Bio 40s first quiz
DNA Structure - Practice Questions
Label the following diagram:
1 Hydrogen bonds
2 Phosphate Backbone
3 deoxyribose sugar
4 nitrogenous base pair
5 nitrogenous base
6 dna nucleotide
What are the 4 nitrogenous bases of DNA? What are the two types of nitrogenous bases and which base belongs to each group?
Adenine guanine cytosine thymine. The two type are purines and pyrimidines Purines have Adenine and Guanine While pyrimidines have cytosine and thymine
In DNA, guanine always forms hydrogen bonds with ____cytosine____.
How is the shape of DNA described?
Double helix
Draw the structure of a nucleotide.

What type of bond connects the sugar and phosphate groups of the DNA backbone? (Recall from Grade 10 Science.) What type of bond connects the nitrogen bases across the DNA strands? What is the difference between the bonds and why is that important?
Covalent bonds connect sugar and phosphate groups while hydrogen bonds connect the nitrogenous bases
The difference are the covalent bonds are really strong which allows the backbone to stay intact and the molecule will stay strong while hydrogen bonds are weak so they will stay together but can separate easily for something like replication
Explain why the structure of a DNA molecule is often described as a zipper.
DNA can be compared to a zipper because of its complementary base pairing (like interlocking teeth of a zipper) and the two parallel strands that run in opposite directions,
How does DNA hold information?
By the sequence of the 4 nitrogenous bases which tells the certain body parts what to do
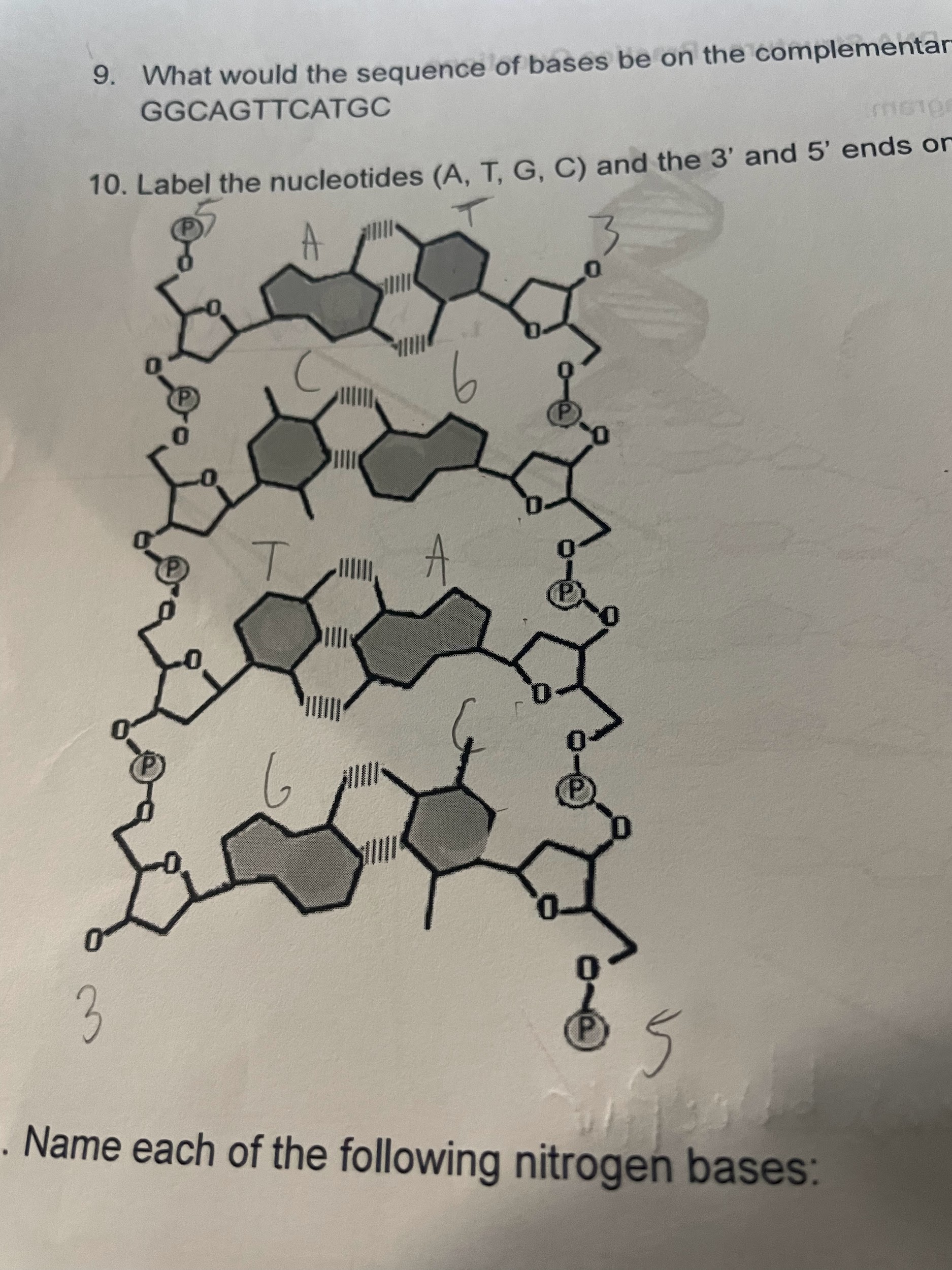
What would the sequence of bases be on the complementary strand of: GGCAGTTCATGC
CCGTCAAGTACGLabel the nucleotides (A, T, G, C) and the 3’ and 5’ ends on the DNA molecule below: