Chapter 13: Chemical Degradation
3/13 (No Quiz)
Material Type
Ceramic
Metal
Polymer
Composite (all 3)
Types of Degradation → depends on material + environment
Chemical
Mechanical
Electrical
Materials degrade (different types) → degradation effects ↔ organism/bio response
Chemical Degradation: oxidation + reduction
usually oxidation of metals
Oxidation is LOSS of electrons
Reduction is GAIN of electrons
You should know top reactive elements on reactivity series*
Approaches of Chem Degradation:
Reactivity Series
Pourbaix Diagram
Corrosion + Electrochemistry Studies
Interesting Values: slide 9 **
FOR BIO STUFF USE STAINLESS STEEL (mostly iron, some carbon + other stuff)
Fe2+ + 2e- → Fe -0.44 V
We expect if we put any of this stuff into the human body, it will corrode
negative values react**
positive values means it requires energy to react
regular bridge use regular steel
Cobalt Chromium Alloys (be careful about circulation in human body bc anemia)
Titanium Alloys (most bio compatible)
If you put a metal in an acidic ==> more likely to react
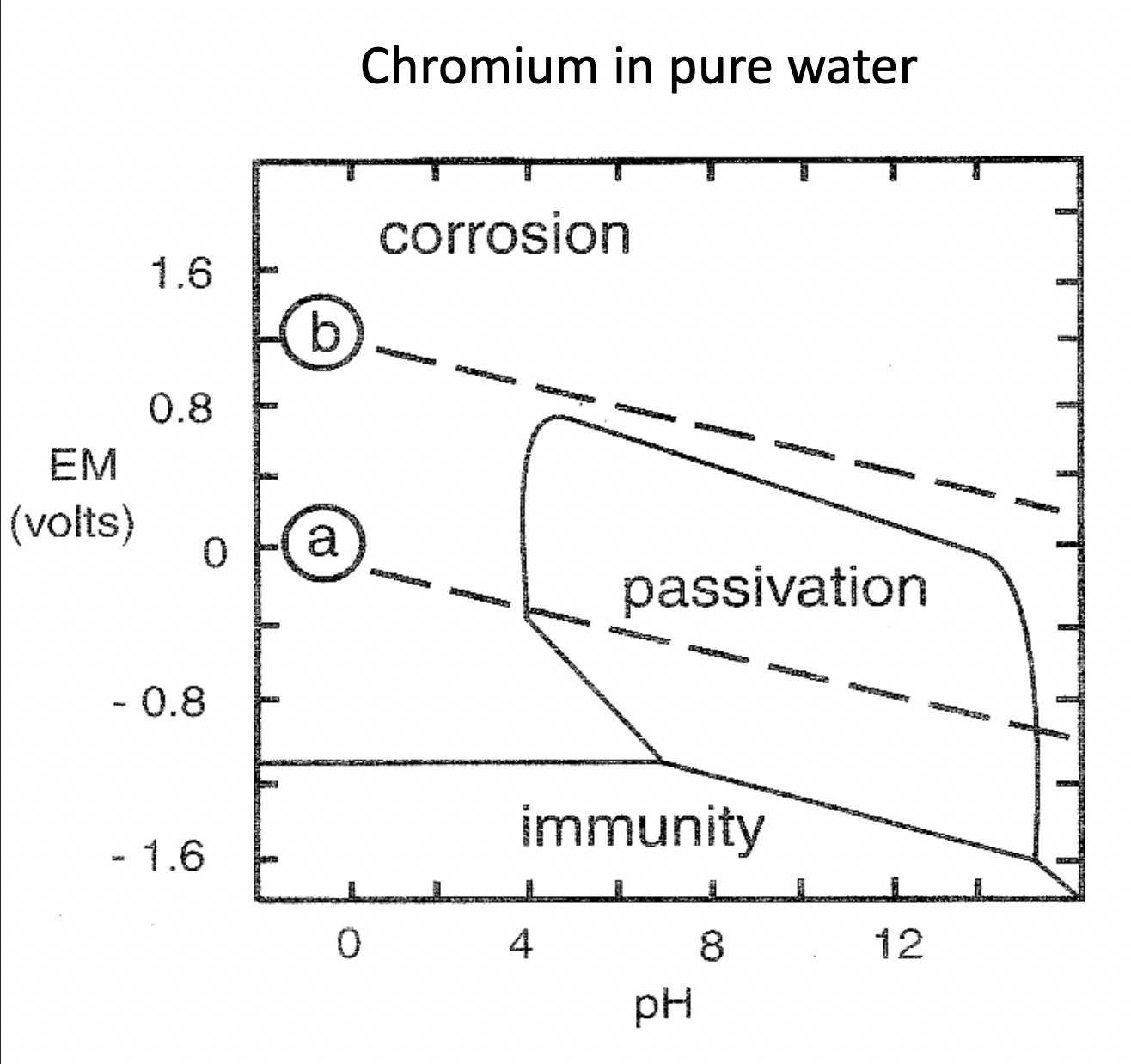
Pourbaix Diagram:
what is this - see when something corrodes dependent on pH and EM (volts)
Immunity - does not react (does not corrode)
Passivation - surface of metal has something else (prevents degradation)
most metals can’t use unless passivated***IMPORTANT owo
Corrosion
how do I read it
SHE: hydrogen equivalent (not important)
tells you if you can use a certain metal like reactivity series (useful but has limitations)
Types of Corrosion: real world corrosion is kind of a mess
Uniform Attack: losing electrons into the surroundings (same everywhere, ALWAYS HAPPENING)
Galvanic Corrosion: two different activities (avoid at all cost)
Crevice Corrosion: two different metals in contact, holes
Pitting Corrosion: at a point due to heterogeneity?
Intergranular Corrosion: in grain structure, when stuff is rotated and still next to each other you get leftover things that don’t have the same number of bonds which will be weaker than the other atoms there
Leaching: lose one but not the other?
Erosion: everything above with FLOW (fluid movement over it)
Stress and Fatigue Corrosion:
Fatigue is repetitive actions: generating and removing stress which creates damage
Have all these, which is the worst (weighted)
Guessing Corrosion (pt1):
Pitting
Uniform Corrosion
Crevice
Crevice Corrosion
Intergranular
Pitting
Guessing Corrosion (pt2):
Galvanic
Erosion
Leaching
Intergranular
Stress + Fatigue
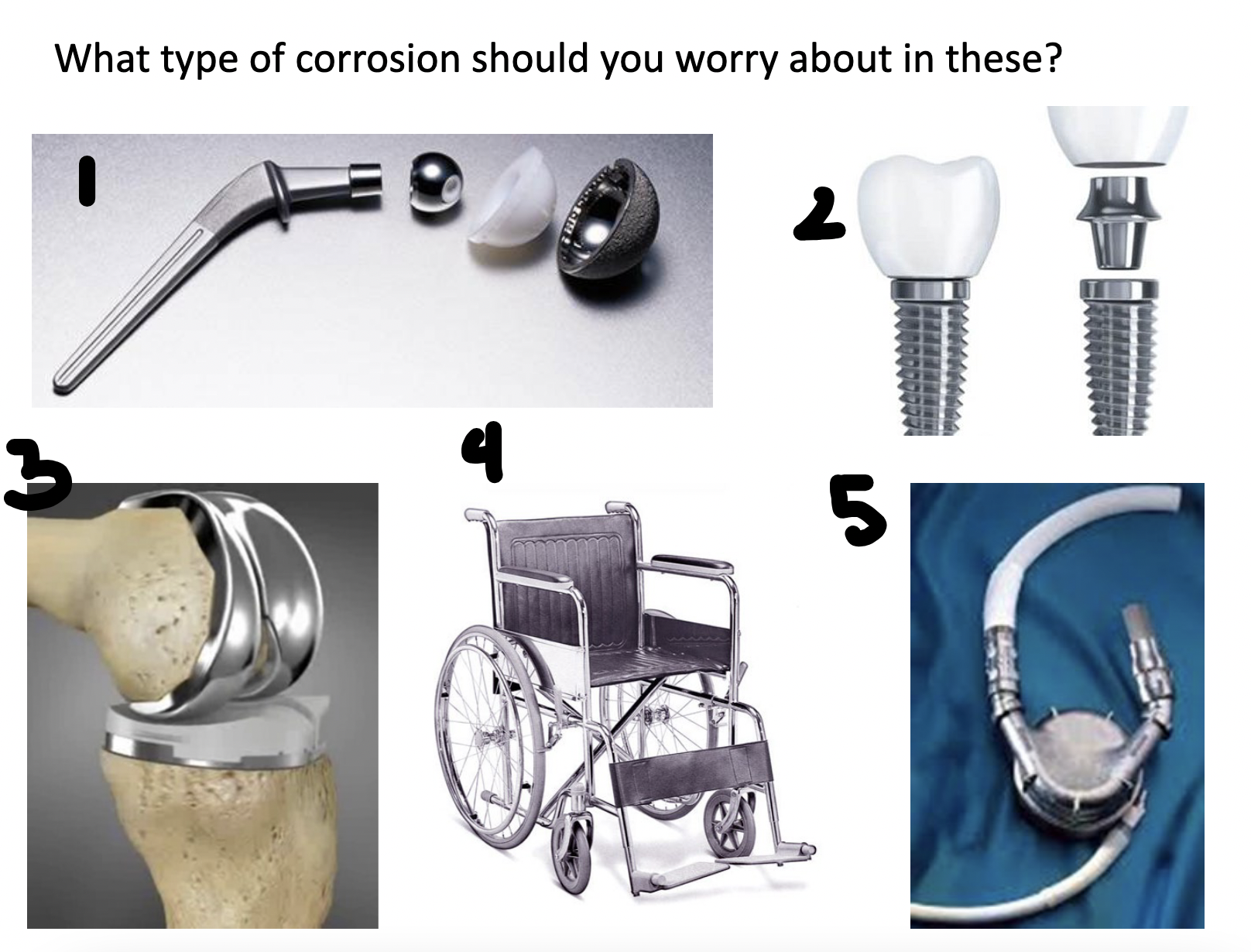
What types of corrosion should you worry about in these start from 11 clockwise:
hip implant: uniform attack, crevice, mechanical stress, fatigue
screw thing: crevice, mechanical stress, uniform attack
knee replacement: mechanical, uniform, fatigue
wheelchair: uniform, crevice, fatigue + mechanical, erosion, pretty much everything
what you don’t wanna see: galvanic
artificial heart: erosion, uniform attack, mechanical stress + fatigue
Mechanical/chem stress → bio response therefore put pacemaker in good location
Quiz 14: What type of corrosion is it?
Pitting: each little dot is a corrosion pit on the saucepan
Crevice
Intergranular
Pitting
Galvanic
Erosion
Leaching (preferencial leaching + grain structure)
Intergranular
Top Left: Crevice