla in the cambrian period
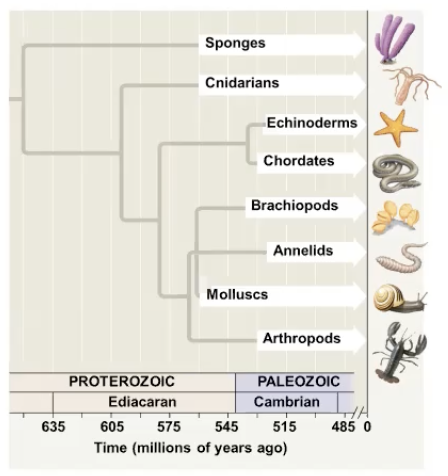
an explosion of diversity
the colonization of land
fungi, plants, and animals began to colonize land about 500 mya
plants and fungi may have colonized land together
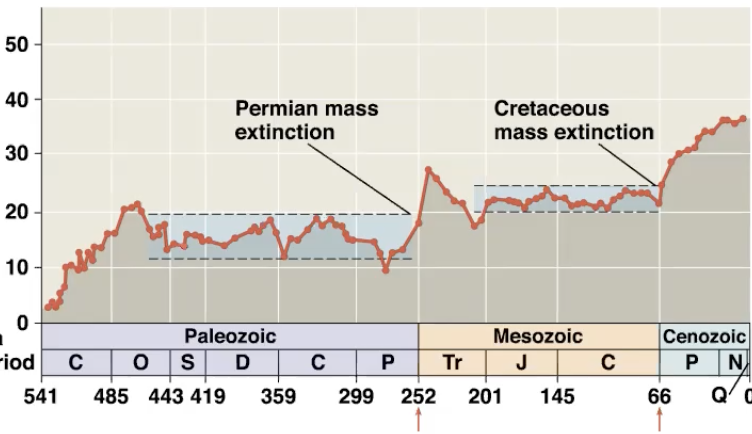
extinction events are part of earths history
groups of life go extinct when their death rates exceed their birth rates over a period of time
mass extinctions
result of disruptive global environmental changes
5/5 mass extinctions 50% or more of marine species became extinct
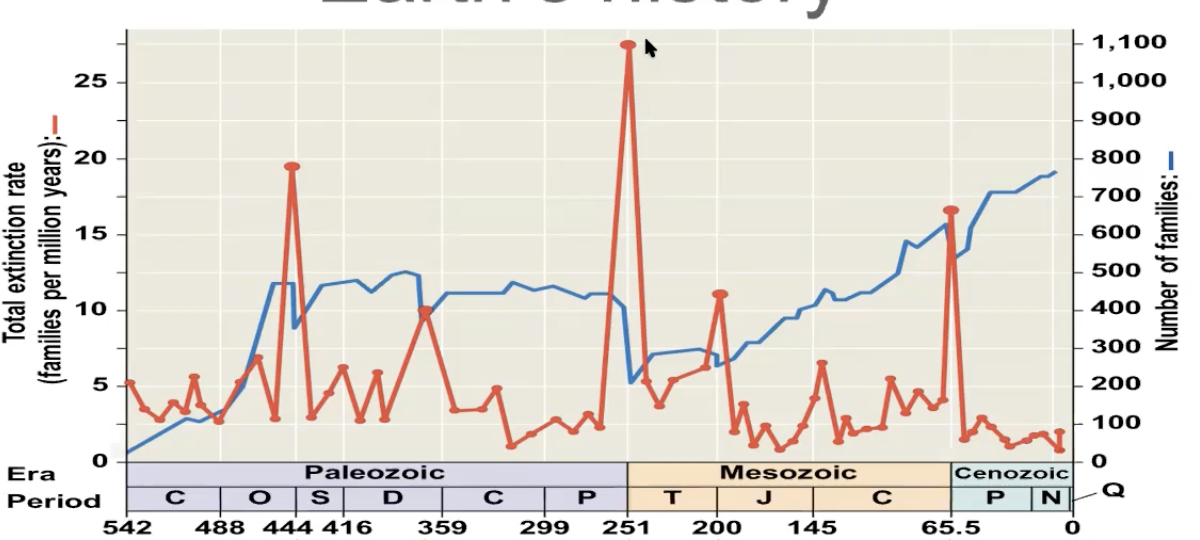
after a mass extinction event
adaptive radiation