LAND AND CLIMATE OF PAKISTAJN
What do you understand by climate?
==Climate refers== to the long-term patterns and variations of weather conditions in a particular region over a period of time, usually at ==least 30 years==. It encompasses various factors such as ==temperature, precipitation, humidity, wind, and atmospheric pressure== that interact with each other to create the overall climate of a region. Climate can be affected by a variety of natural and human factors, including changes in the amount of greenhouse gases in the ==atmosphere, solar radiation, volcanic eruptions,== ==and human activities== such as deforestation and the burning of fossil fuels. Understanding climate patterns and changes is important for predicting and mitigating the impacts of climate change on ==ecosystems, economies, and human societies.==

What are different cimatic regions of pakistan?
Pakistan has a diverse climate with a range of climatic regions due to its location and topography. Here are the different climatic regions of Pakistan:
- ==Coastal region:== The coastal region of Pakistan includes areas along the Arabian Sea, such as Karachi and Gwadar. The climate is hot and humid, with high temperatures and high levels of precipitation.
- ==Desert region:== The desert region includes the Thar Desert, which is located in the southeastern part of the country. The climate is hot and dry, with very little rainfall.
- ==Mountain region:== The mountain region includes the Himalayan and Karakoram mountain ranges, where temperatures are cold and there is heavy snowfall in winter.
- ==Northern Plains region:== The northern plains region includes areas such as Islamabad, Lahore, and Peshawar. The climate is moderate, with hot summers and cool winters.
- ==Western Plateau region:== The western plateau region includes areas such as Quetta and Sibi. The climate is arid, with hot summers and cold winters.
- ==Indus River Valley region:== The Indus River Valley region includes areas along the Indus River, such as Sukkur and Hyderabad. The climate is hot and dry, with low levels of rainfall.
How does climate affect human life?
Climate affects human life in many ways, and the impacts of climate change are becoming increasingly evident. Here are some of the ways in which climate affects human life:
- ==Health:== Changes in climate can affect human health through increased exposure to extreme weather events, air pollution, and the spread of diseases carried by insects such as mosquitoes and ticks.
- ==Agriculture:== Climate conditions can affect agricultural productivity and food security, through changes in temperature, rainfall, and other weather patterns.
- ==Water resources:== Changes in climate can affect water availability and quality, leading to water scarcity, droughts, and water-related conflicts.
- ==Infrastructure and property:== Changes in climate can lead to extreme weather events such as floods, landslides, and storms that can damage infrastructure, property, and homes.
- ==Migration and displacement==: Climate change can lead to displacement of people due to environmental disasters and food and water scarcity, leading to migration and displacement.
- ==Economy:== Changes in climate can impact economic activities such as tourism, agriculture, and fishing, leading to reduced income and increased poverty.
In summary, climate change has far-reaching effects on human life and well-being, and addressing the issue of climate change is crucial for sustainable development and human welfare.
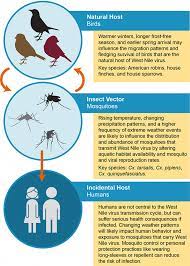
What is Environmental pollution?
Environmental pollution refers to the presence or introduction of harmful substances or contaminants into the natural environment that can cause adverse effects on the ==health of living== ==organisms, damage ecosystems, and disrupt== the natural cycles of the environment. Pollution can take many forms, ==including air pollution, water pollution, soil pollution, and noise pollution.==
Air pollution is caused by the release of harmful gases and particulate matter into the air, usually from human activities such as burning fossil fuels, industrial processes, and transportation. Air pollution can have serious impacts on human health, including respiratory problems and cardiovascular diseases, and can also damage ==crops, forests, and other vegetation.==
Water pollution occurs when harmful substances, such as chemicals, pesticides, and fertilizers, are released into bodies of water, leading to contamination of water sources and aquatic life. Water pollution can also affect human health, leading to diseases such as ==cholera, typhoid,== and other ==waterborne illnesses.==
Soil pollution is caused by the introduction of harmful substances, such as heavy metals and pesticides, into the soil, which can lead to the degradation of soil quality, affecting crop productivity and posing health risks to ==humans and animals.==
Noise pollution is caused by excessive noise, which can lead to hearing loss, stress, and sleep disturbance, and can also affect wildlife and their behavior.
Environmental pollution is a global problem and requires collective action and individual responsibility to mitigate its effects and protect the environment fo==r future generations.==

What is the relationship between the population growth and the environmental pollution?
Population growth can have a significant impact on environmental pollution. As the population grows, so does the demand for natural resources and the production of goods and services. This increased demand can lead to increased pollution and environmental degradation. Here are some ways in which population growth can lead to environmental pollution:
- ==Increased use of fossil fuels:== As the population grows, the demand for energy increases, leading to increased use of fossil fuels, which contribute to air pollution and climate change.
- ==Increased waste generation:== As the population grows, so does the amount of waste generated, including solid waste, hazardous waste, and electronic waste, which can lead to land, air, and water pollution.
- ==Increased land use:== As the population grows, more land is needed for housing, agriculture, and other purposes, leading to deforestation, soil degradation, and habitat destruction.
- ==Increased water use:== As the population grows, more water is needed for domestic, agricultural, and industrial purposes, leading to water scarcity, water pollution, and other water-related problems.
- ==Increased transportation:== As the population grows, so does the demand for transportation, leading to increased use of vehicles, which contribute to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
In summary, population growth can lead to increased pollution and environmental degradation, but this relationship is complex and can be influenced by a range of social, economic, and environmental factors. Addressing the issue of population growth and its impacts on the environment requires a multifaceted approach that includes sustainable development, resource conservation, and environmental protection.
Describe the importance of the location of pakistan in the south asian region?
Pakistan's location in the South Asian region is strategically important due to its geographical position and proximity to major regional powers. Here are some reasons why Pakistan's location is significant:
- ==Gateway to Central Asia:== Pakistan's location provides a gateway to Central Asia and is an important link between South Asia, the Middle East, and Central Asia.
- ==Energy Corridors:== Pakistan is strategically located on several major energy corridors, including the Gulf-Middle East to Central Asia, the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor, and the Turkmenistan-Afghanistan-Pakistan-India gas pipeline.
- ==Economic Potential:== Pakistan's location offers significant economic potential due to its access to major markets in South Asia, the Middle East, and Central Asia. This makes it an important hub for trade and investment.
- ==Regional Stability:== Pakistan's location also makes it important for regional stability, particularly in relation to its neighbors India, Afghanistan, and Iran. Its strategic position has also made it a key partner in the fight against terrorism and extremism in the region.
- ==Regional Integration:== Pakistan's location is important for regional integration initiatives, including the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC), the Economic Cooperation Organization (ECO), and the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO).
In summary, Pakistan's location in the South Asian region has significant strategic, economic, and geopolitical importance, and it plays an important role in regional stability, security, and integration.
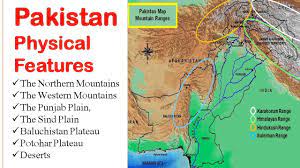
give a brief account of the physical features of pakistan?
Pakistan is a country located in South Asia with a diverse range of physical features, including mountains, plateaus, plains, deserts, and coastal areas. Here is a brief account of the major physical features of Pakistan:
- ==Northern Mountains==: The northern region of Pakistan is dominated by the Himalayas, Karakoram, and Hindu Kush mountain ranges, which include some of the highest peaks in the world, including K2, the second-highest mountain peak. The region is also home to glaciers, lakes, and rivers that originate from the mountains.
- ==Plateaus and Plains:== The Balochistan plateau covers the southwestern region of Pakistan, and is characterized by arid deserts and semi-arid plateaus. The Punjab plains cover the northeastern region of the country, and are primarily agricultural and heavily populated.
- ==Coastal Areas==: The coastal region of Pakistan lies along the Arabian Sea and includes the Makran coast in the southwest and the Indus Delta in the southeast. The region is characterized by sandy beaches, mangrove forests, and important fishing ports.
- ==Rivers and Water Bodies:== The Indus River is the largest river in Pakistan and is a major source of water for agriculture and hydroelectric power. Other important rivers include the Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, and Sutlej. The country also has several large lakes, including Lake Manchar and Lake Keenjhar.
- ==Deserts:== The Thar Desert, also known as the Great Indian Desert, covers parts of southern Pakistan and is characterized by sand dunes and sparse vegetation.
In summary, Pakistan's physical features are diverse and include high mountain ranges, plateaus and plains, coastal areas, rivers and water bodies, and deserts. These physical features have shaped the country's history, economy, and culture, and continue to be an important part of its identity.
Mention the benefits of the northern-eastern mountainous region?
The northern-eastern mountainous region of Pakistan, which includes the Himalayas, Karakoram, and Hindu Kush mountain ranges, has several benefits, including:
- ==Natural Resources:== The mountainous region is rich in natural resources, including minerals, precious stones, and water resources such as rivers, glaciers, and lakes. These resources have significant economic potential and are important for the country's development.
- ==Tourism:== The mountainous region attracts a large number of tourists each year, who come to enjoy the natural beauty, trekking, mountaineering, and adventure sports. This has created job opportunities and contributed to the local economy.
- ==Agriculture:== The mountainous region has fertile land and is suitable for agriculture, particularly for crops such as wheat, maize, and fruits such as apples and apricots. The region also has significant potential for horticulture and livestock farming.
- ==Climate Regulation:== The mountainous region plays an important role in regulating the climate of the surrounding areas, including the Indus River basin. The glaciers and snow cover help maintain a steady water supply for irrigation and other purposes.
- ==Biodiversity==: The mountainous region has a diverse range of flora and fauna, including several endemic species. This biodiversity is important for maintaining ecological balance and provides opportunities for research and conservation.
In summary, the northern-eastern mountainous region of Pakistan has several benefits, including natural resources, tourism, agriculture, climate regulation, and biodiversity. These benefits have significant economic, social, and environmental importance and are important for the sustainable development of the region and the country as a whole.

Name the neighbouring countries of pakistan?
Pakistan is bordered by several neighboring countries, which include:
Afghanistan to the northwest
Iran to the southwest
China to the northeast
India to the east
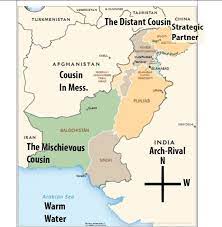
Pakistan's location in South Asia, Central Asia, and the Middle East makes it an important regional player, and its relationships with its neighboring countries have significant economic, political, and strategic implications.