Homeostasis
maintenance of a constant internal environment independent of external conditions
examples of homeostasis
control of blood glucose levels
control of body temperature
osmoregulation
control of water and salt content of body fluids
control of ph of body fluids
feedback system
a sequence of events in which information about the status of a situation is continually reported to a central control system and corrective mechanism applied as a response
negative feedback
negative feedback maintains levels
positive feedback
example of positive feedback
secretion of the hormone oxytocin at the end of pregnancy
Hormones
chemical messengers
released directly into the blood from endocrine glands (no duct)
travel to target cells or organs
only target cells or organs have the receptor specific to the hormone
Endocrine and Exocrine glands
endocrine glands produce hormones that are directly secreted into the blood
exocrine glands produce substances that are secreted into ducts that are used to transport the secretions to their point of use eg sweat glands
some organs are both endocrine and exocrine eg the pancreas different areas producing different substances
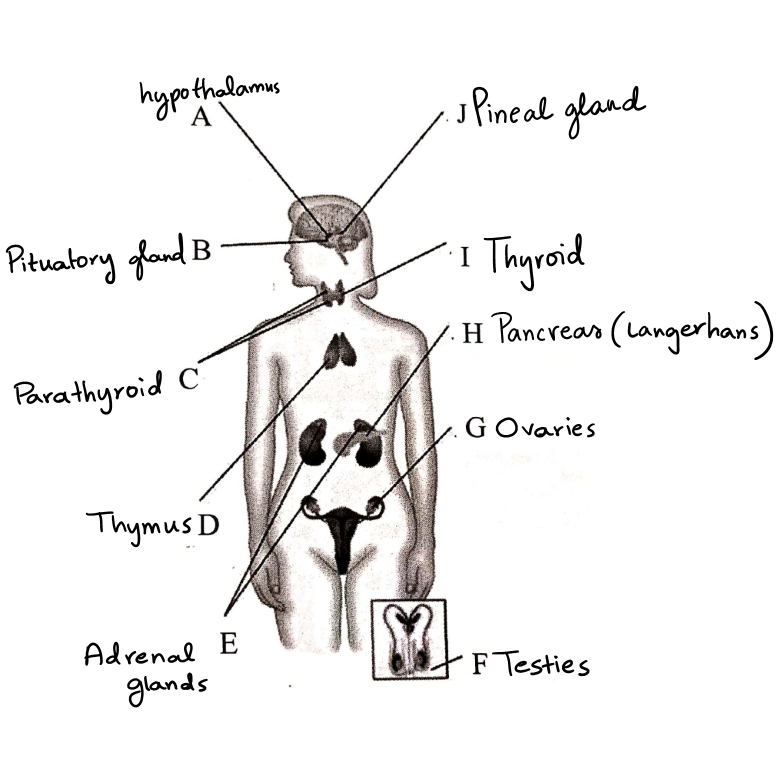
research on glands ⭐
hypothalamus - TRH,GnRH,GHRH and CRH are secreted to maintain the body’s internal balance aka homeostasis
pituitary gland - is known as the master gland because it signals other glands to release hormones . It produces TSH,ACTH,FSH and LH
parathyroid - it regulates the calcium levels in the blood and it triggers the bones to produce calcium
thymus - produces white blood cells called T lymphocytes and it only produces these T cells until we become teenagers and it produces thymosin a hormone necessary for T cells
adrenal glands - they produce a lot of hormones but the main ones are epinephrine(adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and it regulates the metabolism,immune system,blood pressure,response to stress and other essential functions
testis - primary male sex hormone essential for producing sperm and they produce testosterone
ovaries - they contain the egg cells needed for reproduction and they produce progesterone and estrogen
pancreas - produces insulin and glucagon and it helps the body to regulate the blood sugar levels and appetite
thyroid - produces hormones that help regulate the body’s metabolism and it produces thyroxine
pineal gland - revive and convey information about the current light-dark cycle from the environment and it produces melatonin,vasopressin,gastrin and histamine
 Knowt
Knowt
