Unit 3
Types of Bonds:
London dispersion forces: is seen in every intermolecular force between atoms; this is also directly correlated to molar mass and atomic radii
nonpolar atoms especially have these
Dipole-Dipole: polar molecules only
Hydrogen bonding: bonds between H and N, or O, is the strongest bond
Boiling point for a compound depends on strength of intermolecular forces
the stronger the forces, the more energy required for vaporization and the higher the boiling point
Ionic Solids (metal + nonmetal)
molecules to the left tend to lose electrons due to not having much valence electrons
molecules to the right tend to gain electrons to complete the valence shell
Ionic solids are comprised of a cation (positive atom that has lost an valence electron) and an anion (negative atom that has gained an electron). They are held together by electrostatic attractions. Together, it creates a lattice structure

The stronger the magnitude of the charge, the higher the melting point. when you have stronger constituent ions, the electrostatic attraction is stronger. (Ex. NaF has a higher melting point than NaCl).
not good conductors, but when dissolved in water becomes very conductive
Metallic Solids (metal + metal)
Metallic solids are composed of metal cations held together by a delocalized “sea” of valence electrons.
Qualities:
the mobile component of these electrons means they are good conductors
also tend to be malleable and ductile.
Molecular Solids (nonmetal + nonmetal)
Composed of discrete molecules held together by intermolecular forces. Theres enough dispersion forces to induce dipoles in neighboring molecules. This is a temporary dipole. this is able to keep them together as a solid.
Qualities:
soft, low to moderate melting points
poor conductor of electricity
sublime: solid to gas state
Covalent Network Solids
Can be either Two dimensional or Three dimensional
3 dimensional network solids (Diamond or silica) are hard and rigid
2 dimensional solids (such as graphite) are soft
Qualities:
poor conductor of electricity
high melting point
Common Covalent Network Solids to remember: BN, C(diamond), SiO2, ReB2, SiC, Si, Ge, AIN, Sn
Coulomb’s Law: the force of attraction between two ions is stronger when the charges on the ions are larger and the distance between the ions is smaller
Representing solids, liquids, and gases w/ particulate models
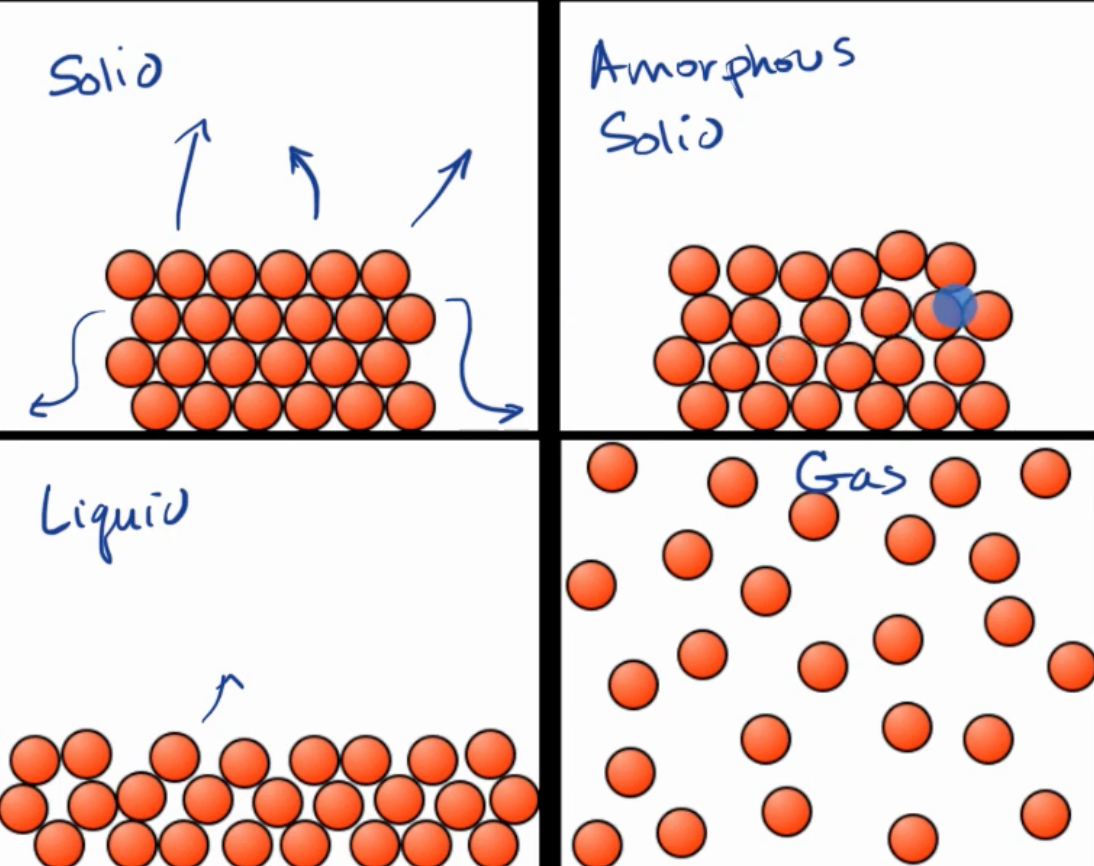
Amorphous solids include rubber and plastic. They are made of polymers.
Polymers are a molecule made of repeated subunits. They are string-like.
Crystalline and Amorphous polymers
amorphous solids are made of polymers, and it is able to vary depending on the treatment.
crystalline and amorphous structures are based on a scale based on crystallinity (percentages)
Ideal Gas Law (PV = nRT)
Also