BIO Units 6.4-6.6
1. Cell Respiration, Gas Exchange, Ventilation
Term | What it is | Simple Example |
|---|---|---|
Ventilation | Breathing in and out (moving air in and out of lungs). | Like blowing up and deflating a balloon. |
Gas Exchange | Swapping gases between lungs and blood: oxygen goes into blood, carbon dioxide leaves. | Like trading goods across a border: O₂ goes in, CO₂ goes out. |
Cell Respiration | Cells using oxygen to make energy (ATP) from food. | Like burning fuel in a car to make it run. |
Easy way to remember:
Ventilation = moving air.
Gas exchange = swapping gases.
Cell respiration = making energy inside cells.
Diabetes
✨ Type 1 Diabetes
Happens suddenly, often in kids or young people.
Lifelong — they need to take insulin shots every day.
The immune system attacks the pancreas (which makes insulin).
Without insulin, sugar stays in the blood instead of going into cells.
Simple sentence to remember:
👉 "Type 1 = No insulin. Need insulin every day."
✨ Type 2 Diabetes
Happens slowly, usually in adults (but kids can get it too now).
At first, body still makes insulin, but cells don’t respond (called "insulin resistance").
Blood sugar levels rise over time.
Can be managed with diet, exercise, medicine, and sometimes insulin later.
Simple sentence to remember:
👉 "Type 2 = Insulin there, but body ignores it."
Feature | Type 1 Diabetes | Type 2 Diabetes |
|---|---|---|
Insulin? | Not made | Made but doesn't work well |
Cause? | Immune attack | Lifestyle and genetics |
Treatment? | Insulin injections | Diet, exercise, meds (sometimes insulin) |
Speed of Appearance? | Fast | Slow |
Age? | Young (usually) | Adult (usually) |
Type 1 = No insulin = Need insulin.
Type 2 = Bad insulin = Fix with healthy habits first.
2. If your client had type 2 diabetes, what would you recommend?
Main ideas:
Healthier diet: Low sugar, high fiber foods.
Exercise regularly: Helps cells use insulin better.
Weight loss if needed: Even small weight loss helps a lot.
Medicine: Sometimes needed to lower blood sugar.
Monitor blood sugar: Keep track to avoid problems.
Easy way to remember:
🏋♂️ Eat better + Move more + Maybe medicine + Watch sugars
Can you prevent diabetes?
Type | Can you prevent it? | Why? |
|---|---|---|
Type 1 Diabetes | ❌ No, you cannot prevent it. | It's caused by the immune system attacking the pancreas — not because of lifestyle. |
Type 2 Diabetes | ✅ Yes, you can often prevent it! | Healthy eating, exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight can lower the risk. |
Type 1 = Not preventable. (It just happens — like an accident.)
Type 2 = Often preventable. (Good habits can protect you.)
How to lower the risk of Type 2 Diabetes:
Eat healthy foods (less sugar and junk, more veggies and fiber 🍎🥦).
Stay active (move your body 🚶♀🏀).
Maintain a healthy weight.
Don’t smoke.
Manage stress.
3. How does neurotransmission work?
Step | What Happens | Simple Image |
|---|---|---|
1. The electrical signal travels down the neuron. | Like a message zipping through a wire. | |
2. Reaches the end of the neuron → triggers release of neurotransmitters. | Like sending a letter to the post office. | |
3. Neurotransmitters cross the gap (synapse) to the next neuron. | Like a boat crossing a river. | |
4. Neurotransmitters bind to receptors → A new electrical signal starts in the next neuron. | Like a key turning on a car. |
Easy way to remember:
⚡️ Electric message → ✉ Release chemicals → 🌉 Cross gap → 🔑 Start next message
Menstrual cycle
4. Progesterone and Estrogen: What they are and what they do
Hormone | What it does | Simple Memory Trick |
|---|---|---|
Estrogen | Grows and thickens the uterine lining (prepares for a baby). | "E" for Expanding lining |
Progesterone | Maintains and stabilizes the uterine lining (keeps it ready). | "P" for Preserving lining |
🔵 Estrogen = builds
🟠 Progesterone = maintains
5. What does FSH do in the menstrual cycle?
FSH = Follicle Stimulating Hormone
Main job:
➔ Stimulates eggs to grow in ovaries inside little sacs called follicles.
➔ Also causes estrogen levels to rise.
Easy way to remember:
🎯 FSH = Finds Starting Help for eggs.
What Happens with Hormones in the Menstrual Cycle:
The menstrual cycle is about 4 main hormones that rise and fall to control the whole process.
Phase | Hormones Involved | What Happens |
|---|---|---|
1. Menstruation (Day 1-5) | Low Estrogen + Low Progesterone | The uterine lining sheds = period. |
2. Follicular Phase (Day 1-13) | FSH rises ➔ Estrogen rises | FSH grows an egg, estrogen rebuilds uterine lining. |
3. Ovulation (Day 14) | LH spike (big jump) | Egg is released from ovary. |
4. Luteal Phase (Day 15-28) | Progesterone rises | Progesterone maintains the lining in case of pregnancy. |
Hormones in the Cycle:
Hormone | Role |
|---|---|
FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) | Stimulates egg to grow. |
LH (Luteinizing Hormone) | Triggers egg to be released (ovulation). |
Estrogen | Builds the uterine lining. |
Progesterone | Keeps the uterine lining thick and stable. |
Easy way to remember the flow:
Start low ➔ Hormones are low during period.
Grow the egg ➔ FSH and Estrogen go up.
Pop the egg ➔ Big LH surge = ovulation.
Prepare for baby ➔ Progesterone rises to protect the lining.
Practice Problems
6.4
Which statement describes the movements of the rib cage during inhalation of air? [1]
a. External intercostal muscles contract moving the ribs up and outwards.
b. Internal intercostal muscles contract moving the ribs down and inwards.
c. External intercostal muscles relax moving ribs down and inwards.
d. Internal intercostal muscles relax moving ribs up and outwards.
Which muscles contract to cause air to pass out from the lungs through the bronchioles? [1]
a. internal intercostal muscles and diaphragm
b. internal intercostal muscles and abdominal wall muscles
c. external intercostal muscles and diaphragm
d. external intercostal muscles and abdominal wall muscles
Distinguish between ventilation, gas exchange, and cell respiration. [4]
Ventilation is the process of breathing in and out, which brings oxygen into the lungs and removes carbon dioxide.
Gas exchange is the diffusion of oxygen from the alveoli into the blood and the diffusion of carbon dioxide from the blood into the alveoli.
Cell respiration is the breakdown of glucose inside cells using oxygen to produce ATP releasing CO2 as a waste product.
6.5
Which event directly leads to an action potential? [1]
a. Fusion of vesicles with the pre-synaptic membrane
b. Diffusion of neurotransmitter across the synaptic cleft
c. Membrane potential reaches the threshold potential
d. Breakdown of the neurotransmitter
The diagram shows events at a synapse. What is happening at the point labeled X? [1]
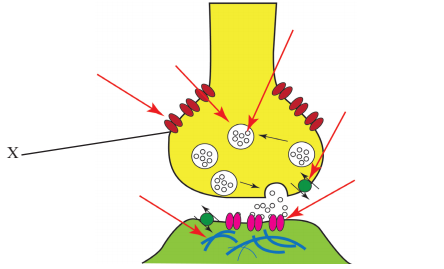
Neurotransmitter binding
Ca2+ diffusing
Neurotransmitter moving across synapse
Na2+ binding
Which element or ion is required for transmission of a nerve impulse? [1]
Phosphorous
Sodium
Sulfur
Iron
Outline how nerve impulses are transmitted along a nerve fibre. [3]
Neurons transmit information in the form of impulses which are short lived changes in electrical potential across the membrane of a neuron. Impulses happen as these ions move in and out through the plasma membrane.
6.5
How does the body respond to an increase in body temperature?
I. Vasoconstriction of skin arterioles
II. Shivering
III. Vasodilation of skin arterioles
I only
I and II only
II and III only
III only
Which hormone shows the greatest fall in blood concentration just before menstruation? [1]
FSH (follicle stimulating hormone)
LH (luteinizing hormone)
Progesterone
Estrogen
Which describes the secretion of hormones in the pancreas in response to low levels of glucose in the blood? [1]
Secretion of glucagon from α cells
Secretion of glucagon from β cells
Secretion of insulin from α cells
Secretion of insulin from β cells
If you were a doctor, how would you go about treating a person with type 1 diabetes vs. type 2 diabetes?
Type 1:If I were a doctor treating someone with Type 1 diabetes, I would give them insulin because their body cannot make it. I would teach them how to check their blood sugar every day and help them plan healthy meals and safe exercise. I would also check on them often to make sure their insulin doses are working correctly.
Type 2: If I were a doctor treating someone with Type 2 diabetes, I would start by helping them eat healthier and exercise more. If that didn’t control their blood sugar enough, I would prescribe medicine. If the medicine stopped working later on, I would add insulin. I would also help them with weight loss if they needed it.