Distillation
Simple
Setup
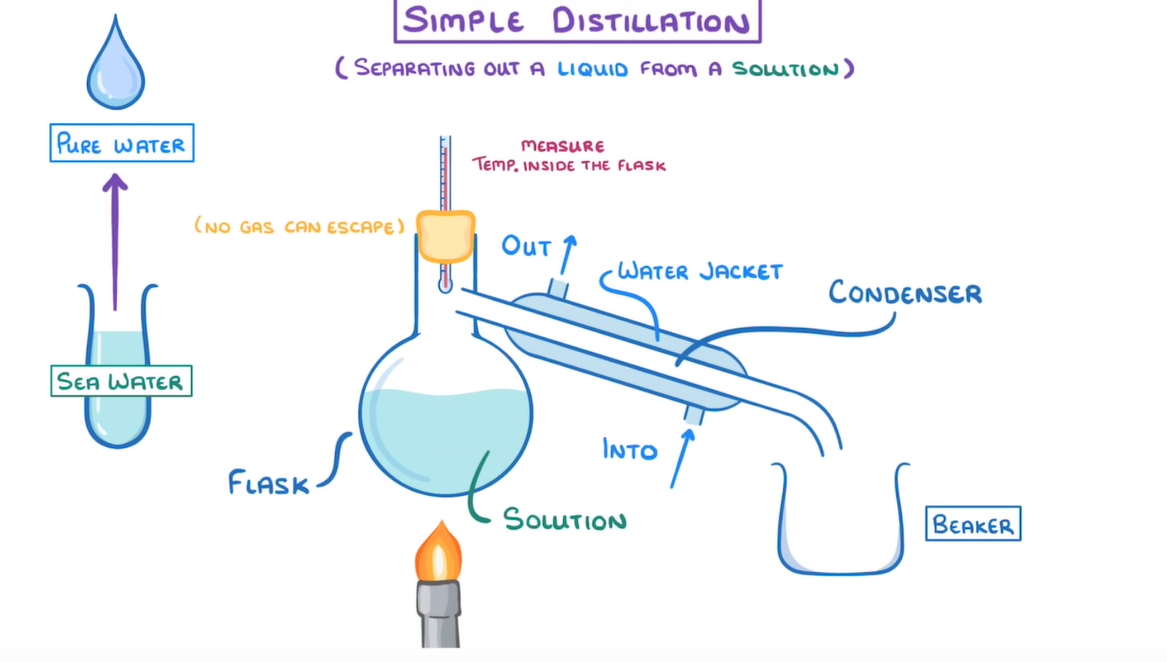
- Flask - contains liquid solution
- Bun - seals flask so no gasses can escape
- Thermometer - placed through bun to measure temp inside the flask
- Condenser - attached to a water jacket to provide a stream of continuously flowing cold water
- Beaker - at the end of the condenser to capture pure liquid
- Bunsen burner - placed beneath the flask to heat the solution
Process
- Heat the mixture using a Bunsen burner so that desired liquid evaporates
- As the gas rises to the top of the flask, the pressure will force it into the condenser
- Because their is a continuous flow of cool water, the gas will condense back into liquid where it is collected in the beaker.
Fractional
Setup
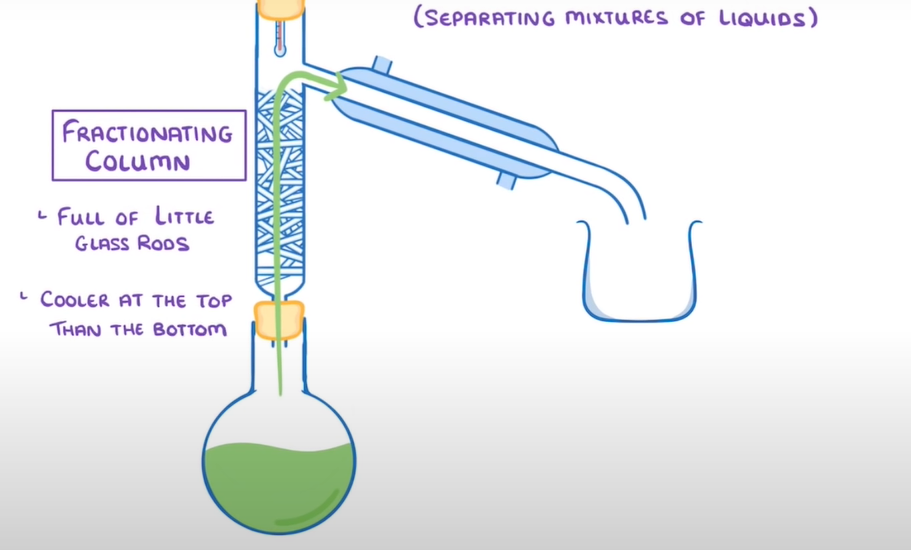
- Flask - contains mixture
- Bun - seals beaker to prevent gasses escaping
- Fractioning column - filled with tiny glass tods to maximise surface area and cooler at the top then the bottom to prevent unwanted gasses evaporating
- Condenser - attached to water jacket to provide a continuous flow of cool water
- beaker - collects pure liquid provided by the condenser
- Bunsen burner - heats mixture in flask
Process
- Flask filled with a mixture containing different liquids of different boiling points
- Flask is heated by Bunsen burner at temperature of the liquid with the lowest boiling point
- This liquid then travels through the fractioning column and is forced into the condenser due to the pressure
- Due to continuous flow of cool water provided by the water jacket the gas condenses back to water and is collected in the beaker
- If any of the other liquids somehow evaporate, the fractioning column condenses them back to liquid as the glass rods are cooler than their boiling points
- Process is repeated at the temperature of each mixtures individual boiling points.