Unit 6 Biology Photosynthesis
Essential Questions:
What is photosynthesis, and what factors affect its rate?
How is a leaf adapted for efficient gas exchange?
How does water move around a plant, and what is transpiration?
Lo 1. Write a chemical equation, in words and symbols, describing photosynthesis
Photosynthesis Equation:
6Co2 + 6H2o —> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Photosynthesis is the process by which plant cells make glucose from carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight.
The process requires a pigment such as chlorophyll found in the chloroplasts and can only occur in certain organisms(plants, algae, certain bacteria)
The required carbon dioxide flows into the leaf from the stomata.
Water enters the plant by the roots, and is transported into the leaves through the xylem.
Lo2 Explain the significance of photosynthesis in maintaing the balance of oxygen and carbondioxide in the air, and in converting into chemical energy stored in food.
If an animal eats a plant they consume the plants nutrients (proteins, and lipids) as food and releases the stored energy via cell respiration.
Autotrophs are things that produce their own food such as plants
Heterotrophs rrely on autotrophs for food and cannot produce their own food. Examples are animal
Uses of Glucose in Respiration
The remaining glucose not used in respiration is converted into starch, cellulose, lipids, and amino acids.
Storage and energy
During the night plants use the starch stored in their leaves as sources of energy as they cannot photosynthesize during the night.
Many plants like wheat and potatoes make starch or oil in their seeds and storage organs.
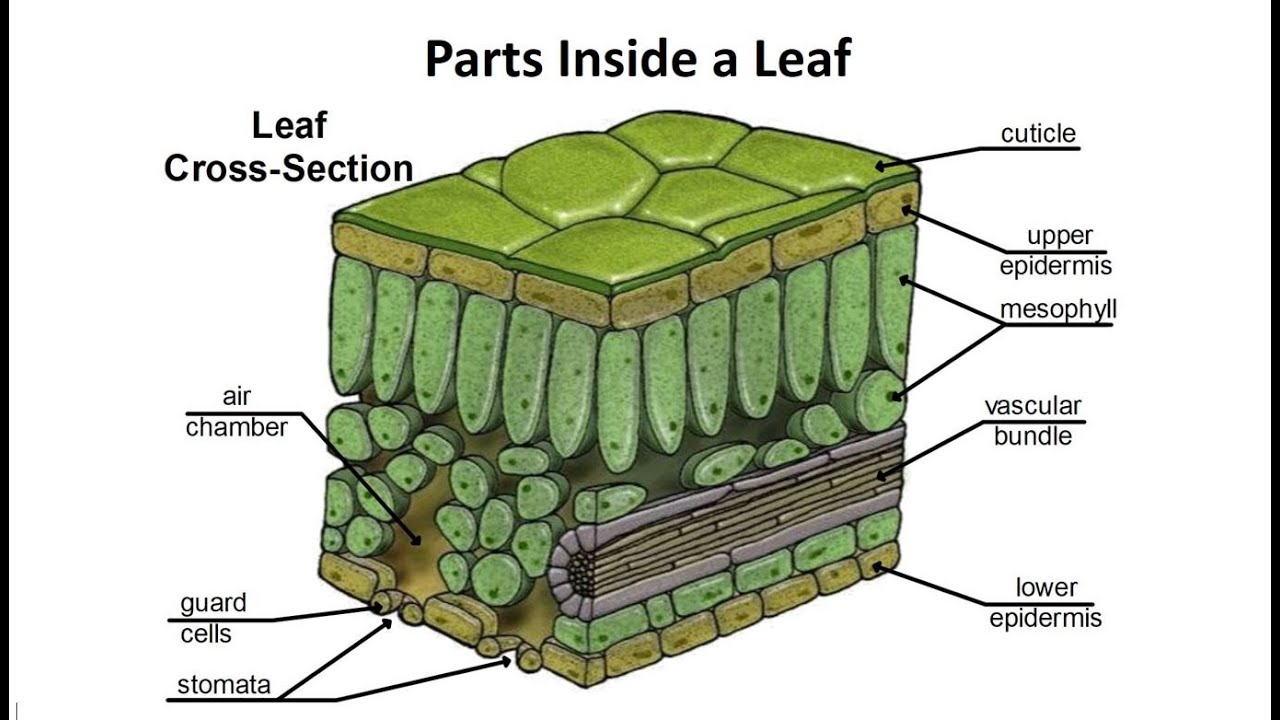
Lo3. Describe the position and function of the following parts of the leaf: cuticle, epidermis, palisade and spongy mesophyll, air spaces, stomata, guard cells, veins, xylem, and phloem.
