Study guide 5
Systematics
Purpose of Systematics:
To study organisms and their evolutionary relationships.
It classifies species into taxa and reconstructs phylogeny
Key Differences in Classification
Phylogeny vs. Taxonomy:
Phylogeny: The evolutionary history and the relationships between species.
Taxonomy: The classification and naming of organisms.
Binomial Nomenclature
are use for 2 part scientific name for a species in latin or greek
less ambiguity compared to common names
Hierarchical Classification
Taxa Levels:
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
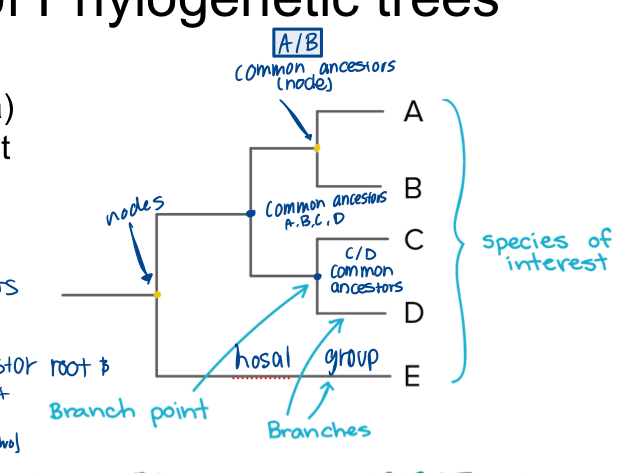
Phylogenetic Trees
Description: Diagrams that represent evolutionary relationships among organisms.
Information Displayed:
Common ancestors
Lineages
Branching patterns indicating speciation
Components:
Branch: Lineages diverging from a common ancestor.
Node: Represents a common ancestor.
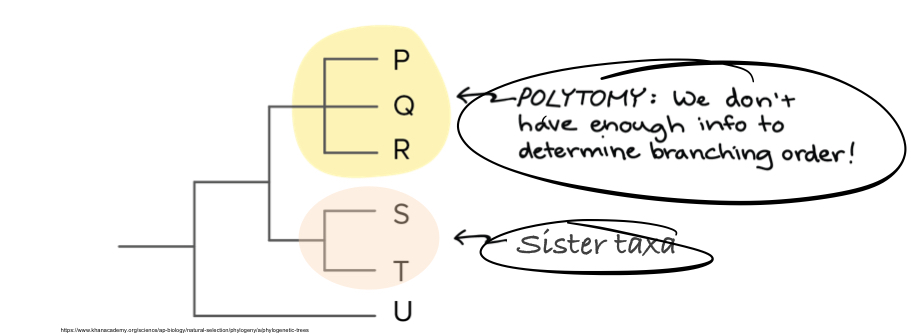
Polytomy: A node that branches into three or more groups.
Sister Taxa: Groups that share a common ancestor.
Analyzing Phylogenetic Trees
Common Ancestor of Taxa A-C: Circle and label on phylogenetic tree.
Alternate Tree Drawing: Concept of rearranging branches without changing relationships.
Types of Homologies
Molecular Homologies:
similarities at molecular dna level between organisms due to shared ancestry
used to construct phylogeneces
Morphological Homologies:
Structural similarities that closely related species have in common
used to construct phylogeneces
why do convergent evolution and the appearance of analogous structures have the potential to complicate tree building
natural selection produces similar adaptation in organism from different evolutionary. lineages can cause misleading construction
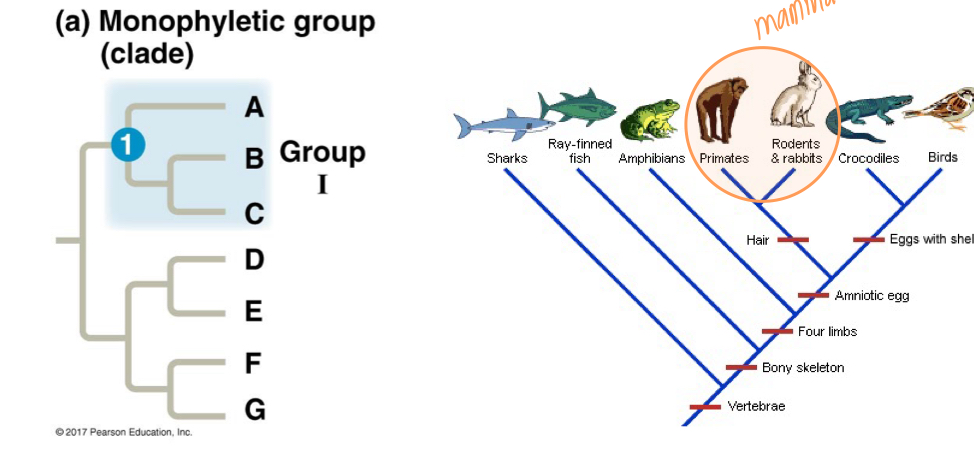
Clades
Definition: A group of organisms with a common ancestor
Types of Groups in Cladistics
Monophyletic Group:
the group that consists of an ancestor and all their decendants
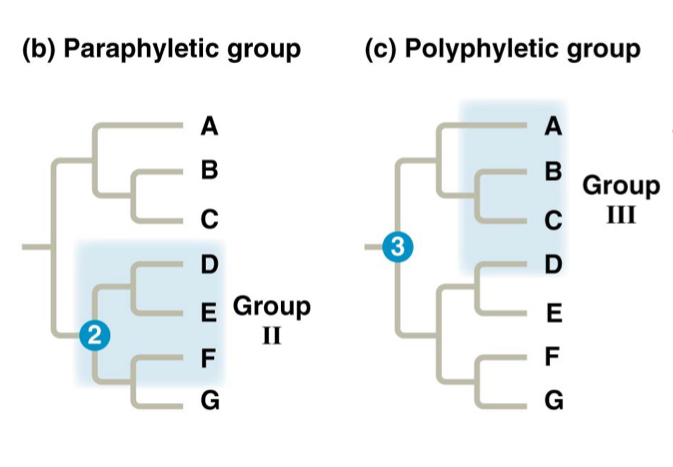
Paraphyletic Group:
Includes ancestral strucutre and some of its decendants
Polyphyletic Group:
consists of distantly related species and not the most recent common ancestor
shared ancestral character
character that originated in an ancestor of the taxon
Shared derived characters
evolutionary novelty unique to a clade