Business Management
(My other note was crashing from word overload)
Nature of management
Traditional definition
Process of coordinating a business’s resources to achieve its goals
Contemporary definition
Process of working with and through other people to achieve business goals in a changing environment
Features of management
Working
Working with and through others
Management is a social process
Managers must be able to communicate
Achieving
Achieving business goals
Without goals, a business can lose direction
Effectiveness measures the degree to which a goal has been achieved
Getting
Getting the most from limited resources
Managers need to coordinate resources efficiently
Efficiency measures the resources used (costs) against what was actually achieved (benefits)
Balancing
Balancing efficiency and effectiveness
The balance of efficiency and effectiveness leads to success
Coping
Coping with a rapidly changing environment
Successful managers anticipate and adapt to change
Role of efficiency & effectiveness
Efficiency is achieved by producing the maximum outputs with the minimum level of inputs
Raw materials, time, and money are not wasted
Increases level of productivity of a firm
Productivity measures how efficiently goods and services are produced
Outputs are the goods or services produced by a firm using inputs
Effectiveness measures the degree to which a goal has been achieved
Features of effective management
Plan and organise
Guide/lead the business
Make decisions
Roles of management
Interpersonal
Create an environment to help staff achieve business goals
Communicate their vision and values
Satisfy the human needs of employees
Informational
Communicate business goals
Communicate decisions and directions
Pass on knowledge and expertise
Decisional
Choose the best course of action from the alternatives
Make informed decisions that best suit the business and its employees
Think in a long-term strategic way
Role of Efficiency & Effectiveness
An effective manager needs to be good at POLC
Planning
Setting objectives and deciding methods to achieve them
Organising
Structuring the organization to turn plans into action
Leading
Influencing or motivating people to work towards organization objectives
Controlling
Process of evaluating performance and taking corrective action to make sure set objectives are being achieved
Features of effective management
Effective managers will plan and organise the functions of the business to ensure the effort of employees is coordinated to produce goods and services demanded
The effectiveness of this process determines the success or failure of the business
A combined effort from employees will bring about the greatest amount of goods and services at least cost = effective
Skills of Management
Every occupation needs certain skills that are needed for success
A skill comes with knowledge, practice, and talent to do something well
Changes in the structure of businesses over the last 10 years
Movement away from tall hierarchical
I Can Swim Very Fast During A Pool Race
Interpersonal
Interpersonal skills are those needed to work and communicate with people and to understand their needs
This involves
Motivating
Encouraging
Gaining respect and loyalty
Knowing the staff, not just their abilities, but recognising their talent
Communication
Includes written, verbal, and non-verbal
Strategic thinking
Looking at the business as a whole and taking a broad, long-term view
Involves thinking about a business’s future direction and goals
In a practical sense, it means being able to:
Determine business objectives
Courses of action needed to meet objectives
How resources need to be allocated to pursue courses of action and thus meet objectives
Vision
Clear, shared sense of direction that allows people to achieve a common goal
Should be broadly understood and agreed to by all employees
The most effective way for managers to share their vision is by communicating the organisation’s goals
To do this, managers have to display leadership skills
Leadership is the ability to influence people to set and achieve specific goals
Flexibility
Decision making
Adaptability
Problem solving
Broad range of activities involved in searching for, identifying, and implementing a course of action to correct an unworkable situation
Managers must understand the different challenges at each stage of the business life cycle
There are 6 steps in this:
Identify the problem and causes
Gather relevant information
Develop alternative solutions
Analyse the alternatives
Choose one and implement it
Evaluate the solution
Reconciling conflicts
Management Approaches
Classic Approach
The classical approach to management emphasises how best to manage and organise workers so as to improve productivity (output)
Features of the management style:
Clear lines of authority (chain of command)
Discipline as a feature of leadership
Autocratic leadership style
Rules and procedures.
Management hierarchy - features
Rigid lines of communication
Numerous levels of management
Clear roles, positions, responsibilities
Most information directed downwards
Specialisation of labour - tasks divided into jobs
Chain of command
There are 2 perspectivesClassical-scientific approachStudies a job in great detail using time and motion studies to reduce a task to an effective minimum standard (e.g. McDonald’s Big Mac)
Classical-bureaucratic approachUses a strict hierarchical structure to break jobs down into individual, specialised tasks, with clear lines of communication and responsibility
Advantages:
Shorter time to make decision
Could lead to improved efficiency
Increased productivity
Clear chain of command
Disadvantages
Specialisation and repetitive tasks could lead to employee boredom
Less job satisfaction, which could lead to increased turnover
Could discourage creativity and innovation
Organisation becomes inflexible
Management as planning
Planning is the preparation of a pre-determined course of action for a business
Levels of planning
Strategic
3-5 Years
Tactical
1-2 Years
Operational
Day to day
Planning provides:
A vision and goals
Strategies to achieve the vision and goals
Ancticipation for future directions for change
Management as organising
Organising is the structuring of the organisation to translate plans and goals into action
The organisation process is the range of activities that translate the goals of a business into reality
Steps;
Determine the work activities
Classify and group activities
Assign work and delegate authority
Management as controlling
Controlling compares what was intended to happen with what has actually occurred
The control process:
Establish standards in line with the firm’s goals and influences from employees, management, industry, and government
Measure performance and determine how comparisons will be made against standards or benchmarks
Take corrective action
Changing activities, processes, and personnel to ensure that the goals of the business have been met
Control methods
Quality control
Checking finished product
Quality assurance
Checking quality during and after production
Total quality management
‘Quality in everything we do’
Hierarchical organisational structure
Management hierarchy is the arrangement that provides increasing authority at higher levels of the hierarchy
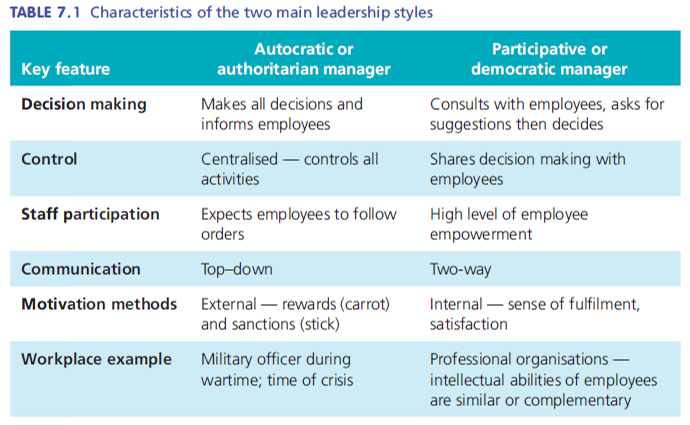
Autocratic Leadership style
A manager using an autocratic leadership style:
Tends to make all the decisions
Dictates work methods
Limits worker knowledge about what needs to be done
Frequently checks employee performance
Sometimes gives feedback that is punitive
Behavioural
The behavioural approach to management stresses that people should be the main focus of the way in which the business is organised
Features:
Employees are the most important resource
Economic and social needs of employees should be satisfied
Employee participation in decision making
Team-based structure
Managers need good interpersonal skills
Democratic leadership
Management functions
Leading
Motivating
Communicating
A successful leader:
Keeps an open mind, seeks out new ideas, and freely shares information
Shows confidence in people, shares credit and recognition
Builds and communicates a clear vision
Sets an example and earns the respect of employees
Delegates tasks to suitable emplyees
Conveys the goals of the business to workers and motivates them
Demonstrates flexibility in dealing with situations
Understands the technical aspects of the industry or business
Management vs. Leadership
Management is:
Coping with complexity
Planning and budgeting
Organising and controlling
Leadership is:
Coping with change
Determining direction
Motivating people
Management as motivating
Motivation is the individual, internal process that energises, directs, and sustains an individual’s behaviour. It is the personal force that causes a person to behave in a particular way
Managers must be aware of the human factor involved in the business organisation, and implement practices that motivate employees
Motivational methods include:
Trust
Respect for the individual
Positive reinforcement
Empowerment
Enhancing self-esteem
Employee participation
Rewarding team performance
Employee encouragement
Management as communicating
One of the most difficult challenges for managers is getting employees to understand and want to achieve the business’ goals
Effective communication are effective communicators and able to share their thoughts and plans, they will find it difficult to influence others
Many studies have shown that the performance of both individuals and businesses improves when managerial communication is effective, especially when they are provided with information regarding goals, plans, and financial results
Teams
Teamwork involves people who interact regularly and coordinate their work towards a common goal
Many businesses are starting to realise that a team approach can be the catalyst for superior performance
It is essential that managers foster a sense of cohesion between team members, otherwise the team is no more than a group of individuals all working separately
The use of teams has the following effects:
Decisions are negotiated rather than imposed
Flatter organisational structures
Manager as facilitator not controller
Move from autocratic to participative style
Participative/democratic leadership style
A participative or democratic leadership style is one in which the manager consults with employees to ask their suggestions and then seriously considers those suggestions when making decisions
Advantages and Disadvantages:
Advantages
Communication is a two-way process
Employer/Employee relationships are positive
Motivation and job satisfaction are optimal
There is a high level of trust
Disadvantages
Reaching decisions and introducing tasks can be time consuming
The role of management may be weakened
Internal conflict can arise if opinions differ
Contingency Management Approach
Contingency approach stresses the need for flexibility and adaptation of management practices and ideas to suit the changing circumstances
Adapting to changing circumstances
Contingency theorists stress that the traditional classical approach to management was not wrong, but is no longer adeuqate for our needs today
They urge managers to borrow and blend from a wide range of management approaches and practices
Ethics
Not exclusive to any approach. Ethics is what society deems right and wrong
It is not concerned with legal obligationgs - often the feelings expressed by society that may one day become the law
Ethical businesses will honour commitments, not engage in misleading or deceptive conduct in marketing and provide a safe working environment for their employees
Ethical management comes at a cost, however, most business owners regard these costs a necessary expense 0 it is an essential part of their business operations
Provides a great deal of pride in their reputation
Allows the busniess to be seen as responsbible corporate citizens, conscious of high standards expected by customers and society
Incorporate CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility)
Broader social welfare of the community including employees, customers, suppliers and the environment when making business decisions
Ethical business management
Businesses who exhibit ethical responsibility are often rewarded with improved business performance
This business performance is measured using the triple bottom line
Focus on provit, the environmental impact, and the social performance
The ‘profit’ bottom line', which is a measure of the traditional ‘profit and loss’ financial bottom line
The ‘people’ bottom line, which is a measure of how socially responsible a business has been
The ‘planet’ bottom line, which is a measure of how sustainable and environmentally responsible the business has been
So what are the qualities of an ethical and socially responsible manager?
Ethics involves
Evaluating personal values
Knowledge of personal standards, community and universal principles
Choices and the impact of these choices on other s and yourself
Both short and long term consequences
Accepting responsibility for the choices you make
Social responsibility means to have a:
Caring attitude towards yourself and others
Sense of control and competence
Recognition and acceptance of individual and cultural diversity
Recognition fof basic human rights of self and others
Open mind to new ideas
Common ethical dilemmas
A loyal, long serving employee cannot adapt to new technology
Access to confidential information about a competitors pricing policy that a disgruntled employee leaked to management
Cash payment bribes offered for quick contract arrangement
Competitors negaging in unethical tactics that require action to manage not losing competitive advantage
Managers must maintain high personal and ethical standards so employees perceive the importance of ethical considerations - good ethics = good business
Fairness and Honesty
Businesses MUST obey laws and regulations or they will incur a fine
Society expects
The truth and not to be misled or deceived by dishonest information
Employees expect
To be dealth with honestly and fairly (e.g follow through with a promotion promise)
Customers and suppliers expect
To be treated honestly and fairly in business dealings
If a product is delivered then the business should pay within the gareed timeframe
Respect for people - Human Resources
If a business owner treats the employees with respect then the employees will also act ethically
Occasionally a stakeholder is placed in a difficult ethical position
If the owner discovers some sort of unethical practice of an employee
An employee discovers some sort of unethical behaviour of another employee
Examples include practical jokes played on others in the workplace
More serious examples include breaches of confidentiality or discrimination
HR must also act ethically in the separation of staff - See Quantas case study
Conflict of interest
When a person takes advantage of a situation or piece of information for their own gain rather than the employers gain
This could be by accepting a gift or payment to make a particular decision
A gift is different from a bribe - but there is a fine line of difference (a gift would occur regardless of the decision but there could still be a perception that it is a bribe - an offering so that a particular decision IS made)
Corruption undermines the integrity of the business and can change the workplace culture
Changing this culture once it is established is very difficult
Small incidents so develop into corruption on a big scale
These then have a significantly negative effect on the business reputation
FInancial management - Finance
Financial management decisions must reflect the objectives of the business and interests of the shareholders
Shareholders rely on accurate infomration presented in the 3 financial statements to determine whether o rnot they invest (buy shares)
Assets on the balance shseet must be valued accurately
Financial records should be regularly audited
Truthful communication - Marketing
Advertising can bring about ethical dilemmas as businesses fight to gain the consumers attention
False or misleading advertising is unethical and illegal
Specific unethical practices include
Using sexual references to sell
Gender stereotyping
Selling to children
Product placement (subliminal advertising)
Ethical operations
In transforming inputs into outputs
Society expects the careful treatment of resources such as energy, waste, and recycling so that future generations are not impacted
Energy conservation and the use of sustainable inputs
Minimising waste that would pollute the environment
Recycling waste and returned products to landfill
Ensuring ethics in the workplace
It is not always easy to maintain a high degree of ethical behaviour in the workplace
A strategy to encourage consistency is to devicse a code of conduct which is a set of ethical standards for managers and employees to abide by
Many businesses document and distribute their code of conduct to all internal stakeholders to ensure workplace practices are employed
Training incorporates these values to ensure they are understood by employees
Formal procedures are also devised for reporting unethical behaviour in the workplace
Management and Change
Responding to internal and external factors
Businesses can control internal factors
Businesses can only respond to external factors