Function of the leaf
For photosynthesis to occur effectively, the leaf needs:
A way to transport water to the leaf
A way to exchange carbon dioxide and water
The ability to absorb water effectively
Transport
Xylem
transports water from the roots to the leaf
Phloem
Carries glucose away from the leaf to the roots
These two (Xylem and phloem) together are called veins
Gas Exchange:
Gas exchange happens in the spongy mesophyll
They have thin layers and are loosely packed.
These features allow carbon dioxide to diffuse into the spongy mesophyll cells, and oxygen out of them
To get into the spongy mesophyll, the gases diffuse through the stomata(small holes) that open or close to control water loss from the leaf by transpiration.
Absorbing Light energy
Light absorption occurs in the Palisade mesophyll
They are column-shaped and highly packed with chloroplasts
Arranged tightly together for maximum light absorption
Sunlight hits the top level of the leaf called the waxy cuticle, then below is the upper epidermis, palisade mesophyll, spongy mesophyll, lower epidermis and another waxy cuticle.
Guard cells allow the exchange of gases through the stoma
Lo 4 perform and interpret to investigate carbon dioxide and oxygen exchange by plants in different lighting conditions.
Experiment 1.
Investigating photosynthesis in Elodea (pondweed)
There is a tube containing pondweed in a darkened room but is next to a lamp.
Assumptions that are being made in this experiment are that the bubbles being produced is directly proportional to the rate of photosynthesis. This is because the products of photosynthesis is both glucose and oxygen so we can assume that there is photosynthesis occuring due to the fact there are bubbles produced. All the bubbles are oxygen and produced by the plant.
Independent variables that could be tested
Temperature
Carbondioxide concentration
Light intensity
Experiment 2.
Student recorded the distance between the light source and the beaker and the numbrer of gas bubbles given out by the pondweed. From the graph what can you conclude about the relationship of gas bubbles given out per minute and the distance between the light source and beaker.
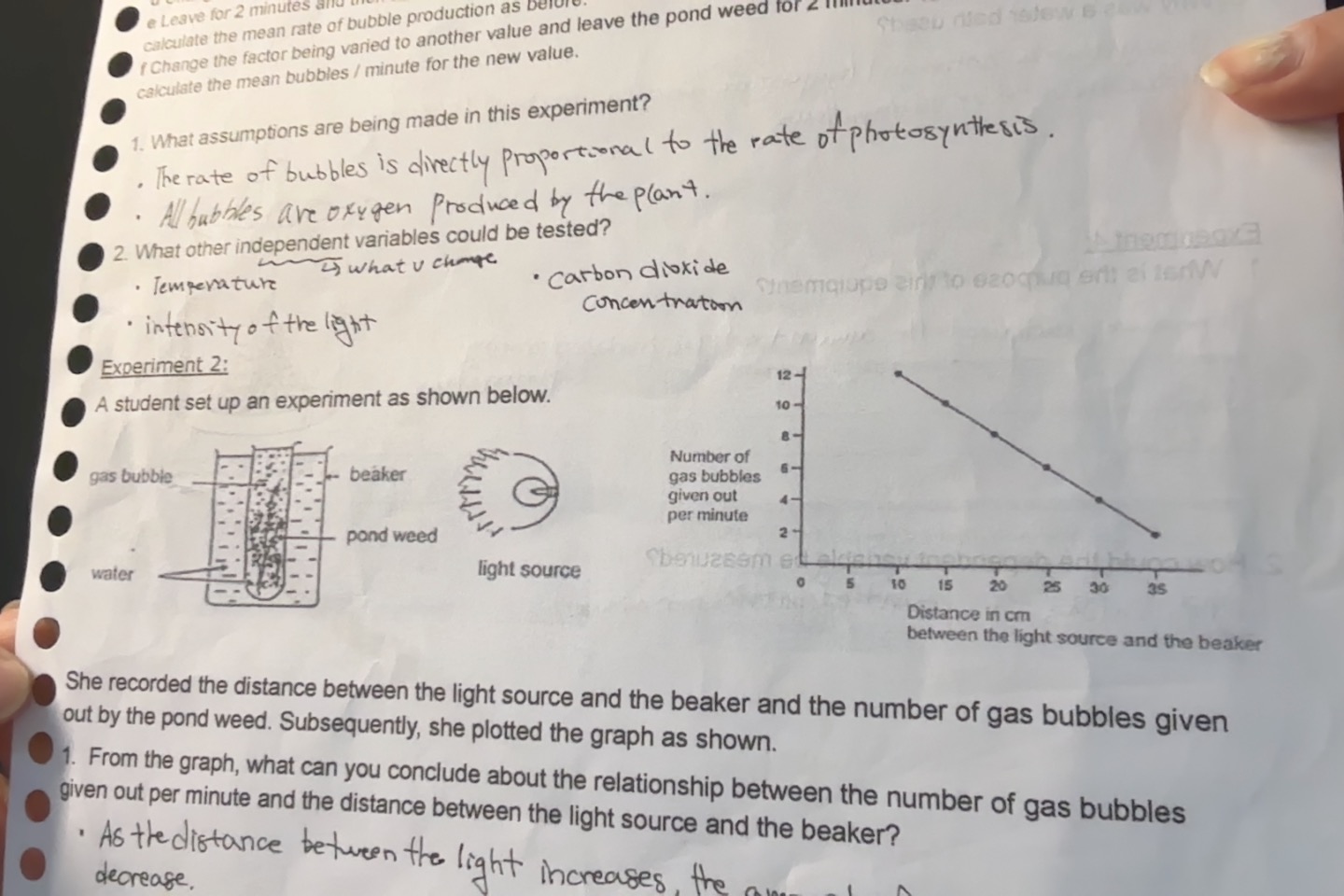
As the distance between the light and beaker increases the amount of bubbles decreases.
Suggesting that light intensity directly varies with the rate of photosynthess. (the closer the light the more photosynthesis that occurs)
Experiment 3.
An experiment testing photosynthesis under different light conditions was conducted. The liquid in the beakers is Hydrogen-carbonate indicator solution .
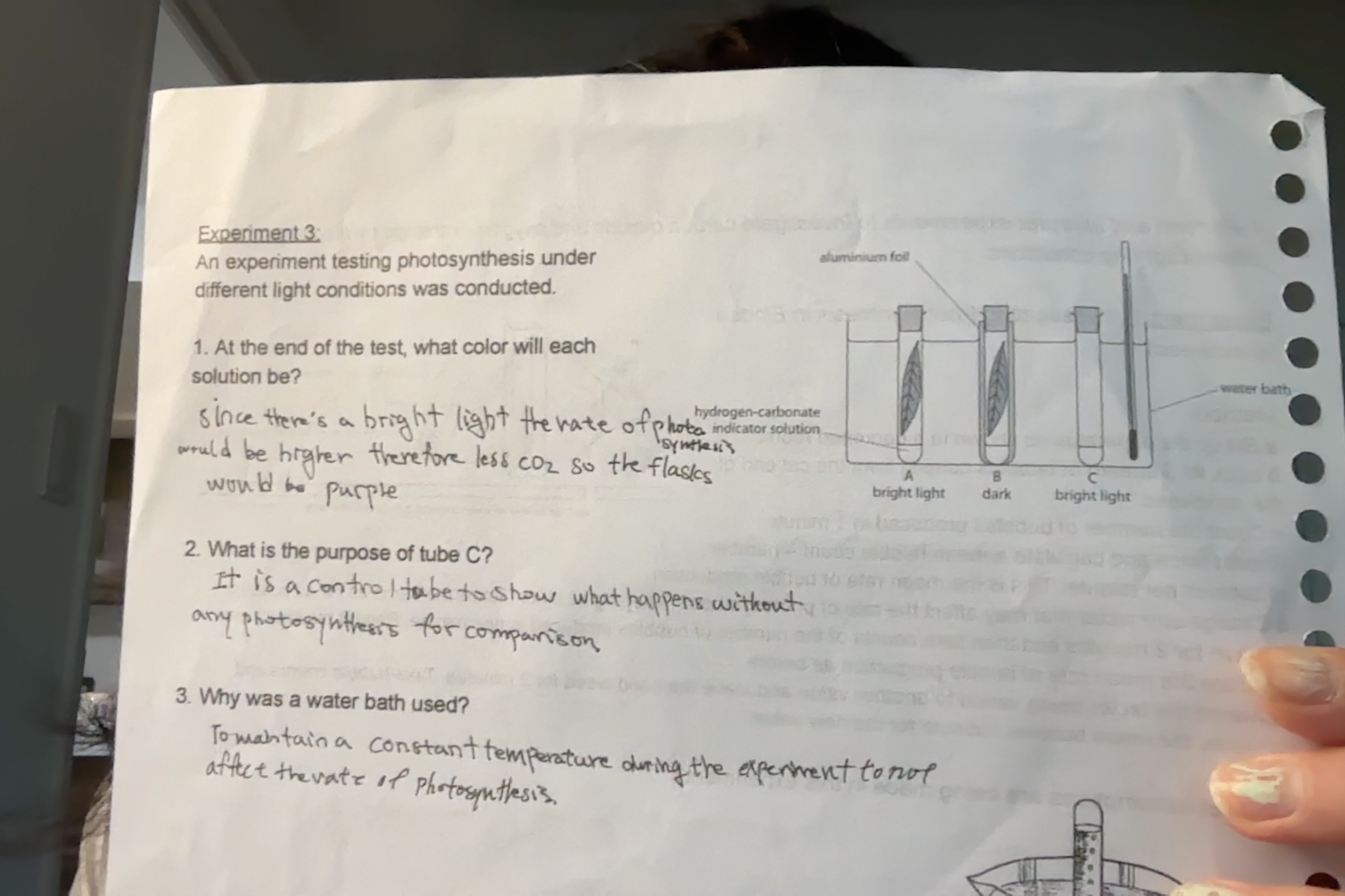
At the end of the test, what color will each solution be?
(A) Since there is a bright light the rate of photosynthesis would be higher for (A) although it is farther away from the light) the second beaker, so it would be purple(less CO2)
(B) would become yellow as the concentration of Co2 becomes larger than O2 as the plant will not photosynthesize without light.
What is the purpose of tube C
It is a control tube to show what will happen without photosynthesis for comparison
Why was a water bath used?
To maintain a constant temperature during the experiment otherwise it will be changing to many variables and not be able to tell which one increased/decreased the rate of photosynthesis.
1. Write the word and chemical equations for photosynthesis.
(Word equation + Balanced chemical equation)
Carbon dioxide + Water + light produces Glucose and Oxygen
CO2 + H2O → C6H1206 + O2
2. Explain how photosynthesis helps maintain the balance of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the atmosphere.
They maintain the balance in the environment by plants taking in excess carbon dioxide in the atmosphere during photosynthesis, which then produces and releases oxygen. This helps maintain the amount of gases in the atmosphere creating a safe environment for animals and humans.
3. Describe how light energy is converted into chemical energy during photosynthesis.
Light energy is absorbed by the chlorophyll, which is then converted into chemical energy.
This chemical energy then is used to produce glucose from carbon dioxide and water.
4. Choose three of the following leaf structures and describe both their position and their function:
5. Imagine you are doing an experiment where a plant is placed in a sealed container with a light on for 24 hours.
a) What changes in oxygen and carbon dioxide levels would you expect?
The oxygen levels would increase as the carbon dioxide levels decreased. This would happen because the plant would photosynthesize for 24 hours, as there would be light the whole time, so the plant would continuously photosynthesize. Taking in the carbon dioxide and releasing the oxygen
b) What would happen if the light were turned off for 24 hours instead?
As there is no light, there would be no photosynthesis, but there would be respiration occurring. SO, oxygen would decrease, and the carbon dioxide would increase.
(respiration Increases CO2 levels C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O )
c) What does this tell you about the role of light in gas exchange during photosynthesis?
This shows how light is a crucial part of photosynthesis, which removes carbon dioxide and produces oxygen.
How do the structure and arrangement of cells in a leaf help the plant perform photosynthesis efficiently?
Leaves have a large surface area, including the flat, thin shape and the arrangement of palisade and spongy mesophyll cells, to capture maximum sunlight