Internet - Is a collection of networks which helps everything connect to each other
World Wide Web - Part of the internet that the user can access as a collection of web pages
URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is used to access a website and display web pages. The user must put in the website's address which is the URL and is a unique text based address that relates to a web page. The web address is made up of (PHDLR)
Protocol - A protocol is a set of rules that allows two devices to communicate
Host - WWW
Domain Name - Official name of a website
Location - Location of what you are searching for in a website
Resource - portion of source where you get the information eg.org
HTTP and HTTPS - Hypertext Transfer Protocol: Is a way for clients and servers to send and receive requests and deliver HTML web pages. The S stands for Security as the website is encrypted and secure and is used with sensitive data and information
A web server is a computer that hosts a website. A web server can host many websites and stores each page of the website and its related content. To retrieve information it is known as downloading. A computer that accesses information from a website server is referred to as a client.
Web servers do :
They can be stored as text, HTML, CSS or Javascript and is stent to a browser with various rules to render it correctly so then can be seen on the receiving/clients screens
Domain Name Server : Websites are written in HTML and hosted on a web server. To display pages from a particular website your browser needs to know the IP address for that website which it looks for in the Domain Name Server, (DNS)
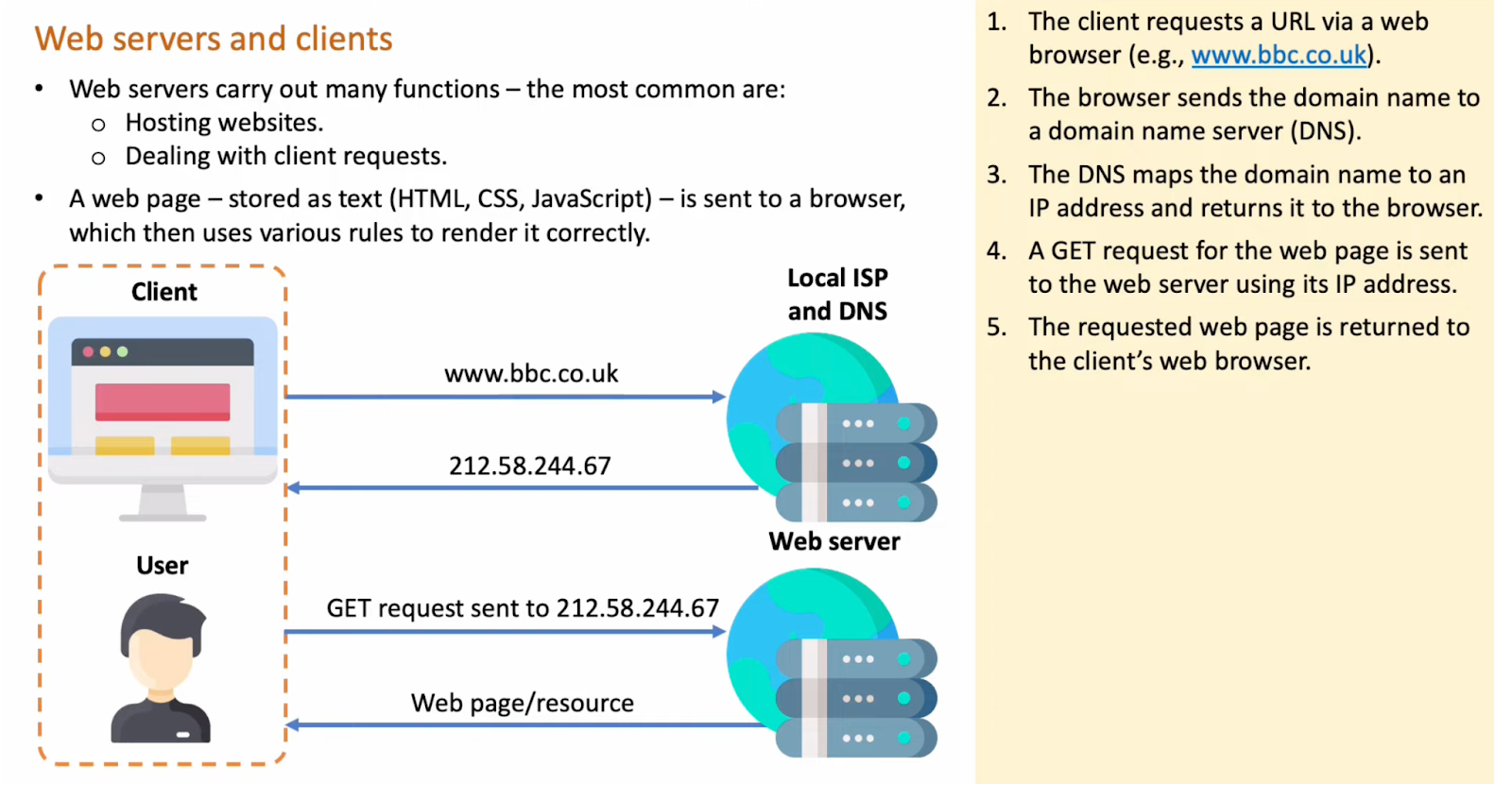
Webserver and Clients : The client requests a URL via a web browser
The browser sends the domain name to a domain name server (DNS)
The DNS maps the domain name to an IP address and returns it to the browser
A GET request for the web page is sent to the web server using its IP address
The requested web page is returned to the client’s web browser
 Note
Note Studied by 33 people
Studied by 33 people Note
Note Studied by 18 people
Studied by 18 people Note
Note Studied by 8 people
Studied by 8 people Note
Note Studied by 3 people
Studied by 3 people Note
Note Studied by 21 people
Studied by 21 people Note
Note Studied by 38 people
Studied by 38 people Knowt
Knowt