Database - Flashcards
Database
is a collection of data stored for a specific purpose.
collection of data organized so you can access, retrieve, and use it
Data VS. Information
Data is raw facts while Information is data that is organized and meaningful
What are the qualities of valuable information?
Useful, Accessible, Organized, Timely, Verifiable, Accurate
What is a hierarchy?
Database contains files, file contains records, record contains fields, field contains characters
What is a field?
Combination of one or more characters. Smallest unit of data users can access
Field size defines the maximum number of characters a field can contain
Field name uniquely identifies each field
Data type specifies kind of data field contains
Record - Group of related fields
Key field, or primary key, uniquely identifies each record
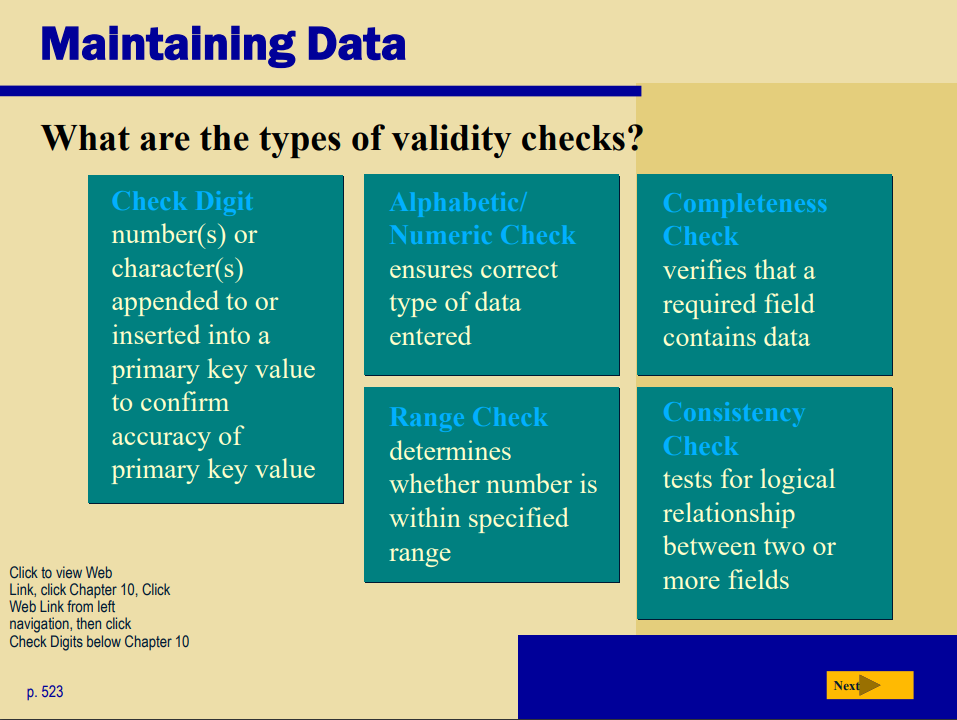
What is validation?
Process of comparing data with a set of rules to find out if data is correct. Reduce data entry errors and enhance data integrity before program writes data on disk
What is a data dictionary?
Contains data about each file in database and each field within those files
What is a query?
Request for specific data from a database. Query language consists of simple, English-like statements that allow users to specify data to display, print, or store
Database Management System
is a software system that allows you to define, construct and manipulate databases that are used for various purposes, such as for storing the customer and financial information of an organization.
prevents data redundancy
secures database by restricting users
Two Types of Databases
Flat File - are simple text files that store data in a single table.
Relational Databases - are complex databases that store information in multiple tables.
Database design refers to a system that stores and retrieves data systematically from the database.
Factors to be considered in the design of database:
Efficiency
Integrity
Privacy
Security
Flexibility
A data model determines the structure of data. It is considered as foundation of a database which determines the sequence of storing, organizing and manipulating the data in a database system.
Types of Data Model:
Hierarchical model, network model, relational model, object oriented model and object relational model
A hierarchical database model is a data model in which the data is organized into a tree-like structure.
The relational data model represents a database as a collection of relation values or relations where a relation resembles a two-dimensional table of values presented as rows and columns.
Relational Terminologies:
Domain - A domain is the set of defined atomic values for an attribute. It is a pool of values from which specific relations draw their actual values. • Attribute - Attribute is the name of a role played by a domain in the relation.
Tuple - Each row in a relation is a set of related data values and is called a tuple.
In network model, a record can have any number of parent records which can have multiple child records.