2.6a - DNS Configuration: Professor Messer
DNS
Translates human-readable domain names into computer-readable IP addresses.
Address
Hierarchical - domain names follow a set structure.
Includes many DNS servers
13 root server clusters (manage the dot (.) for domain names)
Hundreds of generic top-level domains (gTLDs) - .com, .net, .org, etc.
Over 275 country-code level domains (ccTLDs) - .us, .ca, .uk
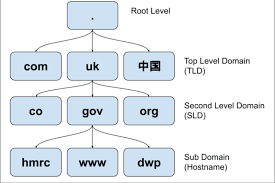
DNS hierarchy breakdown:
Root DNS (.)
Top-Level Domains (TLDs)
Second-Level Domains (SLDs): Directly beneath TLDs and include regular hostnames (“website names”).
Subdomains: Below SLDs (e.g., mail.website.com).
DNS resource records (e.g., A, AAAA) are database records of domain name services that are stored in a host config file.
These are critical configurations - check, backup, and test!
A
DNS records for IPv4 - contain an FQDN with an IPv4 address that it translates to.
Can be edited in the DNS hosts file or a web-based frontend for some hosting services.
AAAA
DNS records for IPv6 - contain an FQDN with an IPv6 address that it translates to.
Can be edited in the DNS hosts file or a web-based frontend for some hosting services.
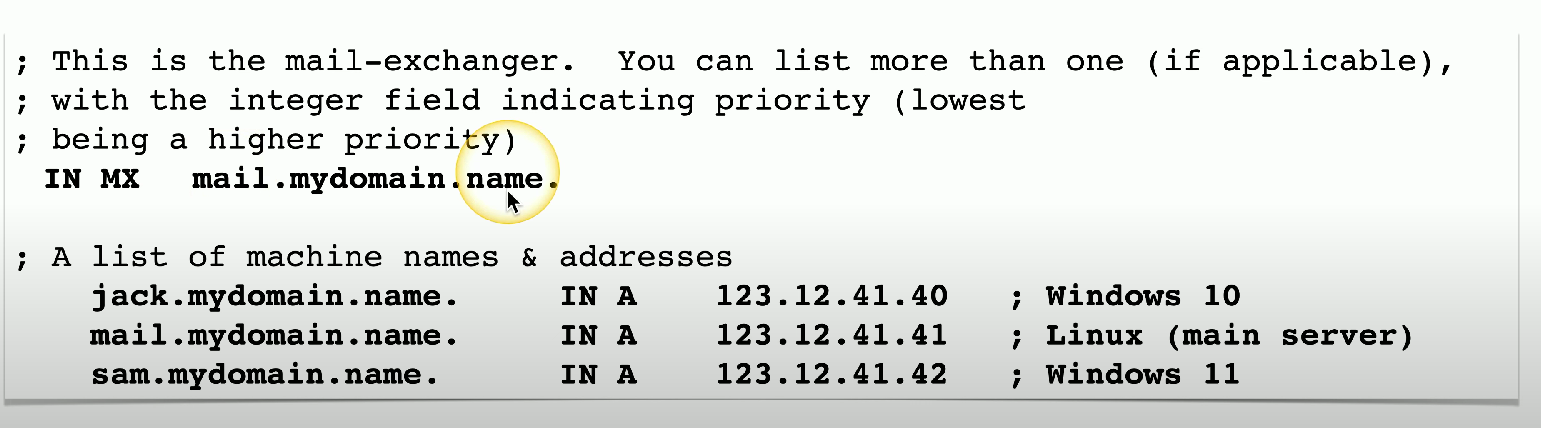
Mail Exchanger (MX)
Determines the hostname for a mail server - not an IP address, but a name.
Typically a subdomain that references the webserver IP address in a previously established A record.
Text (TXT)
Human-readable text information - typically used for public/informal information.
Can be used for verification purposes - DNS server configuration is typically very secure, so changing a domain requires a specific entry into the DNS server; only DNS/network admins have the required permissions.
Commonly used for email security
Spam Management
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM): Provides a public key to verify a domain’s outgoing mail. Validated by mail servers and not typically seen by end users.
Found in a DKIM TXT record.
Sender Policy Framework (SPF): List of all servers authorized to send emails for the domain - prevents mail spoofing (fake email servers); allows mail servers to check if incoming mail comes from an authorized host.
Found in an SPF TXT record.
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC): Provides instructions that tell email servers how to handle emails that fail authentication checks.
Policy written to a DMARC TXT recordd.
Instructions may include accepting all, sending emails to spam, or rejecting all noncompliant emails.
Compliance reports are sent to an email administrator.