Science notes
Topics/Questions
What is Genetic engineering - IVF?
Genetic engineering
- when a scientist tweaks the genes to create a more desirable organism
- alters the DNA of an organism
- can involve changing a single base pair (A-T or C-G)
- e.g. corn has been modified to be more resistant to bugs (GMO)
IVF
- mature eggs are retrieved from ovaries & fertilised by sperm in a lab
- then the embryos are are transferred to a uterus
- one full cycle of IVF takes about 3 weeks
What do you mean by Biodiversity?
- biodiversity is the different kinds of life found in one area
- can be defined by
- genetic diversity
- species diversity
- ecosystem diversity.
What is a karyotype and how does it relate to Down's Syndrome.
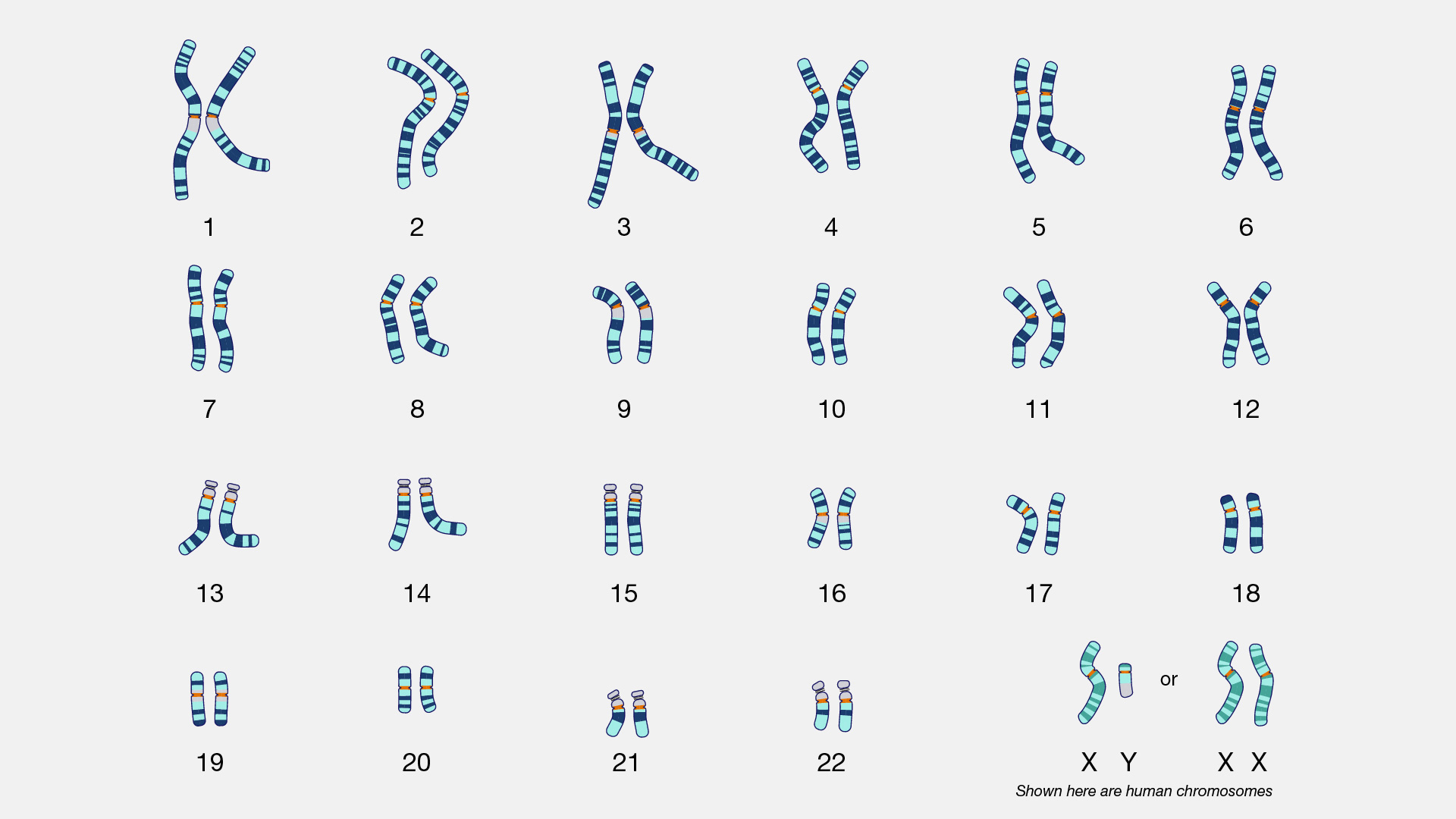
- an individual’s complete set of chromosomes
- a karyotype can be used to look for abnormalities in chromosome number or structure
- using karyotypes can help diagnose down syndrome
Carbon dating technique and half-life.
