bio10-ch 8
wow u found this, congrats good job. now u have notes.
CHAPTER 8
The nervous system ~
Section 8.1:
Nervous system: one of the most amazing designs in God’s living creation
Neurobiologist: a biologist who studies the nervous system
Neurologist: a physician who specializes in disorders of the nervous system
Central nervous system: includes the brain and the spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system: consists of the nerves that branch from the brain and spinal cord
Central nervous system:
Brain: the principal organ of the nervous system
Protected by the cranium
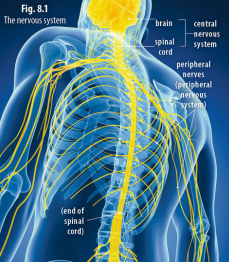
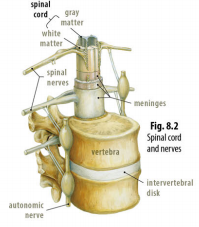
Spinal cord: thick bundle of nerve fibers located within the spinal cavity
Spinal nerves: transmit nerve signals to and from the rest of the body
Cranial nerves: branch directly from the brain stem and transmit nerve signals to and from the eyes, ears, mouth, face, and scalp
Meninges: composed of an outer layer called the dura mater, a middle layer called the arachnoid mater, and an inner layer called the pia mater
Dura mater: one of the strongest tissues of the body; serves primarily as a flexible protective layer
Arachnoid mater: composed of thin fibers, like the fibers of a spider’s web, that form an intricate three-dimensional network around the brain
Pia mater: forms a delicate covering that rests directly against the brain and spinal cord
Cerebrospinal fluid: clear fluid that circulates through the fibers of the arachnoid mater, cushioning the brain when you bump your head
Glial cells: support and insulate nerve tissue
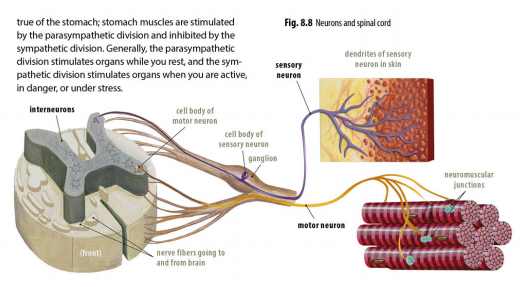
Neurons: the actual nerve cells
Cell body: contains a nucleus (which controls its metabolic activities) and most of the nerve cell’s cytoplasm
Dendrite: a short, branched extension of the cell that receives nerve impulses from other neurons and conducts them toward the cell body
Axon: a long extension that relays nerve impulses from the cell body to other neurons
Nerve impulses travel in one direction in a nerve fiber–from the dendrites toward the cell body and from the cell body toward the axon
Gray matter: found within the brain and spinal cord; consists largely of the cell bodies of neurons and is gray because the cell bodies lack the white, specialized covering known as myelin
Myelin: white, specialized covering
White matter: composed of axons and glial cells that are white because of their myelin content
Ganglia: masses of cell bodies
Plexus: a network of interconnected nerve fibers going to or from a region
Brachial plexus: located at the back of the neck and shoulder; branches to form the median nerve and other arm nerves
Nerve center: group of cell bodies in the brain or spinal cord
For example, the nerve centers in the medulla oblongata of the brain stem control your breathing
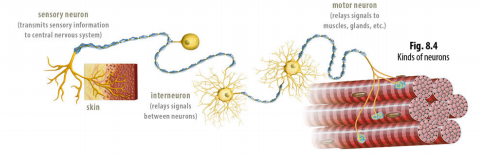
Sensory neurons: neurons that transmit information to the central nervous system from the senses of sight, hearing, taste, touch, and smell, as well as those that transmit pain signals
Motor neurons: neurons that relay signals from the central nervous system to the other parts of the body
Interneurons: found only in the central nervous system; relay signals between neurons or groups of neurons and are responsible for the processing of information by the brain, like the logic circuits of a computer
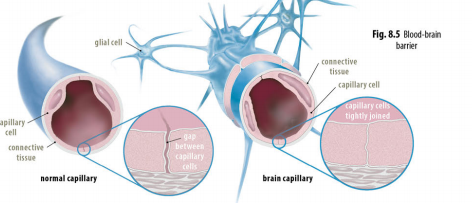
Blood-brain barrier: protect the central nervous system from being permanently damaged every time you get sick
Microglia: help protect the brain from infection
Meningitis: disease caused when invading microorganisms enter the nerve tissue and infect the meninges
Coma: a state of prolonged unconsciousness
Poliomyelitis (polio): a serious disease that attacks the spinal cord
It is caused by a virus that enters the motor neurons of the spinal cord (the anterior horn cells) and destroys some of them
Peripheral nervous system:
Peripheral nervous system: consists of nerves
Nerves: bundles of nerve fibers (axons) branching from the brain and spinal cord and connecting the central nervous system to the extremities of the body
Sciatic nerve: one of the longest nerves in the body; connects the leg extremities with the spinal cord in the lower back
There are twelve pairs of cranial nerves (branching directly from the brain) and thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves (connected to the brain through the spinal cord)
Mixed nerves: nerves contain both sensory and motor fibers
Sensory nerve fibers: carry impulses from light, taste, sound, touch, and pain from other parts of the body to the spinal cord and brain for analysis
Motor nerve fibers: carry impulses from the brain and spinal cord to produce action in muscles and organs
Autonomic nervous system: the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the heart and other internal organs
Hypothalamus: controls the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system
Sympathetic division: generally responds to your body’s needs during increased activity and in emergency situations by causing heartbeat and breathing rates to increase, thus supplying more blood to your body so that you can respond quickly
Parasympathetic division: acts as a balance to counteract the actions of the sympathetic division
Section 8.2:
Structure of a Human Nerve
Median nerve: controls the muscles of the forearm and the muscles and skin of the hand
Like the other nerves of the peripheral nervous system, the median nerve consists of bundles of nerve fibers surrounded by connective tissues.
Nerve cells
Neurons: responsible for the process of nerve impulse conduction
Neurons, unlike most other body cells, rarely reproduce.
Schwann cells: produce layers of myelin sheathing that acts much like the insulation on an electrical wire
In the brain and spinal cord, myelin sheaths for axons are provided by special glial cells called oligodendrocytes instead of by Schwann cells
Defective impulse transmission:
Multiple Sclerosis: a disease of the brain and spinal cord; occurs when the body’s immune system attacks the glial cells that provide myelin sheaths for nerve cell axons
Paralysis: the inability of the muscles to move
How neurons work
Action potential: a neuron is triggered to fire, a brief pulse of positive charge sweeps through the neuron and races down the axon like the fuse of a firecracker
Synaptic Transmission:
Synapse: an enclosed junction between two neurons or a neuron and another cell
Neuromuscular junction: a synapse between a neuron and a muscle fiber
Neurotransmitter: tis a chemical that tis released when the action reaches the synapse
Inhibitors of nerve impulses:
Botulinum toxin: powerful poison that is responsible for the most deadly type of food poisoning
Clostridium botulinum: manufactures the Botulinum toxin
Parkinson’s disease: affects the patient’s control of posture and movement
Dopamine: a lack of this can cause Parkinson’s disease
Reflex Action
Reflex: a quick, automatic response; simplest act of the nervous system
Reflex arc: simplest nerve pathway