- determines the age of old material based on how much carbon content there is
- half life is half the amount of time it takes for a radioactive material to decay naturally
Mitosis and Meiosis
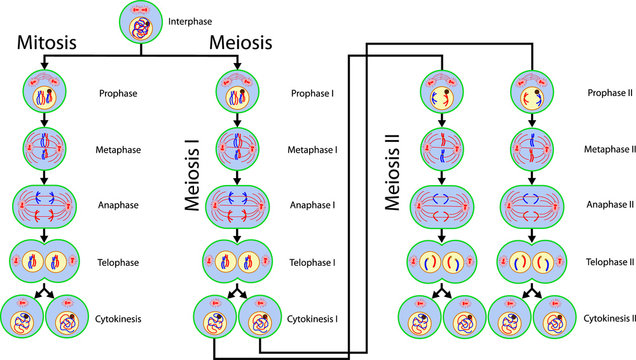
Mitosis
- Interphase
- Normal cell/getting ready
- Prophase
- coil up
- Metaphase
- Move to the centre of the cell
- Anaphase
- Pulled apart by the poles
- Telophase
- Cells divide
- Cytokinesis
- two cells are formed
Meiosis
Interphase I
- Normal cell/getting ready
Prophase I
- coil up
Metaphase I
- Move to the centre of the cell
Anaphase I
- Pulled apart by the poles
Telophase I
- Cells divide
Cytokinesis I
- two cells are formed
Interphase II
- Normal cell/getting ready
Prophase II
- coil up
Metaphase II
- Move to the centre of the cell
Anaphase II
- Pulled apart by the poles
Telophase II
- Cells divide
Cytokinesis II
- two cells are formed out of the two that were made in Meiosis I
Types of evolution
- artificial selection
- The process by which humans choose to breed particular organisms with desirable features.
- natural selection
- Natural selection is the process where an environmental factor acts on a population and results in some organisms having more offspring than others.
- The environmental factor that acts on the population is known as the selective agent.
- The selective agent can be a biotic factor (bacterial infection, competitor or predator) or an abiotic factor (temperature, water, soil nutrients or fire).
- Selective agent can act by killing individuals if they are less suited to surviving (e.g. predators can see white moths better in a dark environment and therefore less white moths live there)
- A mate can select a certain feature in the opposite sex which increases the incidence of the selected feature - known by Darwin as sexual selection
- Individuals favoured by a selection for traits pass those on to the next generation
- variation
- Variation is caused by differences in genes which result in difference in characteristics
- species
- In the past the test for species would be to see if two organisms could be interbred to produce fertile offspring
- Currently, biologists use DNA and the study of amino acids to identify species.
Respiration and combustion difference and similarities along with equations
Relationship between DNA, Chromosomes, and genes.
Base pair rule for DNA and structure of DNA.
What are isotopes?
Types of chemical reactions.
Formulas and calculations for Speed, velocity, terminal velocity, average velocity and acceleration.
Balancing chemical equations.
Evidence of big bang?
- red shift
- the expanding of the universe
- the further that the universe has expanded, the redder it appears
- doppler effect
- Doppler Effect refers to the change in wave frequency during the relative motion between a wave source and its observer
- the process of increase or decrease of starlight that depends on the relative movement of the star.
- cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB)
- The Big Bang theory predicts that the early universe was a very hot place and that as it expands, the gas within it cools.
- Therefore the universe should be filled with radiation that is literally the remnant heat left over from the Big Bang, called the “cosmic microwave background", or CMB.
Nuclear Radiation
‘Nuclear Radiation should only be used to improve human health’. Evaluate this statement in terms of ONE of the following factors: Social, Economic, Environmental, Political, Cultural, Moral or Ethical.
- nuclear bombs
- effects of nuclear bomb testing can leave areas uninhabitable
- radiation can give people radiation sickness
- radiation can get rid of cancers
- radiation can help diagnose stuff
OR
Environmental
- can be used as a substitute for coal energy as it is greener
- if a nuclear power station explodes then it can be detrimental for the environment
- if nuclear waste isn’t disposed of correctly it can be detrimental for the environment
Zoe’s notes:
https://www.notion.so/SCIENCE-6addc90dc3a64befae490d09bdc5b663